vSphere cluster design must consider the requirements for standard, stretched and remote clusters and for the life cycle management of the ESXi hosts in the clusters according to the characteristics of the workloads.
Logical vSphere Cluster Design for VMware Cloud Foundation
The cluster design must consider the characteristics of the workloads that are deployed in the cluster.
When you design the cluster layout in vSphere, consider the following guidelines:
Compare the capital costs of purchasing fewer, larger ESXi hosts with the costs of purchasing more, smaller ESXi hosts. Costs vary between vendors and models. Evaluate the risk of losing one larger host in a scaled-up cluster and the impact on the business with the higher chance of losing one or more smaller hosts in a scale-out cluster.
Evaluate the operational costs of managing a few ESXi hosts with the costs of managing more ESXi hosts.
Consider the purpose of the cluster - management, compute only, edge and compute or edge only clusters.
For NSX Edge-only clusters, consider the number of physical NICs for the ESXi nodes in the vSphere cluster.
Consider the total number of ESXi hosts and cluster limits.
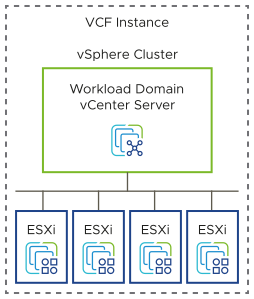
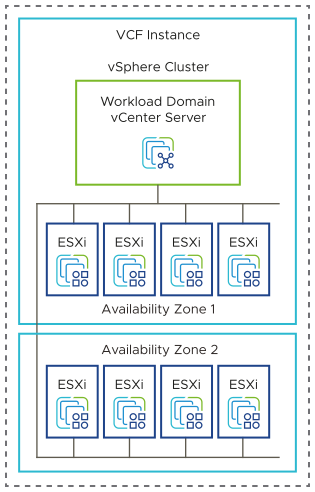
Remote Cluster Design Considerations
Remote clusters are managed by the management infrastructure at the central site.
Remote Cluster Attribute |
Consideration |
|---|---|
Number of hosts per remote cluster |
|
VI Workload domains having Remote Clusters in a VMware Cloud Foundation instance. |
|
| Number of remote clusters per VI workload domain |
|
Cluster types per VI workload domain |
A VI workload domain can include either local clusters or a remote cluster. |
Latency between the central site and the remote site |
|
Bandwidth between the central site and the remote site |
|
vSphere Cluster Lifecycle Method Design for VMware Cloud Foundation
vSphere Lifecycle Manager is used to manage the vSphere clusters in each workload domain.
When deploying a workload domain, you can choose a vSphere cluster lifecycle management method based on your organization's requirements. For additional clusters within the workload domain, you have the flexibility to select a different vSphere cluster lifecycle management method to meet specific requirements.
Cluster Lifecycle Management Method |
Description |
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
vSphere Lifecycle Manager images |
vSphere Lifecycle Manager images contain base images, vendor add-ons, firmware, and drivers. |
|
|
vSphere Lifecycle Manager baselines |
An upgrade baseline contains the ESXi image and a patch baseline contains the respective patches for ESXi host. |
|
|
vSphere Cluster Design Requirements and Recommendations for VMware Cloud Foundation
The design of a vSphere cluster is a subject to a minimum number of hosts, design requirements, and design recommendations.
For vSAN design requirements and recommendations, see vSAN Design Requirements and Recommendations for VMware Cloud Foundation.
The requirements for the ESXi hosts in a workload domain in VMware Cloud Foundation are related to the system requirements of the workloads hosted in the domain. The ESXi requirements include number, server configuration, amount of hardware resources, networking, and certificate management. Similar best practices help you design optimal environment operation
vSphere Cluster Design Considerations
You consider different number of hosts per cluster according to the storage type and specific resource requirements for standard and stretched vSAN clusters.
Attribute |
Specification |
Management Domain (Default Cluster) |
Management Domain (Additional Clusters) or VI Workload Domain (All Clusters) |
|---|---|---|---|
Minimum number of ESXi hosts |
vSAN (single availability zone) |
4 |
3 |
vSAN (two availability zones) |
8 |
6 |
|
NFS, FC, or vVols |
Not supported |
|
|
Reserved capacity for handling ESXi host failures per cluster |
Single availability zone |
|
|
Two availability zones |
|
|
vSphere Cluster Design Requirements VMware Cloud Foundation
You must meet the following design requirements for standard and stretched clusters in your vSphere cluster design for VMware Cloud Foundation. The cluster design considers the storage type for the cluster, the architecture model of the environment, and the lifecycle management method.
Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-001 |
Create a cluster in each workload domain for the initial set of ESXi hosts. |
|
Management of multiple clusters and vCenter Server instances increases operational overhead. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-002 |
Allocate a minimum number of ESXi hosts according to the cluster type being deployed. |
|
To support redundancy, you must allocate additional ESXi host resources. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-003 |
If using a consolidated workload domain, configure the following vSphere resource pools to control resource usage by management and customer workloads.
|
|
You must manage the vSphere resource pool settings over time. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-004 |
For vSAN clusters, except for vSAN Max clusters, configure the vSAN network gateway IP address as the isolation address for the cluster. |
vSphere HA can validate if a host is isolated from the vSAN network. |
You must allocate an additional IP address. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-005 |
For vSAN clusters, except for vSAN Max clusters, set the advanced cluster setting |
Ensures that vSphere HA uses the manual isolation addresses instead of the default management network gateway address. |
None. |
Requirement ID |
Design Requirement |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-006 |
Configure the IP address of the vSAN network for the second availability zone as an additional isolation addresses for the cluster. |
Enables vSphere HA to validate if a host is isolated from the vSAN network for hosts in both availability zones. |
The IP address of the vSAN network gateway must be highly available and reply to ICMP requests. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-007 |
Enable the Override default gateway for this adapter setting on the vSAN VMkernel adapters on all ESXi hosts. |
Enables routing the vSAN data traffic through the vSAN network gateway rather than through the management gateway. |
vSAN networks across availability zones must have a route to each other. |
VCF-CLS-REQD-CFG-008 |
Create a host group for each availability zone and add the ESXi hosts in the zone to the respective group. |
Makes it easier to manage which virtual machines run in which availability zone. |
You must create and maintain VM-Host DRS group rules. |
vSphere Cluster Design Recommendations for VMware Cloud Foundation
In your vSphere cluster design, you can apply certain best practices for standard and stretched clusters.
Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-001 |
Use vSphere HA to protect all virtual machines against failures. |
vSphere HA supports a robust level of protection for both ESXi host and virtual machine availability. |
You must provide sufficient resources on the remaining hosts so that virtual machines can be restarted on those hosts in the event of a host outage. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-002 |
For vSAN clusters, set host isolation response to Power Off and restart VMs in vSphere HA. |
vSAN requires that the host isolation response be set to Power Off and to restart virtual machines on available ESXi hosts. |
If a false positive event occurs, virtual machines are powered off and an ESXi host is declared isolated incorrectly. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-003 |
Configure admission control for 1 ESXi host failure and percentage-based failover capacity. |
Using the percentage-based reservation works well in situations where virtual machines have varying and sometimes significant CPU or memory reservations. vSphere automatically calculates the reserved percentage according to the number of ESXi host failures to tolerate and the number of ESXi hosts in the cluster. |
In a cluster of 4 ESXi hosts, the resources of only 3 ESXi hosts are available for use. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-004 |
Enable VM Monitoring for each cluster. |
VM Monitoring provides in-guest protection for most VM workloads. The application or service running on the virtual machine must be capable of restarting successfully after a reboot or the virtual machine restart is not sufficient. |
None. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-005 |
Set the advanced cluster setting |
Enables triggering a restart of a management appliance when an OS failure occurs and heartbeats are not received from VMware Tools instead of waiting additionally for the I/O check to complete. |
If you want to specifically enable I/O monitoring, you must configure the das.iostatsinterval advanced setting. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-006 |
Enable vSphere DRS on all clusters, using the default fully automated mode with medium threshold. |
Provides the best trade-off between load balancing and unnecessary migrations with vSphere vMotion. |
If a vCenter Server outage occurs, the mapping from virtual machines to ESXi hosts might be difficult to determine. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-007 |
Enable Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) on all clusters in the management domain. |
Supports cluster upgrades without virtual machine downtime. |
You must enable EVC only if the clusters contain hosts with CPUs from the same vendor. You must enable EVC on the default management domain cluster during bringup. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-008 |
Set the cluster EVC mode to the highest available baseline that is supported for the lowest CPU architecture on the hosts in the cluster. |
Supports cluster upgrades without virtual machine downtime. |
None. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-LCM-001 |
Use images as the life cycle management method for all workload domains. |
|
|
Recommendation ID |
Design Recommendation |
Justification |
Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-009 |
Increase admission control percentage to half of the ESXi hosts in the cluster. |
Allocating only half of a stretched cluster ensures that all VMs have enough resources if an availability zone outage occurs. |
In a cluster of 8 ESXi hosts, the resources of only 4 ESXi hosts are available for use. If you add more ESXi hosts to the default management cluster, add them in pairs, one per availability zone. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-010 |
Create a virtual machine group for each availability zone and add the VMs in the zone to the respective group. |
Ensures that virtual machines are located only in the assigned availability zone to avoid unnecessary vSphere vMotion migrations. |
You must add virtual machines to the allocated group manually. |
VCF-CLS-RCMD-CFG-011 |
Create a should-run-on-hosts-in-group VM-Host affinity rule to run each group of virtual machines on the respective group of hosts in the same availability zone. |
Ensures that virtual machines are located only in the assigned availability zone to avoid unnecessary vSphere vMotion migrations. |
You must manually create the rules. |