Cloud providers can create and assign custom storage policies for tenants who use the Cloudian platform.
A storage policy is a set of rules that define how data can be managed and distributed within the organization. VMware Cloud Director Object Storage Extension offers a default storage policy for each region. In addition, you can create custom storage policies if your tenants use the Cloudian platform. Tenants can then apply these policies when creating buckets and objects. Use storage policies to protect your data and to avoid data losses if any type of failure occurs. Storage policies make your data highly available.
- Replication
- Erasure Coding Across Data Centers
- Replicated Erasure Coding
- Replication
-
Replication is the process in which data is copied to multiple locations. The system creates a configurable number of copies of each data object, and each copy is stored on a different node. There is no limitation of the data centers that can be used. Replication within a single data center or replication across multiple data centers are both supported, if the number of copies is not greater than the number of the nodes. When creating a replication storage policy, you should always specify at least two copies.
For example, with 4x replication, 4 copies of each object are created, and each copy is stored on a different node. This can be done within a single data center, or across multiple data centers.
Figure 1. Replication within a single data center

Figure 2. Replication across multiple data centers
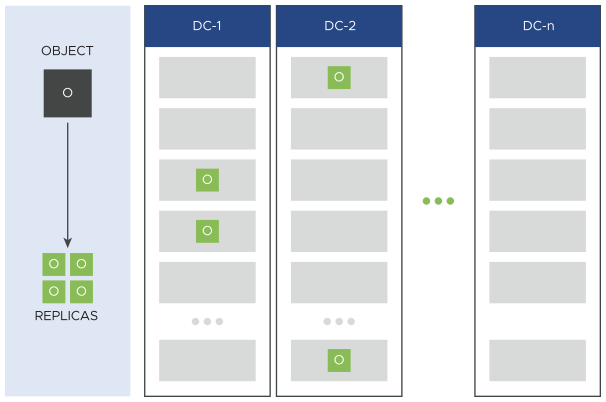
- Erasure Coding Across Data Centers
-
Erasure coding breaks data into a configurable number of data fragments, known as the "k" value, plus a configurable number of parity fragments - the "m" value. The fragments are distributed across a set of storage systems, with each fragment stored on a different node. Choosing the right configuration for you, depends on how many nodes you have in your data center. A minimum of three data centers and six nodes is required.
When you access an object, it is reassembled using the stored fragments. If a data or parity fragment is lost or corrupted, the object can be decoded from any "k" number of fragments and the object remains readable even if a "m" number of nodes are unavailable.
The diagram shows an object divided into eight fragments, each stored on a different node in three data centers.
Figure 3. Erasure coding across data centers
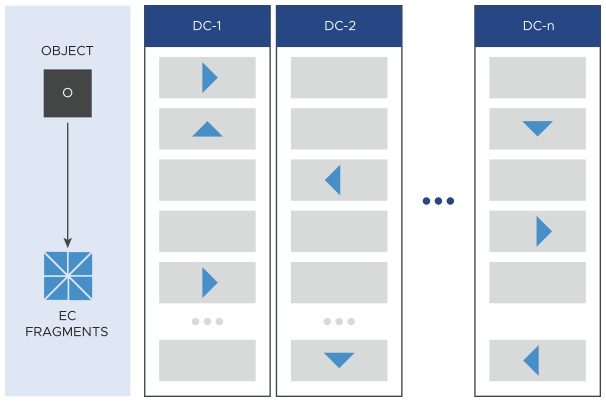
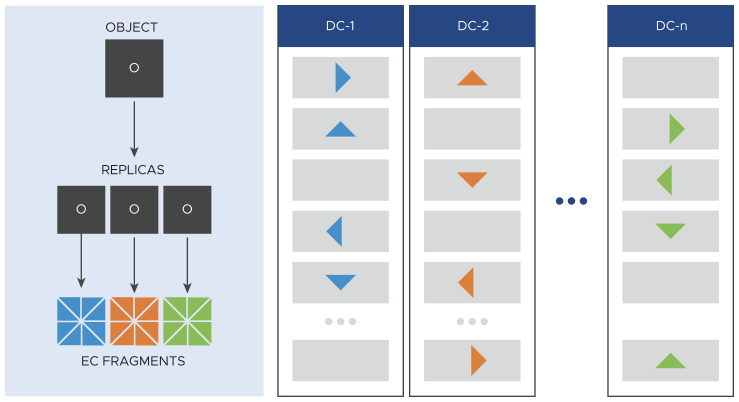
- Replicated Erasure Coding
-
Replicated erasure coding is a distribution method that falls between the replication and erasure coding methods. The system creates copies, or replicas, of the data object. The number of copies must be equal to the number of data centers selected. Each copy is then broken into fragments, the same way the erasure coding method works, and the fragments are distributed within a single data center, or across multiple data centers.
When you have only one data center available, the replicated erasure coding method works the same as erasure coding. The data object is split into fragments, which are then distributed within the data center, each on a separate node.
Figure 4. Replicated erasure coding within a single data center

When you select replicated erasure coding across multiple data centers as your preferred distribution method, copies of the data object are created first - three copies for three data centers. Each copy is then broken into fragments, which are then distributed across the data centers, each on a separate node.
Figure 5. Replicated erasure coding across multiple data centers
The following table lists the replicated erasure coding "k" + "m" configuration that is currently supported by VMware Cloud Director Object Storage Extension 2.2.
Table 2. Replicated Erasure Coding Distribution Configuration Supported "k" + "m" configuration 4+2 6+2 8+2 9+3 12+4