NSX-T Data Center provides networking services to customer workloads in VMware Cloud Foundation such as load balancing, routing, and virtual networking.
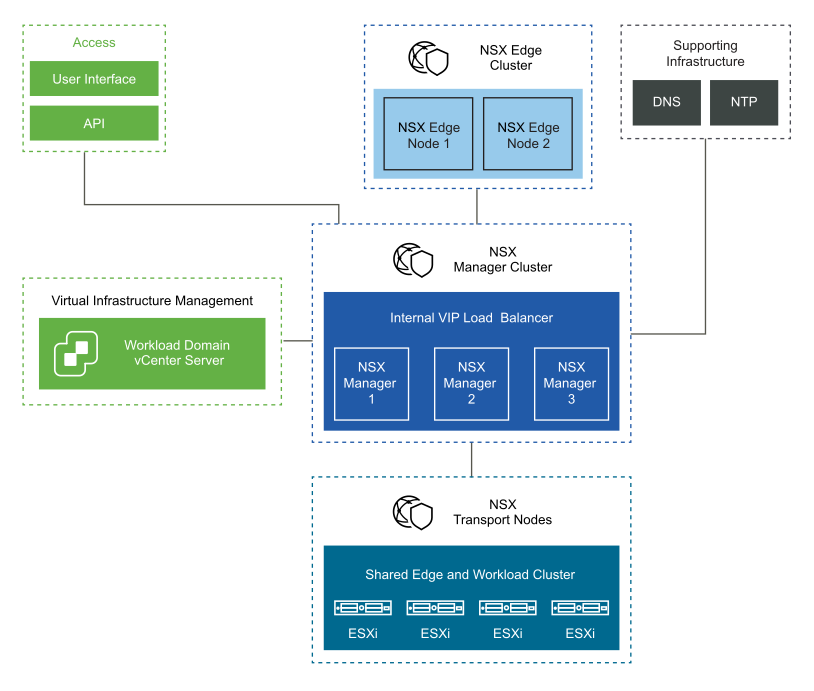
An NSX-T Data Center deployment consists of these components:
Unified appliances that have both the NSX Local Manager and NSX Controller roles. They provide management and control plane capabilities.
NSX Edge nodes that provide advanced services such as load balancing, and north-south connectivity.
The ESXi hosts within the VI workload domain are registered as NSX transport nodes to provide distributed routing and firewall services to customer workloads.
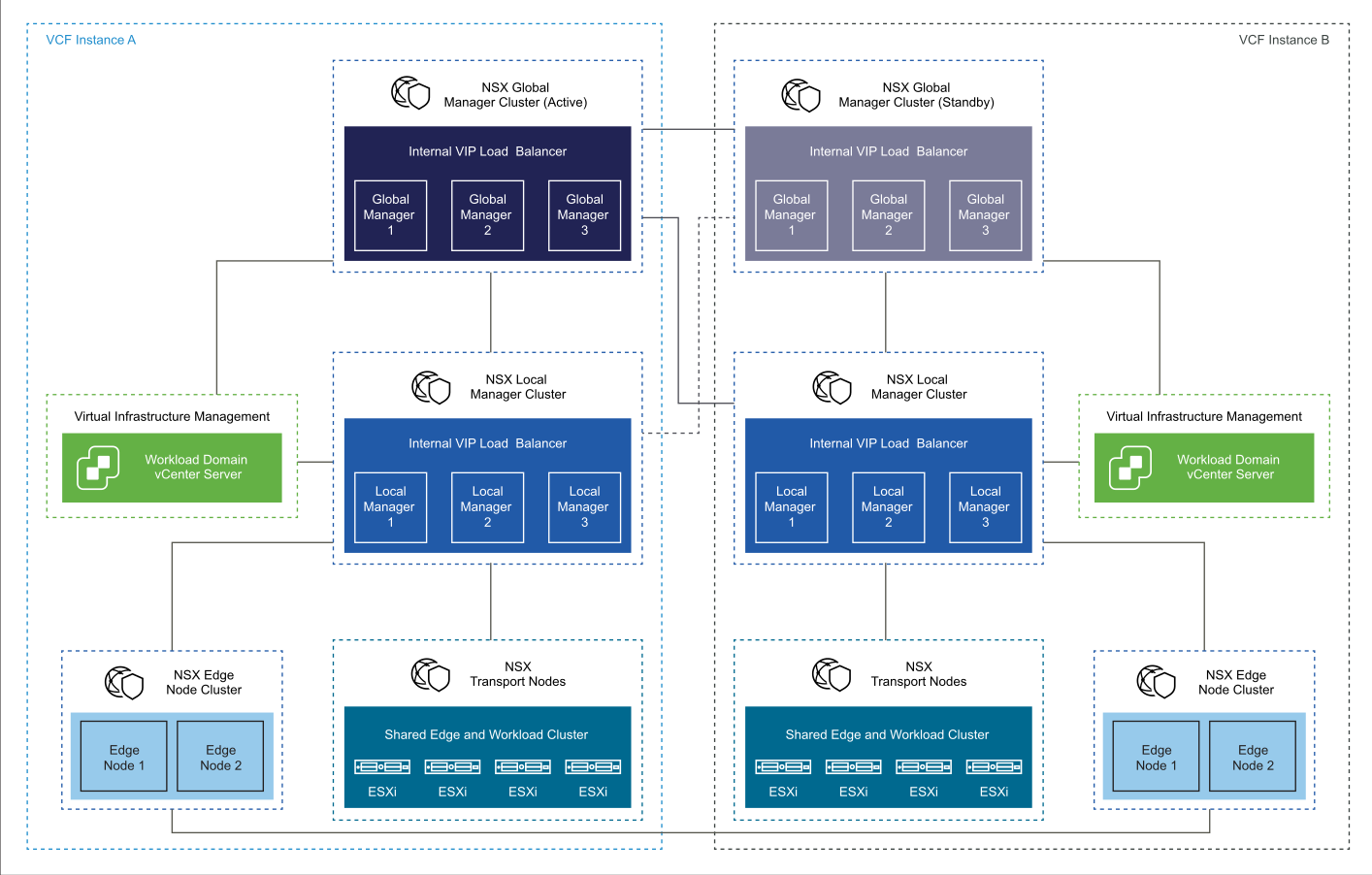
To support the requirements for NSX Federation with multiple VMware Cloud Foundation instances, you add the following components:
NSX Global Manager cluster in each of the first two VMware Cloud Foundation instances.
You deploy the NSX Global Manager cluster in each VMware Cloud Foundation instance so that you can use NSX Federation for global management of networking and security services.
An additional infrastructure VLAN in each VMware Cloud Foundation Instance to carry VMware Cloud Foundation instance-to-instance traffic.
Component |
Single VMware Cloud Foundation Instance with a Single Availability Zone |
Single VMware Cloud Foundation Instance with Multiple Availability Zones |
Multiple VMware Cloud Foundation Instances |
|---|---|---|---|
NSX Manager Cluster |
|
|
In the first VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
In the second VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
|
NSX Edge Cluster |
|
|
In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
|
Transport Nodes |
|
|
In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
|
Transport Zones |
|
|
In each VMware Cloud Foundation instance:
|
VLANs and IP Subnets Allocated to NSX-T Data Center For information about the networks for virtual infrastructure management, see vSphere Networking Design for a Virtual Infrastructure Workload Domain. |
See VLANs and Subnets in a Single VMware Cloud Foundation Instance with a Single Availability Zone. |
Networks for the first availability zone:
Networks for the second availability zone:
See VLANs and Subnets in a Single VMware Cloud Foundation Instance with Multiple Availability Zones. |
In each VMware Cloud Foundation Instance in an SDDC with two or more VMware Cloud Foundation instances:
|
Routing Configuration |
BGP |
BGP with ingress and egress traffic to the first availability zone with limited exceptions. |
BGP |
Logical Design for Multiple VI Workload Domains
When deploying another VI workload domain in a VMware Cloud Foundation instance, the additional domain can have its own dedicated NSX Manager instance (one NSX Manager to one VI workload domain) or share an NSX Manager instance already deployed for another VI workload domain (one NSX Manager to many VI workload domains).
You set a deployed NSX Manager as shared when you create the other VI workload domain. After you associate a VI workload domain with an NSX Manager instance, the domain cannot be reassigned another NSX Manger instance unless you delete and the domain again.
An NSX Manager instance can not be shared between the management domain and a VI workload domain.
Feature |
Dedicated NSX Manager Instance |
Shared NSX Manager Instance |
|---|---|---|
Overlay network isolation |
Each VI workload domain has its own overlay transport zone. As a result, overlay-backed segments are isolated to a single workload domain. Each VI workload domain requires its own NSX Edge cluster which integrates with the data network fabric. |
All VI workload domains connected to the shared NSX Manager instance share a single overlay transport zone. As a result, all overlay segments are created in all workload domains. You can use one NSX Edge cluster for all VI workload domains that are connected to the NSX Manager instance or multiple edge clusters for traffic separation if needed. |
Security policy |
Each VI workload domain has it own security policy. You can use tags for objects only in this VI domain. |
All VI workload domains can share a common security policy. You can use tags for objects in any of the VI workload domains that are connected to the NSX Manager instance |
BOM and life cycle management |
You can manage the life cycle of the components of the VI workload domain individually. |
All VI workload domains under a shared NSX Manager instance must have a consistent BOM. As a result, you must perform life cycle management operations in all domains together. All clusters under a shared NSX Manager instance must use the same ESXi life cycle method - either vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines and baseline groups (formerly known as vSphere Update Manager) or vSphere Lifecycle Manager images. See Life Cycle Management Design for ESXi for a Virtual Infrastructure Workload Domain. |
NSX Manager scale |
Enables greater scale of NSX-T Date Center because each VI workload domain has its own NSX Manager instance and associated scale limits. |
All VI workload domains under a shared NSX Manager instance must fit within the scale limits of this NSX Manager instance. |
NSX Federation scale |
NSX Federation supports a limited number of NSX Local Managers in an NSX Federation. If many VI workloads are expected, you must consider the total number of NSX Manager instances. |
|