Google Cloud VMware Engine is one of the fastest and easiest ways to extend, migrate and run your VMware-based applications in Google Cloud without changes to your apps, tools, or processes. It is a fully managed service that lets you run the VMware platform in Google Cloud and provides you with VMware operational continuity, to benefit users from a cloud consumption model and lower your total cost of ownership. The VMware Engine also offers on-demand provisioning, pay-as-you-grow, and capacity optimization. The service provides all the hardware and VMware licenses you need to run in a dedicated VMware SDDC in Google Cloud.
Your VMware environment runs natively on Google Cloud bare metal, single-tenant infrastructure in Google Cloud locations and fully integrates with the rest of Google Cloud. Google manages the infrastructure and all the necessary networking and management services to let you consume the VMware platform efficiently and securely.
VMware Engine includes vSphere, vCenter, vSAN, NSX-T, HCX, and corresponding tools. So it is fully compatible with your existing VMware tools, processes, and skills training. This compatibility enables your team to manage workloads without disrupting existing policies, such as those related to networking, security, data protection, and auditing.
The following are the advantages of using a Google Cloud VMware Engine:
Continue to run your workloads in a fully compatible Software Defined Datacenter (SDDC) stack while leveraging the same tools and processes as you use on-premises today.
Free up time to develop next-gen hybrid apps and services while reducing the operational burden on IT.
Increase business agility by unlocking intelligent insights with Google services through BigQuery to analyze your data in real time and better connect with your customers.
Network Services in Google Cloud VMware Engine
The following diagram demonstrates high-level network architecture of Google Cloud VMware Engine - Private Cloud VMware Network services:
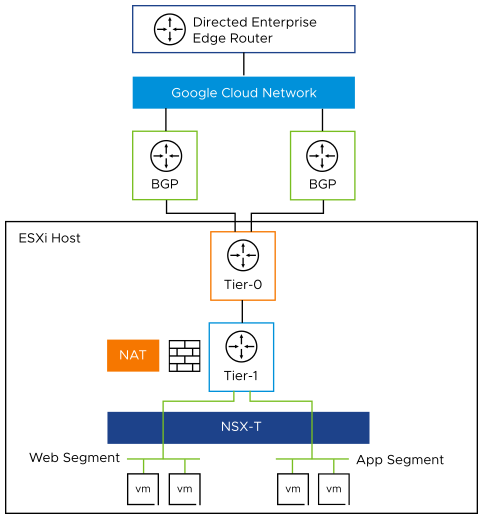
As shown in the diagram, Google Cloud VMware Engine is pre-provisioned with the following NSX-T network configuration:
Tier-0 Gateway configured for ECMP.
Northbound connectivity through BGP on Tier-0 Gateway.
Pre-provisioned Tier-1 Gateway for workload segment connectivity.
Route advertisement enabled on pre-provisioned Tier-1 Gateway.
Route redistribution enabled on Tier-0 Gateway.
Default Internet Access for SDDC workloads with an option to enable/ deactivate.
The service allows you to add the following NSX-T network configuration:
Create overlay segments and connect workloads.
Deploy additional Tier-1 Gateways.
Deploy distributed services such as DFW.
Deploy stateful services such as Load Balancer, DNS, and DHCP on Tier-1 Gateway.
Avi Load Balancer for Google Cloud VMware Engine
The Avi Load Balancer provides load Balancing for applications running in Google Cloud VMware Engine SDDC. It integrates as a 2nd party load balancing solution, with communication between the Controller, Manager, and VMware vCenter within Google Cloud VMware Engine. This integration enables the Avi Load Balancer to deploy and manage Service Engines automatically based on demand, providing for an elastic, automated approach to load balancing.
The Avi Load Balancer also leverages the NSX-T Cloud Connector mode of operation in Google Cloud VMware Engine. This is facilitated by the similarity in the VMware infrastructure between an on-premises NSX-T deployment and the Google Cloud VMware Engine deployment.
The following schematic provides an overview of the integration:
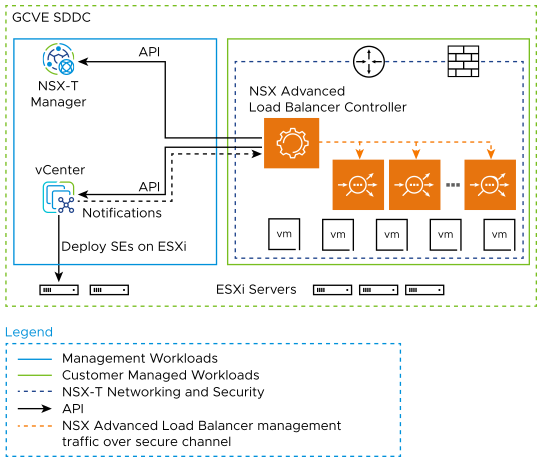
From the deployment shown above:
The Avi Load Balancer Controller is a cluster of three control plane VMs. The Controllers can run within the Google Cloud VMware Engine SDDC, or outside it in your on-premises datacenter or Google Cloud native VPC. The Controllers need IP reachability from the Service Engines.
The Controller connects with the NSX-Manager and VMware vSphere vCenter within Google Cloud VMware Engine and discovers the VMware objects such as Port groups, clusters, NSX T1 and Segments.
The Controller automatically deploys an SE, which is the data path instance. The SE is a virtual machine running within the Google Cloud VMware Engine SDDC.
The Controller ensures that the NSX-T DFW is programmed correctly to allow traffic.
The Avi Load Balancer allows for various deployment configurations of the underlying NSX system, such as shared segment for the Virtual Service front-end IP (VS IP) and pool members, and dedicated segments for each.
The Avi Load Balancer also supports the default Tier 1 gateway as well as additional Tier 1 gateways created within Google Cloud VMware Engine by the customer.
Though the Avi Load Balancer supports various VLAN backed segment topologies, these are not applicable in the context of Google Cloud VMware Engine, as the service supports overlay segments created by customers.
Prerequisites for Installing Avi Load Balancer in Google Cloud VMware Engine
- Licensing
-
Avi Load Balancer only supports Enterprise Edition license for Google Cloud VMware Engine integration. To know more about the Enterprise Edition license, see License Management on Avi Load Balancer in VMware Avi Load BalancerAdministration guide.
Avi Load Balancer Licenses can be added to the Controller at any time as per the requirement. The licenses are available at my.vmware.com. Login to your account at my.vmware.com to access the VMware serial key(DLF).
Avi Load Balancer Controllers manage licenses and central capacity pool for Avi Load Balancer Service Engines.
Avi Load Balancer allows for a 10% overage of the total license capacity.
- Role Requirements
-
The Avi Load Balancer Controller requires:
The NSX Network Engineer role or higher if you are running NSX-T Data Center 3.0.x, or the NSX Network Admin role or higher if you are running NSX-T Data Center 3.1.x or later.
Configuring Roles and Permissions for vCenter and NSX-T Users.
You can use the CloudAdmin role provided for Google Cloud VMware Engine. This role is a superset of the required permissions and is sufficient for the integration.
Content Library
For information on setting the content library, see Creating a Content Library.
Deploying the Avi Load Balancer Controller OVA
For information on deploying the Controller OVA, see Deploying the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller OVA.
Setting up the Avi Load Balancer Controller
For information on setting up the Controller, see Setting up the Avi Load BalancerController section in VMware Avi Load BalancerAdministration guide.
Creating an NSX-T Cloud
To create an NSX-T cloud, log in in to the Controller and follow the steps given below:
From the Avi Load Balancer UI, navigate to .
Click Create.
Provide a Name.
Select NSX-T as the Credentials Type.
Enter the Username and Password.
Click Save. Similarly, create vCenter Credentials.
Configuring the NSX-T Cloud
For information on configuring the NSX-T Cloud, see Creating an NSX-T Cloud section in VMware Avi Load BalancerAdministration guide.
Creating a Virtual Service
From the Avi Load Balancer UI,
Go to Applications.
Click .
Select the NSX-T cloud which was created.
Enter the details related to the virtual service IP, Pool members, Tier 1 Logical Router, and more as required.
Click Save to create the virtual service.
On successful creation of a Service Engine, the Virtual Service comes up and becomes ready to process traffic.