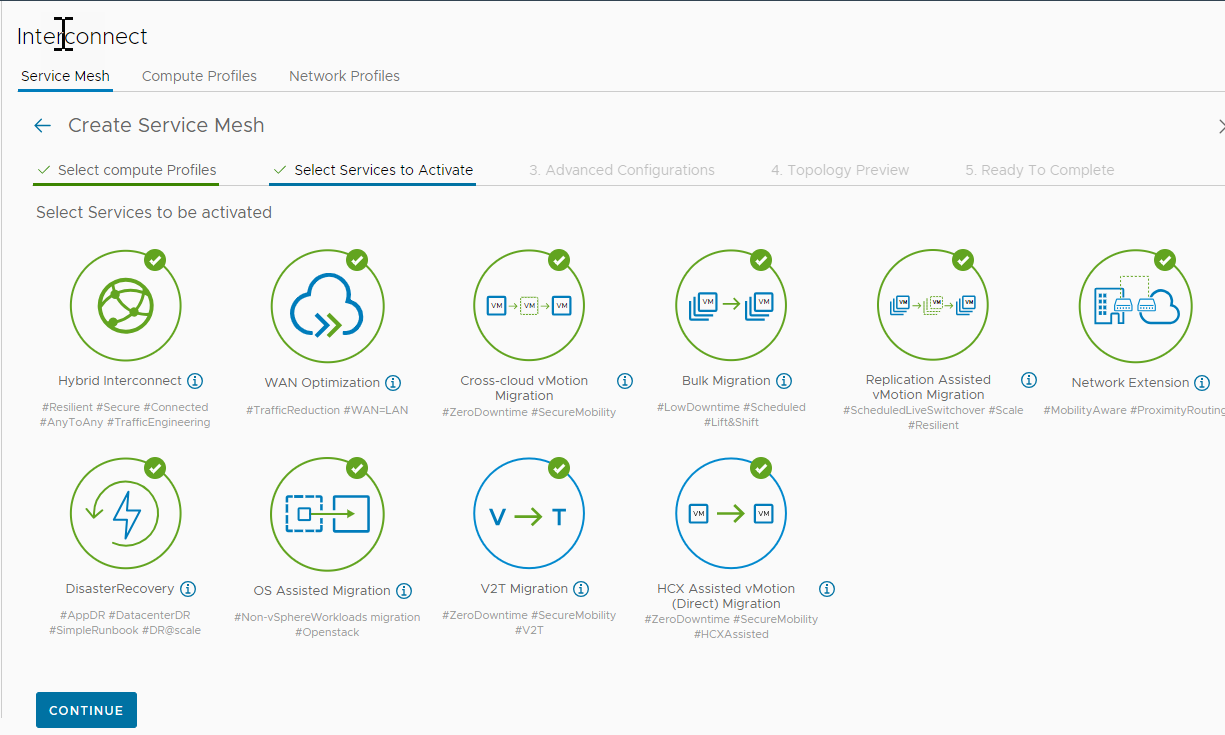
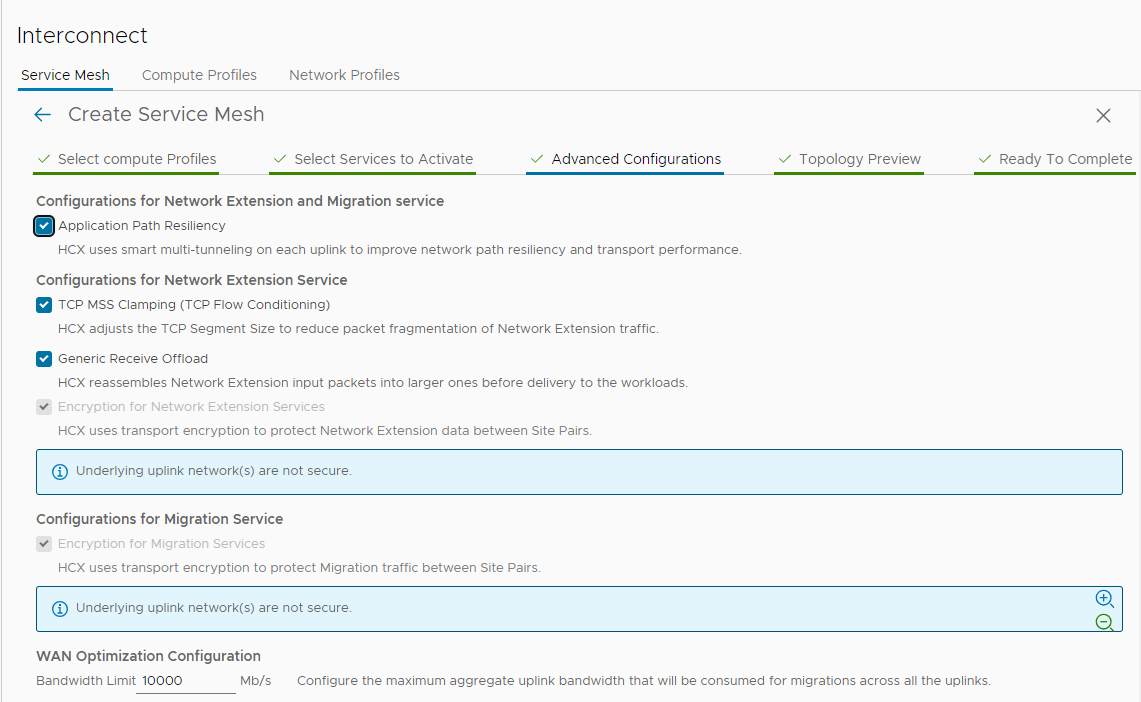
An HCX Service Mesh provides the HCX services configuration for a Site Pair. This section describes the procedure for creating a Service Mesh for a vSphere-based HCX Site Pair.
Adding a Service Mesh initiates the deployment of HCX Interconnect virtual appliances on both of the sites. A Service Mesh is always created at the source site.
Prerequisites
Creating a Service Mesh requires:
A connected Site Pair.
A valid Compute Profile at the HCX source and HCX destination site.
Virtual Switches (for Network Extension) and Network Profiles selected in each Compute Profile must span across all hosts in every selected deployment cluster. If these objects do not span all hosts, it is possible that the appliances will be deployed in a host missing the needed networks. In this case, the Service Mesh deployment can fail or services may not function properly.
Procedure
What to do next
After the Service Mesh configuration is complete, verify the underlay network performance for each Uplink Network. The underlay network performance must meet the minimum requirements for HCX services. See Understanding HCX Transport Analytics.
If you are migrating guest workloads using OS Assisted Migration, download and install the Sentinel software on each guest workload. See Sentinel Management.
If it is necessary to edit an existing Service Mesh, such as activating or deactivating services and overriding uplinks, select . The editing workflow includes a preview screen, listing the changes and describing the impact of those changes on related services prior to finishing the procedure. You can select to complete or cancel the update.