| VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 | 23 JUL 2024 | Build 24108943 Check for additions and updates to these release notes. |
What's New
The VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 5.2 release includes the following:
-
Support for Identity Federation with Entra ID: VCF users can now configure Microsoft Entra ID (formerly known as Azure AD) as an identity provider.
-
APIs for Auditing PCI Compliance: VCF users can now use a new set of APIs that audit VCF configuration for compliance with 9 relevant PCI-DSS controls.
-
vSAN Max support: vSAN Max is a disaggregated storage offering which enables petabyte scale storage-only clusters. vSAN Max is powered by ESA as the underlying storage platform, which is a high-performance file system that can scale up to high densities with no penalty to performance. ESA also provides other benefits such as built-in, efficient, scalable snapshots, and low overhead data services such as encryption and compression.
-
vSAN ESA Stretched Cluster: VCF users can now configure ESA Stretched Cluster in vSAN Ready Nodes. It enables customers to take the concept of fault domains to protect an environment spanning two physical sites from downtime in the event of a site failure.
-
VCF Import Tool (for vSphere & vSAN): The VCF Import Tool integrates existing vSphere environments into VMware Cloud Foundation, centralizing management and optimizing resources without needing a full rebuild.
-
Support for additional principal storage types with a converted management domain: If you use the VCF Import Tool to convert an existing vSphere environment to a VCF management domain, that management domain can use VMFS-FC and NFS v3 as principal storage, in addition to vSAN.
-
Dual DPU Support: VCF users can now leverage Dual DPU support. Dual DPU support boosts availability and performance. Active/Standby ensures continuity against failures, while dual independent DPUs double offload capacity and provide isolation.
-
Avi Load Balancer Integration with VCF: VCF users can now deploy Avi (formerly NSX Advanced Load Balancer) as part of a new workload domain and perform password rotation and certificate management of the ALB infrastructure from SDDC Manager.
-
Out of Band Changes from vCenter: Out of Band changes from vCenter can be manually synced with SDDC Manager. This includes inventory changes (for example, adding a host to a cluster) and object name changes (for example, datacenter name, datastore name, port group name).
-
ESXi Live Patching : VCF users can now apply ESXi security patches without requiring VM evacuation on ESXi hosts.
-
Flexible Target BOM for Upgrades: VCF users can now create a composite and customized BOM using patches when upgrading workload domains. Customers can plan an upgrade along with patches in one orchestrated workflow instead of performing an upgrade and applying patches in separate maintenance windows.
-
Async Patching with SDDC Manager: Customers previously used the standalone Async Patch Tool to apply patches to the VCF BOM components. VCF 5.2 provides the ability to apply BOM component patches from the SDDC Manager UI.
-
Day N workflows with Embedded Async Patching: VCF users can now add new workload domains and clusters with patched versions of individual BOM components from SDDC Manager.
-
Asynchronous SDDC Manager Upgrades: VCF users can now upgrade SDDC Manager independently from the rest of the BOM to apply critical fixes, security patches, and to enable specific features related to SDDC Manager.
-
Authenticated Proxy: VCF users can now use proxy authentication from SDDC Manager to enable secure connectivity from SDDC Manager to the internet.
-
Offline Depot: VCF users can now perform lifecycle bundle downloads in offline/air-gapped environments in a simplified manner. The offline depot downloads and stages VCF SDDC Manager and BOM component bundles and enables customers to configure SDDC Manager to download the bundles directly from the offline depot.
-
Isolated Workload Domains Sharing NSX: VCF users can now create and manage isolated workload domains that can share an NSX Manager instance between them.
Available Languages
Beginning with the next major release, VCF will be supporting the following localization languages:
-
Japanese
-
Spanish
-
French
The following languages will no longer be supported:
-
Italian, German, and Simplified Chinese.
Impact:
-
Customers who have been using the deprecated languages will no longer receive updates in these languages.
-
All user interfaces and help documentation will be available only in English or in the three supported languages mentioned above.
Because VCF localization utilizes the browser language settings, ensure that your settings match the desired language.
Deprecation Notices
-
VMware End Of Availability of Perpetual Licensing and SaaS Services. See https://blogs.vmware.com/cloud-foundation/2024/01/22/vmware-end-of-availability-of-perpetual-licensing-and-saas-services/ for more information.
-
The Composable Infrastructure feature is deprecated and removed.
-
In a future release, the "Connect Workload Domains" option from the VMware Aria Operations card located in SDDC Manager > Administration > Aria Suite section will be removed and related VCF Public API options will be deprecated.
Starting with VMware Aria Operations 8.10, functionality for connecting VCF Workload Domains to VMware Aria Operations is available directly from the UI. Users are encouraged to use this method within the VMware Aria Operations UI for connecting VCF workload domains, even if the integration was originally set up using SDDC Manager.
-
Deprecation announcements for VMware NSX. See the VMware NSX 4.2.0 Release Notes for details.
-
NSX Manager APIs and NSX Advanced UIs
-
NSX embedded (NSXe)
-
Some parameters in Switch IPFIX
-
NSX Migration Coordinator
-
VMware Cloud Foundation Bill of Materials (BOM)
The VMware Cloud Foundation software product is comprised of the following software Bill-of-Materials (BOM). The components in the BOM are interoperable and compatible.
| Software Component |
Version |
Date |
Build Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Builder VM |
5.2 |
23 JUL 2024 |
24108943 |
| SDDC Manager |
5.2 |
23 JUL 2024 |
24108943 |
| VMware vCenter Server Appliance |
8.0 Update 3a |
18 JUL 2024 |
24091160 |
| VMware ESXi |
8.0 Update 3 |
25 JUN 2024 |
24022510 |
| VMware vSAN Witness Appliance |
8.0 Update 3 |
25 JUN 2024 |
24022510 |
| VMware NSX |
4.2 |
23 JUL 2024 |
24105817 |
| VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle |
8.18 |
23 JUL 2024 |
24029603 |
-
VMware vSAN is included in the VMware ESXi bundle.
-
You can use VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle to deploy VMware Aria Automation, VMware Aria Operations, VMware Aria Operations for Logs, and Workspace ONE Access. VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle determines which versions of these products are compatible and only allows you to install/upgrade to supported versions.
-
VMware Aria Operations for Logs content packs are installed when you deploy VMware Aria Operations for Logs.
-
The VMware Aria Operations management pack is installed when you deploy VMware Aria Operations.
-
You can access the latest versions of the content packs for VMware Aria Operations for Logs from the VMware Solution Exchange and the VMware Aria Operations for Logs in-product marketplace store.
Supported Hardware
For details on supported configurations, see the VMware Compatibility Guide (VCG) and the Hardware Requirements section on the Prerequisite Checklist tab in the Planning and Preparation Workbook.
Documentation
To access the VCF documentation, go to the VMware Cloud Foundation product documentation.
To access the documentation for VMware software products that SDDC Manager can deploy, see the product documentation and use the drop-down menus on the page to choose the appropriate version:
-
VMware vSphere product documentation, includes the documentation for ESXi and vCenter Server
Browser Compatibility and Screen Resolutions
The VMware Cloud Foundation web-based interface supports the latest two versions of the following web browsers:
-
Google Chrome
-
Mozilla Firefox
-
Microsoft Edge
For the Web-based user interfaces, the supported standard resolution is 1920 by 1080 pixels.
Installation and Upgrade Information
You can install VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 as a new release or perform a sequential or skip-level upgrade to VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2.
Installing as a New Release
The new installation process has three phases:
-
Phase One: Prepare the Environment: The Planning and Preparation Workbook provides detailed information about the software, tools, and external services that are required to implement a Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) with VMware Cloud Foundation, using a standard architecture model.
-
Phase Two: Image all servers with ESXi: Image all servers with the ESXi version mentioned in the Cloud Foundation Bill of Materials (BOM) section. See the VMware Cloud Foundation Deployment Guide for information on installing ESXi.
-
Phase Three: Install Cloud Foundation 5.2: See the VMware Cloud Foundation Deployment Guide for information on deploying Cloud Foundation.
Upgrading to Cloud Foundation 5.2
You can perform a sequential or skip-level upgrade to VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 from VMware Cloud Foundation 4.5.0 or later. If your environment is at a version earlier than 4.5.0, you must upgrade the management domain and all VI workload domains to VMware Cloud Foundation 4.5.0 or above and then upgrade to VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2. For more information see VMware Cloud Foundation Lifecycle Management.
Before you upgrade a vCenter Server, take a file-based backup. See Manually Back Up vCenter Server.
Since VMware Cloud Foundation disables the SSH service by default, scripts that rely on SSH being enabled on ESXi hosts will not work after upgrading to VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2. Update your scripts to account for this new behavior. See KB 86230 for information about enabling and disabling the SSH service on ESXi hosts.
Resolved Issues
The following issue is resolved in this release:
-
VCF ESXi Upgrade with 'quick boot' option fails for hosts configured with TPM
-
Deploying the management domain using vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) images fails
-
VM MANAGEMENT port group may get created on the wrong vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS)
-
Entering pNICs in non-lexicographic order in the deployment parameter workbook does not work as expected
-
Entering more than two pNICs for the primary vDS in the deployment parameter workbook does not work as expected
-
SDDC Manager UI is showing a vSAN License as Active even though it was not assigned
-
Filtering bundles by "Downloaded" in the SDDC Manager UI does not show any results
-
Cannot add unused vmnics to an existing vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS)
Known Issues
- VMware Cloud Foundation Known Issues
- Upgrade Known Issues
- Bring-up Known Issues
- SDDC Manager Known Issues
- Workload Domain Known Issues
VMware Cloud Foundation Known Issues
-
VCF Import Tool does not support clusters that use vSphere Configuration Profiles
If you use the VCF Import Tool to import/convert an existing vSphere environment that includes clusters that use vSphere Configuration Profiles, the task fails during NSX deployment.
Workaround: None. Clusters that use vSphere Configuration Profiles do not support NSX.
-
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2 does not support the "License Now" option for vSAN add-on licenses based on capacity per tebibyte (TiB)
With vSphere 8.0 Update 3, you can license your use of vSAN storage based on TiB capacity. When using a per-TiB vSAN license with VMware Cloud Foundation, if you enter the license key using the "License Now" option either during bringup of the management domain, or when deploying or expanding a VI workload domain, the workflow fails.
Workaround: Use the "License Later" option and assign the per-TiB vSAN license key later using the vSphere Client.
-
Primary datastore is not getting set for imported workload domains with NFS 4.1 datastore
When you use the VCF Import Tool to import a cluster for which NFS 4.1 is the only shared datastore, the primary datastore and datastore type is not getting set in VCF and the workload domain is not visible in the SDDC Manager UI. See https://knowledge.broadcom.com/external/article/372424 for details.
Workaround: None.
-
Limitations for importing vSAN clusters
When you use the VCF Import Tool to import a vSAN cluster, you should avoid importing clusters with certain configurations. SDDC Manager day-N operations will not be supported on imported vSAN clusters with these configurations. See https://knowledge.broadcom.com/external/article/371494 for details.
Workaround: None.
-
Lifecycle Management Precheck does not throw an error when NSX Manager inventory is out of sync
The Lifecycle Management Precheck displays a green status and does not generate any errors for NSX Manager inventory.
Workaround: None
-
Upgrade Pre-Check Scope dropdown may contain additional entries
When performing Upgrade Prechecks through SDDC Manager UI and selecting a target VCF version, the Pre-Check Scope dropdown may contain more selectable entries than necessary. SDDC Manager may appear as an entry more than once. It also may be included as a selectable component for VI domains, although it's a component of the management domain.
Workaround: None. The issue is visual with no functional impact.
-
Converting clusters from vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines to vSphere Lifecycle Manager images is not supported.
vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines (previously known as vSphere Update Manager or VUM) are deprecated in vSphere 8.0, but continue to be supported. See KB article 89519 for more information.
VMware Cloud Foundation 5.0 does not support converting clusters from vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines to vSphere Lifecycle Manager images. This capability will be supported in a future release.
Workaround: None
-
Workload Management and NSX Federation
While you cannot deploy Workload Management (vSphere with Tanzu) to a workload domain using stretched NSX segments and T1/T0 when that workload domain’s NSX Data Center instance is participating in an NSX Federation, you can deploy NSX local segments and local dedicated T0/T1 from NSX Local Manager that are not stretched between two VCF instances using NSX Federation. Make sure to configure NSX Federation before deploying Workload Management to avoid any potential NSX import issues to NSX Global Manager.
Workaround: None.
Upgrade Known Issues
-
Bundle Transfer Utility fails to upload the NSX Advanced Load Balancer install bundle
If you on a pre-5.2 version of VMware Cloud Foundation and use the Bundle Transfer Utility to download all bundles for VCF 5.2, then uploading the NSX Advanced Load Balancer install bundle fails. This bundle is only supported with SDDC Manager 5.2 and later.
Workaround: Upgrade SDDC Manager to 5.2 and then retry uploading the NSX Advanced Load Balancer install bundle.
-
NSX host cluster upgrade fails
If you are upgrading a workload domain that uses vSphere Lifecycle Manager images and its cluster image was created from an ESXi host that uses vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines, then NSX host cluster upgrade will fail. A cluster image created from an ESXi host that uses vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines contains an NSX component that causes this issue.
NOTE: This issue is resolved in you have ESXi and vCenter Server 8.0 Update 3 or later.
Workaround: Do not create cluster images from an ESXi host that uses vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines. If you encounter this issue, you can resolve it by using the vSphere Client to remove the NSX LCP Bundle component from the cluster image.
-
SDDC Manager UI shows the incorrect source version when upgrading SDDC Manager
When you view the VMware Cloud Foundation Update Status for SDDC Manager, the UI may show the incorrect source version.
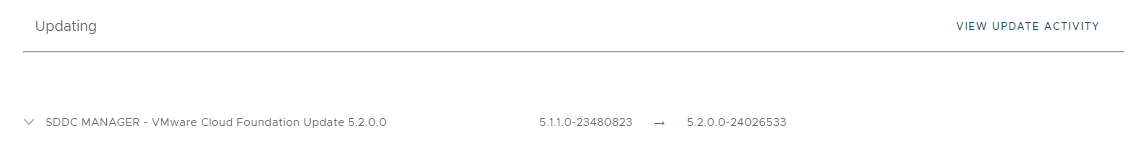
Workaround: None. This is a cosmetic issue only and does not affect the upgrade.
-
Workspace ONE Access inventory sync fails in SDDC Manager after upgrading VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle
After upgrading Aria Suite Lifecycle to version 8.12 or later, triggering a Workspace ONE Access inventory sync from Aria Suite Lifecycle fails. The SDDC Manager UI reports the following error:
Failed to configure WSA <wsa_fqdn> in vROps .vrops_fqdn>, because Failed to manage vROps adapter.Workaround: Download the bundle for your version of Aria Suite Lifecycle to SDDC Manager and retry the inventory sync.
-
VCF ESXi upgrade fails during post validation due to HA related cluster configuration issue
The upgrade of ESXi Cluster fails with error that is similar to below error message:
Cluster Configuration Issue: vSphere HA failover operation in progress in cluster <cluster-name> in datacenter <datacenter-name>: 0 VMs being restarted, 1 VMs waiting for a retry, 0 VMs waiting for resources, 0 inaccessible vSAN VMsWorkaround: See KB article 90985.
-
Lifecycle Management Precheck does not throw an error when NSX Manager inventory is out of sync
Workaround None.
-
NSX upgrade may fail if there are any active alarms in NSX Manager
If there are any active alarms in NSX Manager, the NSX upgrade may fail.
Workaround: Check the NSX Manager UI for active alarms prior to NSX upgrade and resolve them, if any. If the alarms are not resolved, the NSX upgrade will fail. The upgrade can be retried once the alarms are resolved.
-
SDDC Manager upgrade fails at "Setup Common Appliance Platform"
If a virtual machine reconfiguration task (for example, removing a snapshot or running a backup) is taking place in the management domain at the same time you are upgrading SDDC Manager, the upgrade may fail.
Workaround: Schedule SDDC Manager upgrades for a time when no virtual machine reconfiguration tasks are happening in the management domain. If you encounter this issue, wait for the other tasks to complete and then retry the upgrade.
-
Parallel upgrades of vCenter Server are not supported
If you attempt to upgrade vCenter Server for multiple VI workload domains at the same time, the upgrade may fail while changing the permissions for the vpostgres configuration directory in the appliance. The message
chown -R vpostgres:vpgmongrp /storage/archive/vpostgresappears in the PatchRunner.log file on the vCenter Server Appliance.Workaround: Each vCenter Server instance must be upgraded separately.
-
When you upgrade VMware Cloud Foundation, one of the vSphere Cluster Services (vCLS) agent VMs gets placed on local storage
vSphere Cluster Services (vCLS) ensures that cluster services remain available, even when the vCenter Server is unavailable. vCLS deploys three vCLS agent virtual machines to maintain cluster services health. When you upgrade VMware Cloud Foundation, one of the vCLS VMs may get placed on local storage instead of shared storage. This could cause issues if you delete the ESXi host on which the VM is stored.
Workaround: Deactivate and reactivate vCLS on the cluster to deploy all the vCLS agent VMs to shared storage.
-
Check the placement of the vCLS agent VMs for each cluster in your environment.
-
In the vSphere Client, select Menu > VMs and Templates.
-
Expand the vCLS folder.
-
Select the first vCLS agent VM and click the Summary tab.
-
In the Related Objects section, check the datastore listed for Storage. It should be the vSAN datastore. If a vCLS agent VM is on local storage, you need to deactivate vCLS for the cluster and then re-enable it.
-
Repeat these steps for all vCLS agent VMs.
-
-
Deactivate vCLS for clusters that have vCLS agent VMs on local storage.
-
In the vSphere Client, click Menu > Hosts and Clusters.
-
Select a cluster that has a vCLS agent VM on local storage.
-
In the web browser address bar, note the moref id for the cluster.
For example, if the URL displays as https://vcenter-1.vrack.vsphere.local/ui/app/cluster;nav=h/urn:vmomi:ClusterComputeResource:domain-c8:503a0d38-442a-446f-b283-d3611bf035fb/summary, then the moref id is domain-c8.
-
Select the vCenter Server containing the cluster.
-
Click Configure > Advanced Settings.
-
Click Edit Settings.
-
Change the value for
config.vcls.clusters.<moref id>.enabledtofalseand click Save.If the
config.vcls.clusters.<moref id>.enabledsetting does not appear for your moref id, then enter its Name andfalsefor the Value and click Add. -
Wait a couple of minutes for the vCLS agent VMs to be powered off and deleted. You can monitor progress in the Recent Tasks pane.
-
-
Enable vCLS for the cluster to place the vCLS agent VMs on shared storage.
-
Select the vCenter Server containing the cluster and click Configure > Advanced Settings.
-
Click Edit Settings.
-
Change the value for
config.vcls.clusters.<moref id>.enabledtotrueand click Save. -
Wait a couple of minutes for the vCLS agent VMs to be deployed and powered on. You can monitor progress in the Recent Tasks pane.
-
-
Check the placement of the vCLS agent VMs to make sure they are all on shared storage
-
-
You are unable to update NSX Data Center in the management domain or in a workload domain with vSAN principal storage because of an error during the NSX transport node precheck stage
In SDDC Manager, when you run the upgrade precheck before updating NSX Data Center, the NSX transport node validation results with the following error.
No coredump target has been configured. Host core dumps cannot be saved.:System logs on host sfo01-m01-esx04.sfo.rainpole.io are stored on non-persistent storage. Consult product documentation to configure a syslog server or a scratch partition.
Because the upgrade precheck results with an error, you cannot proceed with updating the NSX Data Center instance in the domain. VMware Validated Design supports vSAN as the principal storage in the management domain. However, vSAN datastores do no support scratch partitions. See VMware Knowledge Base article 2074026.
Disable the update precheck validation for the subsequent NSX Data Center update.
-
Log in to SDDC Manager as vcf using a Secure Shell (SSH) client.
-
Open the
application-prod.propertiesfile for editing:vi /opt/vmware/vcf/lcm/lcm-app/conf/application-prod.properties -
Add the following property and save the file:
lcm.nsxt.suppress.prechecks=true -
Restart the life cycle management service:
systemctl restart lcm -
Log in to the SDDC Manager user interface and proceed with the update of NSX Data Center.
-
Bring-up Known Issues
SDDC Manager Known Issues
-
The SDDC Manager UI displays incorrect CPU and memory utilization information for hosts
When you view CPU and memory usage for hosts in the SDDC Manager UI (Inventory > Hosts), the information may not reflect actual utilization.
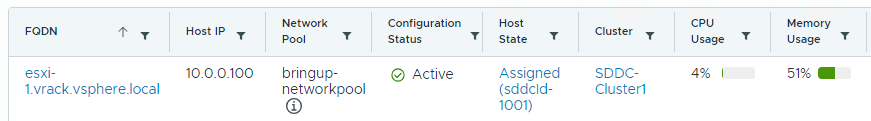
Workaround: Use the vSphere Client to view CPU and memory utilization information for hosts.
-
Install bundle for VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle 8.18 displays incomplete information
The SDDC Manager UI displays incomplete information for the VMware Aria Suite Lifecycle 8.18 install bundle.

Workaround: None. This is a cosmetic issue and does not impact your ability to download or use the bundle.
-
When creating a network pool, the IP addresses you provide are not validated to ensure that they are not in use
SDDC Manager does validate the included IPs for a new network pool against other network pools and against all other network types (vSAN, NFS, and so on) being added to the new network pool. However, it does not validate them against other components that are already deployed in the VMware Cloud Foundation instance (for example, ESXi hosts, NSX Managers, and so on). This can result in duplicate IP address errors or failed workflows.
Workaround: When creating a network pool, do not include any IP addresses that are already in use. If you already created a network pool that includes IP addresses that are used by other components, contact Broadcom Support to resolve the issue.
-
vSphere Lifecycle Manager images that utilize “removed components” are not supported
Starting with vSphere 8.0 Update 3, you can remove the Host Client and VMware Tools components from a base image, remove unnecessary drivers from vendor add-ons and components, and override existing drivers in a desired image. SDDC Manager does not support this functionality yet for imported or extracted cluster images.
Workaround: None.
Workload Domain Known Issues
-
Deploying Avi Load Balancer fails
When you deploy Avi Load Balancer (formerly known as NSX Advanced Load Balancer), the deployment may fail with the message
OVA upload to NSX failed. This can happen if the certificates of the management domain NSX Manager nodes do not include their IP addresses in their Subject Alternative Names (SANs).Workaround: Generate new CSRs for the management domain NSX Manager nodes, making sure to include IP addresses for the SANs. For example:
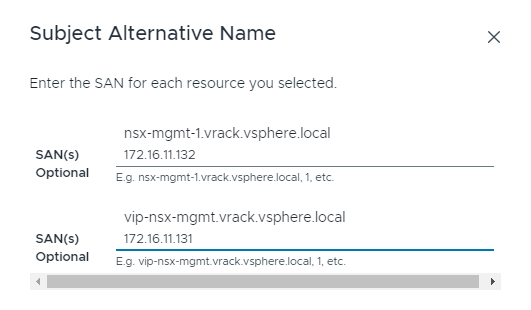
Generate the signed certificates using the CSRs and then install the signed certificates in the NSX Manager nodes. See Managing Certificates in VMware Cloud Foundation for more information.
Once the new certificates are installed, retry deploying Avi Load Balancer.
-
Switch configuration error when deploying a VI workload domain or adding a cluster to a workload domain with hosts that have two DPUs
If you are using ESXi hosts with two data processing units (DPU) to deploy a new VI workload domain or add a cluster to a workload domain, you may see the following error during switch configuration:
Error in validating Config Profiles. This can be caused by the presence of a vusb0 network adapter on the hosts.Workaround: Contact Broadcom Support to remove the vusb0 interface from the SDDC Manager inventory.
-
Deploying a VI workload domain or adding a cluster to a workload domain fails with hosts that have two DPUs
If you are using ESXi hosts with two data processing units (DPU) to deploy a new VI workload domain or add a cluster to a workload domain, the task fails when adding the ESXi hosts to the vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) with the error
Cannot complete a vSphere Distributed Switch operation for one or more host members.The VDS created by SDDC Manager for dual DPU hosts has all 4 uplinks in Active mode and this does not work with an NSX uplink profile where one set of DPU uplinks is Active and a second set of DPU uplinks is Standby.
Workaround: Use the vSphere Client to manually update the DPU failover settings for the VDS and then retry the workflow from SDDC Manager.
-
In the vSphere Client, browse to the VDS in the vCenter that contains the hosts.
-
Click the Configure tab and select DPU Failover Settings.
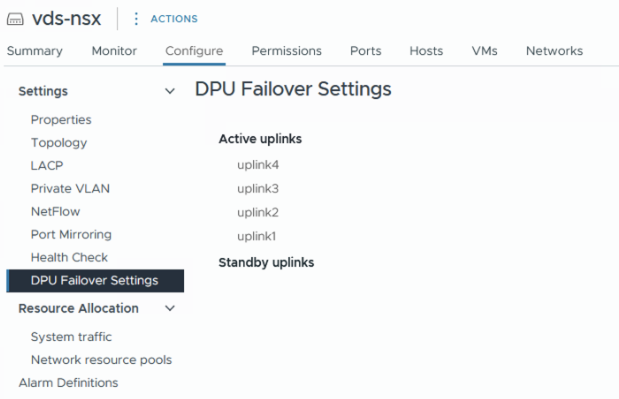
-
Click Edit and move uplink3 and uplink4 from Active to Standby.
-
Click OK.
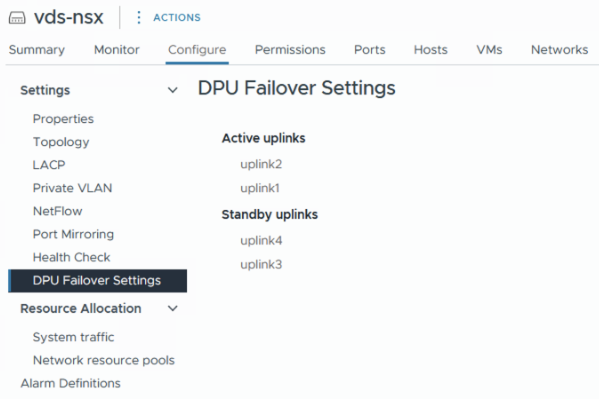
-
In the SDDC Manager UI, retry the failed workflow.
-
-
NSX Edge cluster deployment fails at "Create VLAN Port Group" stage with message "Invalid parameter: port group already exists"
When you deploy an NSX Edge cluster for VI workload domain and you select the option "USE ESXI MANAGEMENT VMK'S VLAN", the management portgroup name and VLAN ID are auto-populated. SDDC Manager tries to create a portgroup with same VLAN and portgroup name as ESXi management, but since the portgroup name already exists in vCenter the operation fails.
Workaround: If you select the option "USE ESXI MANAGEMENT VMK'S VLAN", change the auto-populated portgroup name to something else so that there is no conflict. If the environment is already in failed state, remove the partially deployed edge cluster. See https://knowledge.broadcom.com/external/article/316110/vmware-cloud-foundation-nsxt-edge-clust.html.
-
Remove unresponsive ESXi Host fails when SDDC Manager certificate does not have subject alternative name
When trying to remove an unresponsive ESXi Host from a cluster, if the SDDC Manager certificate does not have subject alternative name (SAN), the removal of the host will fail at the task "Remove vmknics(s) from ESXi Hosts".
Workaround: Rotate the certificate of the SDDC Manager which will include the SAN. Once the certificate is rotated and it has SAN, the failed remove host workflow can be retried.
-
Failure when deploying multiple isolated workload domains with the same SSO domain in parallel
If you are deploying more than one isolated workload domain at the same time and those workload domains use the same SSO domain, then only the first workload domain is created successfully. Creation of the additional workload domains fails during validation with a message saying that the SSO domain name is already allocated.
Workaround: Deploy the workload domains sequentially. Wait until the first workload domain deploys successfully and then create the additional workload domains.
-
Heterogeneous operations "Cluster Creation" and "VI Creation" are not supported to be run in parallel when they are operating against same shared NSX instance.
If there is a running VI Creation workflow operating on an NSX resource, then creating a cluster on domains that are sharing that NSX is not possible.
Workaround: None. The VI Creation workflow should complete before the cluster creation workflow can be started.
-
Adding host fails when host is on a different VLAN
A host add operation can sometimes fail if the host is on a different VLAN.
-
Before adding the host, add a new portgroup to the VDS for that cluster.
-
Tag the new portgroup with the VLAN ID of the host to be added.
-
Add the Host. This workflow fails at the "Migrate host vmknics to dvs" operation.
-
Locate the failed host in vCenter, and migrate the vmk0 of the host to the new portgroup you created in step 1. For more information, see Migrate VMkernel Adapters to a vSphere Distributed Switch in the vSphere product documentation.
-
Retry the Add Host operation.
NOTE: If you later remove this host in the future, you must manually remove the portgroup as well if it is not being used by any other host.
-
-
Deploying partner services on an NSX workload domain displays an error
Deploying partner services, such as McAfee or Trend, on a workload domain enabled for vSphere Update Manager (VUM), displays the “Configure NSX at cluster level to deploy Service VM” error.
Attach the Transport node profile to the cluster and try deploying the partner service. After the service is deployed, detach the transport node profile from the cluster.
-
If the witness ESXi version does not match with the host ESXi version in the cluster, vSAN cluster partition may occur
vSAN stretch cluster workflow does not check the ESXi version of the witness host. If the witness ESXi version does not match the host version in the cluster, then vSAN cluster partition may happen.
-
Upgrade the witness host manually with the matching ESXi version using the vCenter VUM functionality.
-
Replace or deploy the witness appliance matching with the ESXi version.
-
-
vSAN partition and critical alerts are generated when the witness MTU is not set to 9000
If the MTU of the witness switch in the witness appliance is not set to 9000, the vSAN stretch cluster partition may occur.
Set the MTU of the witness switch in the witness appliance to 9000 MTU.
-
Adding a host to a vLCM-enabled workload domain configured with the Dell Hardware Support Manager (OMIVV) fails
When you try to add a host to a vSphere cluster for a workload domain enabled with vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM), the task fails and the domain manager log reports "The host (host-name) is currently not managed by OMIVV." The domain manager logs are located at /var/log/vmware/vcf/domainmanager on the SDDC Manager VM.
Update the hosts inventory in OMIVV and retry the add host task in the SDDC Manager UI. See the Dell documentation for information about updating the hosts inventory in OMIVV.
-
The vSAN Performance Service is not enabled for vSAN clusters when CEIP is not enabled
If you do not enable the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) in SDDC Manager, when you create a workload domain or add a vSphere cluster to a workload domain, the vSAN Performance Service is not enabled for vSAN clusters. When CEIP is enabled, data from the vSAN Performance Service is provided to VMware and this data is used to aid VMware Support with troubleshooting and for products such as VMware Skyline, a proactive cloud monitoring service. See Customer Experience Improvement Program for more information on the data collected by CEIP.
Enable CEIP in SDDC Manager. See the VMware Cloud Foundation Documentation. After CEIP is enabled, a scheduled task that enables the vSAN Performance Service on existing clusters in workload domains runs every three hours. The service is also enabled for new workload domains and clusters. To enable the vSAN Performance Service immediately, see the VMware vSphere Documentation.
-
Creation or expansion of a vSAN cluster with more than 32 hosts fails
By default, a vSAN cluster can grow up to 32 hosts. With large cluster support enabled, a vSAN cluster can grow up to a maximum of 64 hosts. However, even with large cluster support enabled, a creation or expansion task can fail on the sub-task Enable vSAN on vSphere Cluster.
-
Enable Large Cluster Support for the vSAN cluster in the vSphere Client. If it is already enabled skip to step 2.
-
Select the vSAN cluster in the vSphere Client.
-
Select Configure > vSAN > Advanced Options.
-
Enable Large Cluster Support.
-
Click Apply.
-
Click Yes.
-
-
Run a vSAN health check to see which hosts require rebooting.
-
Put the hosts into Maintenance Mode and reboot the hosts.
For more information about large cluster support, see https://kb.vmware.com/kb/2110081.
-
-
Removing a host from a cluster, deleting a cluster from a workload domain, or deleting a workload domain fails if Service VMs (SVMs) are present
If you deployed an endpoint protection service (such as guest introspection) to a cluster through NSX Data Center, then removing a host from the cluster, deleting the cluster, or deleting the workload domain containing the cluster will fail on the subtask Enter Maintenance Mode on ESXi Hosts.
-
For host removal: Delete the Service VM from the host and retry the operation.
-
For cluster deletion: Delete the service deployment for the cluster and retry the operation.
-
For workload domain deletion: Delete the service deployment for all clusters in the workload domain and retry the operation.
-
-
vCenter Server overwrites the NFS datastore name when adding a cluster to a VI workload domain
If you add an NFS datastore with the same NFS server IP address, but a different NFS datastore name, as an NFS datastore that already exists in the workload domain, then vCenter Server applies the existing datastore name to the new datastore.
If you want to add an NFS datastore with a different datastore name, then it must use a different NFS server IP address.