Application profiles determine the behavior of virtual services, based on application type.
The application profile types and their options are described in the following sections.
Dependency on TCP/UDP Profile
The application profile associated with a virtual service can have a dependency on an underlying TCP/UDP profile. For example, an HTTP application profile can be used only if the TCP/UDP profile type used by the virtual service is set to type TCP Proxy. The application profile associated with a virtual service instructs the Service Engine (SE) to proxy the service’s application protocol, such as HTTP, and to perform functionality appropriate for that protocol.
Application Profiles in NSX Advanced Load Balancer
To view the Application Profiles in NSX Advanced Load Balancer navigate to .
NSX Advanced Load Balancer displays all the application profiles created and their type as shown here.
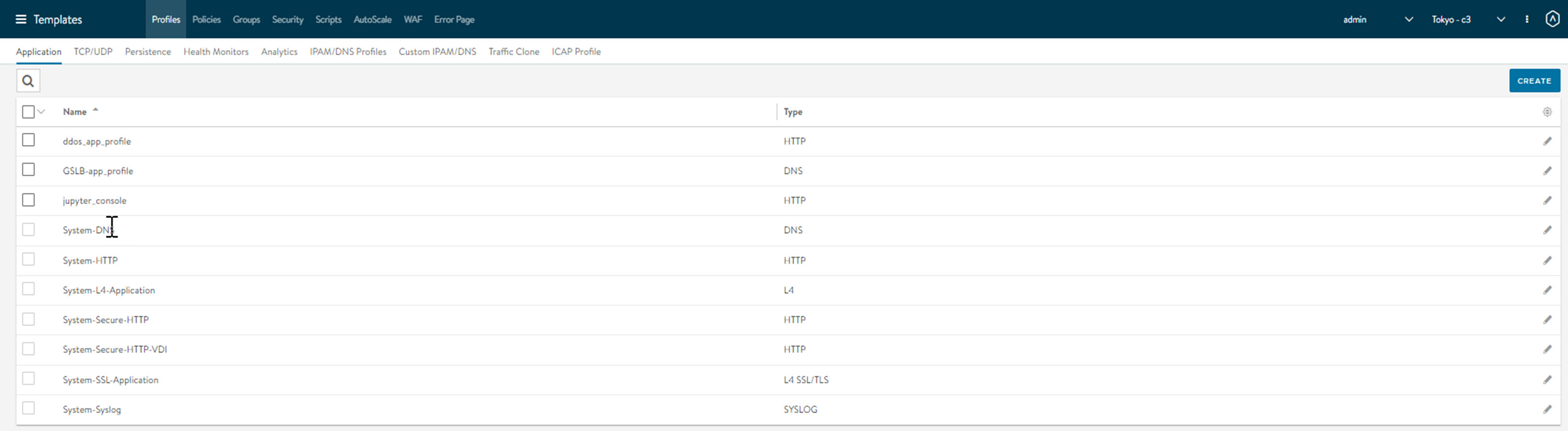
In this screen, you can perform the following functions.
Click search icon and start typing the name of the application profile to find it.
Create a new application profile.
Click edit icon against an application profile to modify the configuration.
Delete an existing application profile if it is not assigned to a virtual service.
If the profile is still associated with any virtual services, the profile cannot be removed. In this case, an error message lists the virtual service that still is referencing the application profile. Neither can any one of the system-standard profiles (as illustrated below) be deleted.
Create/Edit an Application Profile
Click Create and select the type of application profile from the drop-down menu according to the traffic to be processed.
- DNS
-
Default for processing DNS traffic
- HTTP
-
Default for processing Layer 7 HTTP traffic
- L4
-
Catch-all for any virtual service that is not using an application-specific profile.
- L4 SSL/TLS
-
Catch-all for any virtual service that is SSL-encrypted and not using an application-specific profile.
- SIP
-
Default for processing SIP traffic.
- Syslog
-
Default for processing Syslog traffic.
Configure the application profile in the New Application Profile screen.
The New Application Profile and the Edit Application Profile screens share the same interface regardless of the application profile chosen.
HTTP Profile
The HTTP application profile allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to be a proxy for any HTTP traffic. HTTP-specific functionality such as redirects, content switching, or rewriting server responses to client requests may be applied to a virtual service. The settings apply to all HTTP services that are associated with the HTTP profile. HTTP-specific policies or DataScripts also may be attached directly to a virtual service.
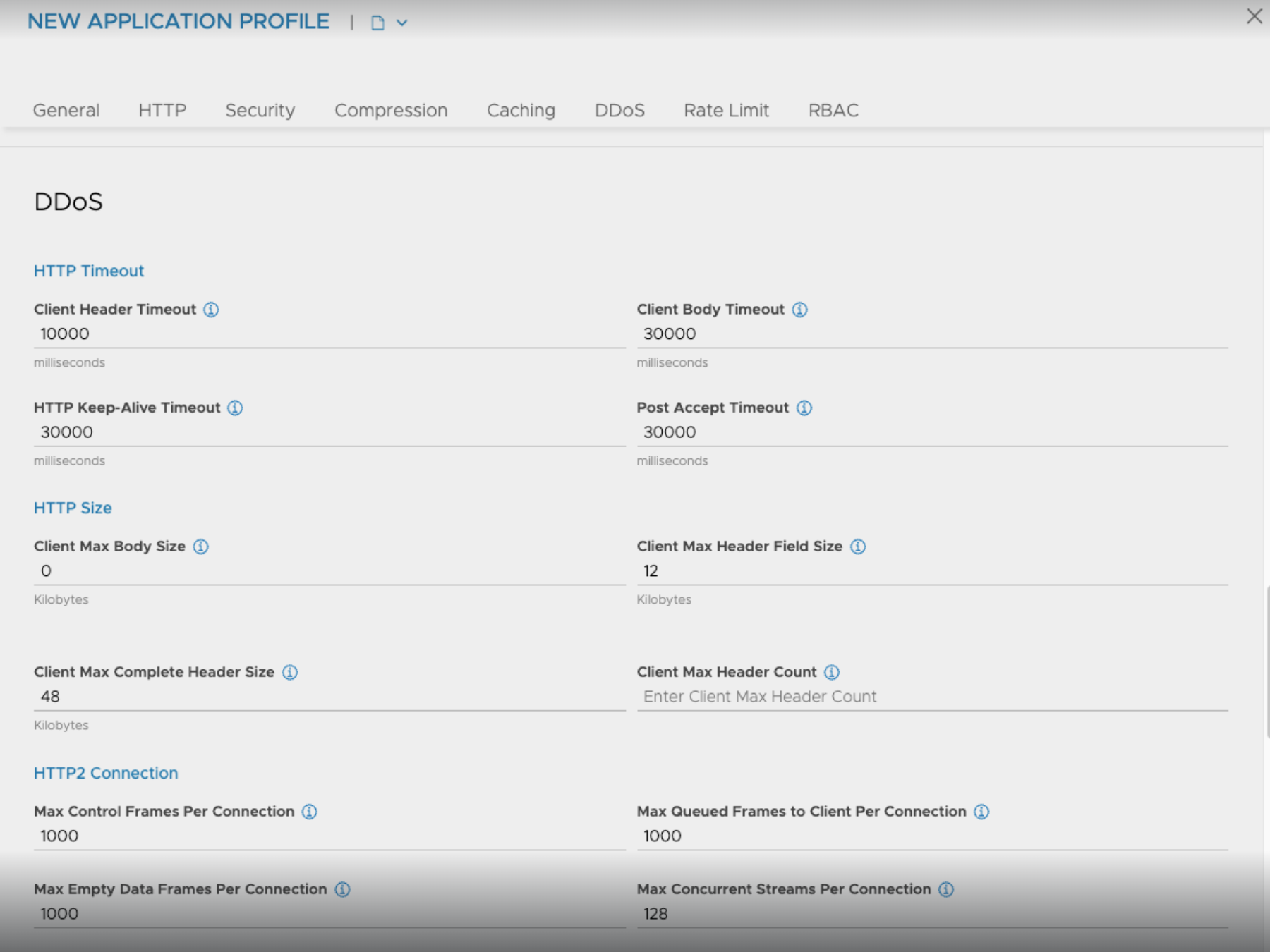
Max Header Count
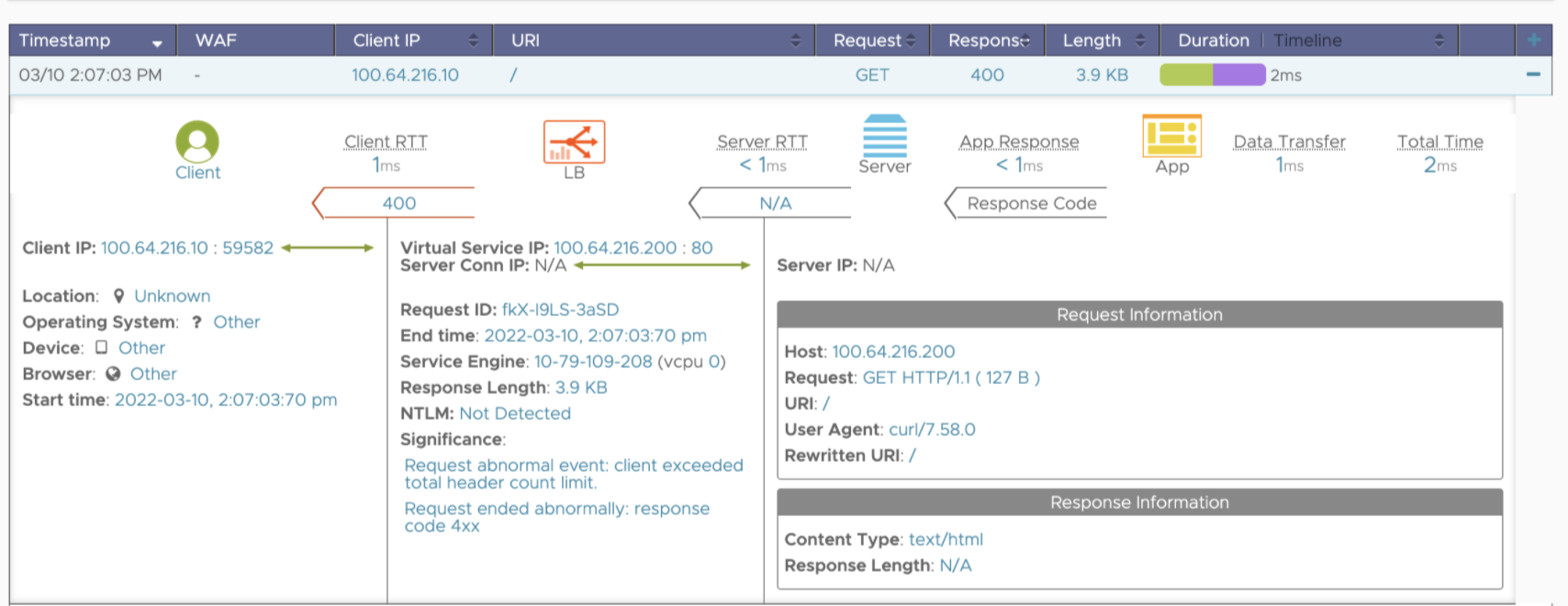
The max_header_count knob defines the total number of headers in the HTTP request and response. The default value of the max_header_count is 64, and the value range is 0-4096. If the number of headers exceeds the value specified, then NSX Advanced Load Balancer rejects the HTTP request with the significant application logs as shown below:
Log into the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller and use the
System-HTTP application profile under the configure application profile mode to set the value of max header count as shown below.
[admin:ctrl]: > configure applicationprofile System-HTTP [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile> http_profile [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile:http_profile> max_header_count [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile:http_profile> max_header_count 256 Overwriting the previously entered value for max_header_count [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile:http_profile> save [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile> save
To enable the Max Header Count option from the NSX Advanced Load Balancer UI, navigate to and enter the value for Client Max Header Count.
Pass through X-Accel header
NSX Advanced Load Balancer supports passing along the X-Accel headers to the HTTP response sent to the client. These headers include:
X-Accel-Expires
X-Accel-Redirect
X-Accel-Limit-Rate
X-Accel-Buffering
X-Accel-Charset
The HTTP application profile supports a new configuration knob, pass_through_x_accel_headers. By default, this field is set to False, which means NSX Advanced Load Balancer will not pass along the X-Accel headers in the HTTP response sent to the client. If it is set to True, NSX Advanced Load Balancer passes the X-Accel headers along with the HTTP response sent to the client.
If an object with the X-Accel-Buffering was cached and a user modifies the configuration, the user is expected to clear the cache to take effect.
To enable Pass through X-Accel headers, follow the configuration steps mentioned below:
[admin:ctrl]: > configure applicationprofile System-HTTP [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile> http_profile [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile:http_profile> pass_through_x_accel_headers Overwriting the previously entered value for pass_through_x_accel_headers [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile:http_profile> save [admin:ctrl]: applicationprofile> save
General Configuration
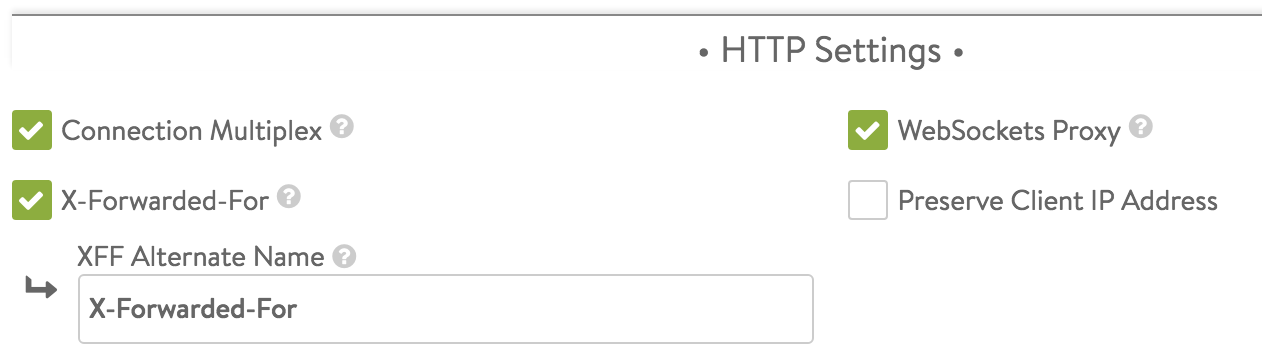
- Connection Multiplex
-
This option controls the behavior of HTTP 1.0 and 1.1 request switching and server TCP connection reuse. This allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to reduce the number of open connections maintained by servers and better distribute requests across idle servers, thus reducing server overloading and improving performance for end-users. The exact reduction of connections to servers will depend on how long-lived the client connections are, the HTTP version, and how frequently requests/responses are utilizing the connection. It is important to understand that “connection” refers to a TCP connection, whereas “request” refers to an HTTP request and subsequent response. HTTP 1.0 and 1.1 allow only a single request/response to go over an open TCP connection at a time. Many browsers attempt to mitigate this bottleneck by opening around six concurrent TCP connections to the destination website.
- WebSockets Proxy
-
Enabling WebSockets allows the virtual service to accept a client’s upgrade header request. If the server is listening for WebSockets, the connection between the client and server will be upgraded. WebSocket is a full-duplex TCP protocol. The connection will initially start over HTTP, but once successfully upgraded, all HTTP parsing by NSX Advanced Load Balancer will cease and the connection will be treated as a normal TCP connection.
Note:NSX Advanced Load Balancer supports HTTP/2 WebSockets. In addition to supporting WebSockets clients and servers with the same HTTP Version, starting with version 22.1.3, the NSX Advanced Load Balancer also supports the combination of WebSocket clients of HTTPv2 and servers of HTTPv1.
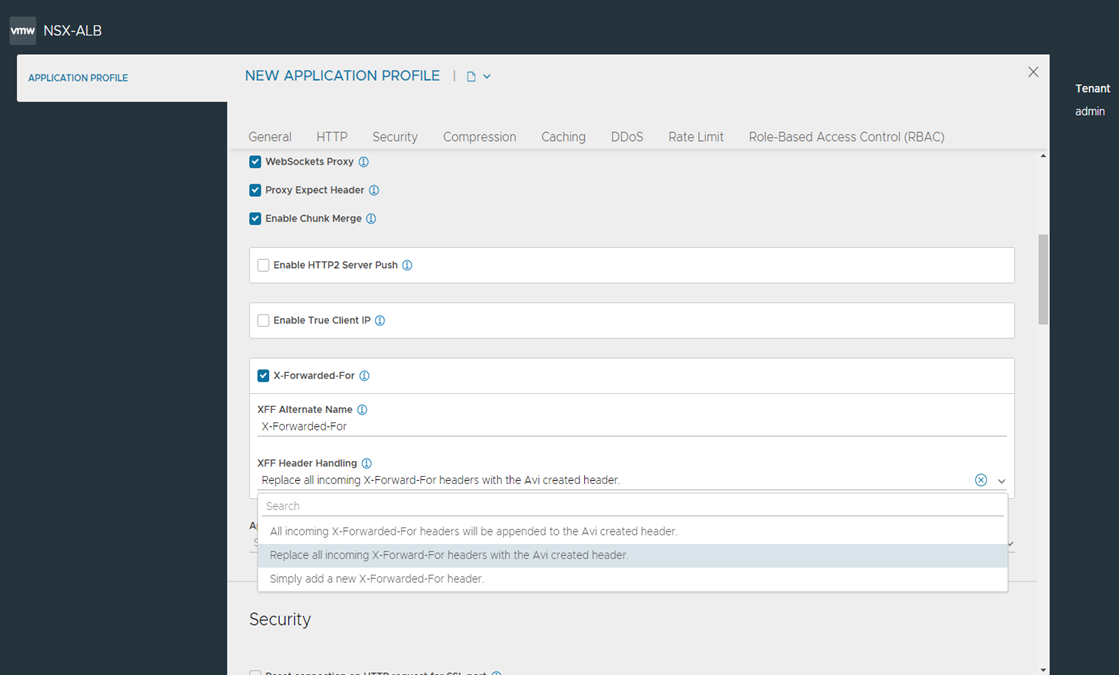
- X-Forwarded-For
-
With this option, NSX Advanced Load Balancer will insert an X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header into the HTTP request headers when the request is passed to the server. The XFF header value contains the original client source IP address. Web servers can use this header for logging client interaction instead of using the layer 3 IP address, which will incorrectly reflect the Service Engine’s source NAT address. When enabling this option, the XFF Alternate Name field appears, which allows the XFF header insertion to use a custom HTTP header name. If the XFF header or the custom name supplied already exists in the client request, all instances of that header will first be removed. To add the header without removing pre-existing instances of it, use an HTTP request policy.
To retain one or more X-Forwarded-For headers coming with the request, starting with NSX Advanced Load Balancer 22.1.3, when X-Forwarded-For is enabled, the option for XFF Header Handling is available.
Select Replace XFF Headers to replace all incoming X-Forwarded-For headers with the header created in NSX Advanced Load Balancer as shown in the example below:
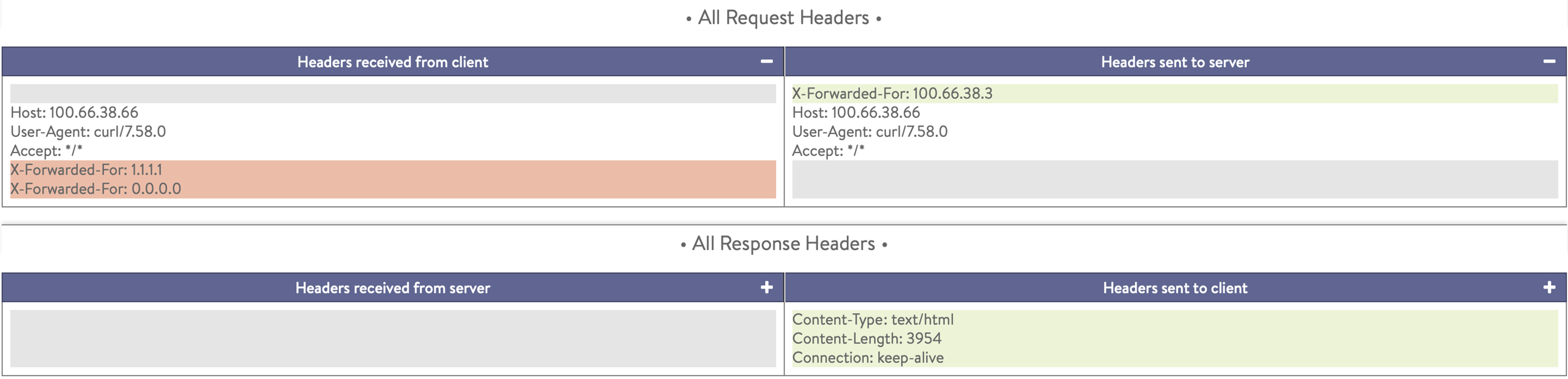
Select Append XFF Headers to append all the incoming XFF headers and the client IP address together as shown in the example below:
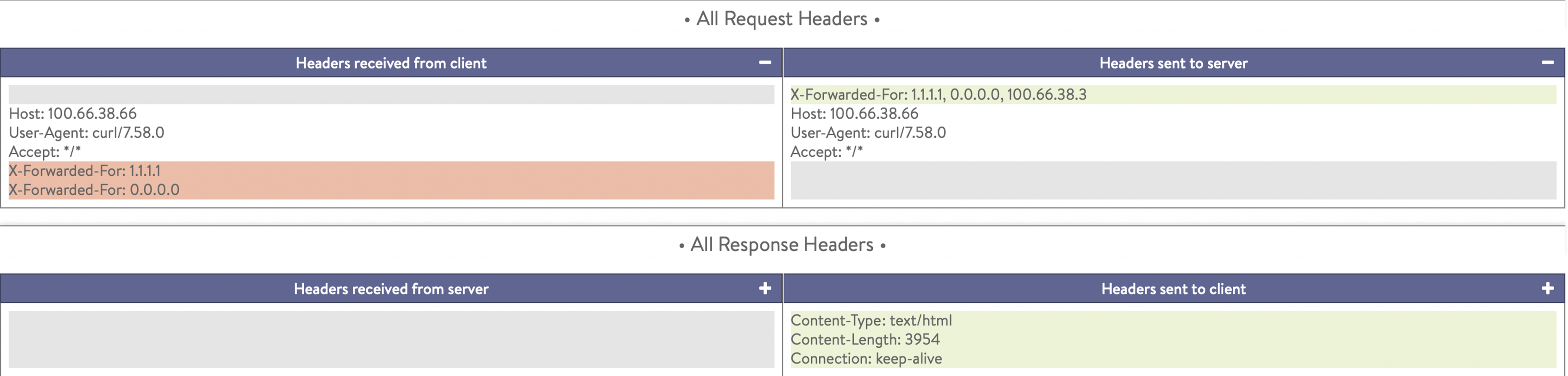
Select Add new XFF Header to adds new XFF headers with the client IP address as shown in the example below:
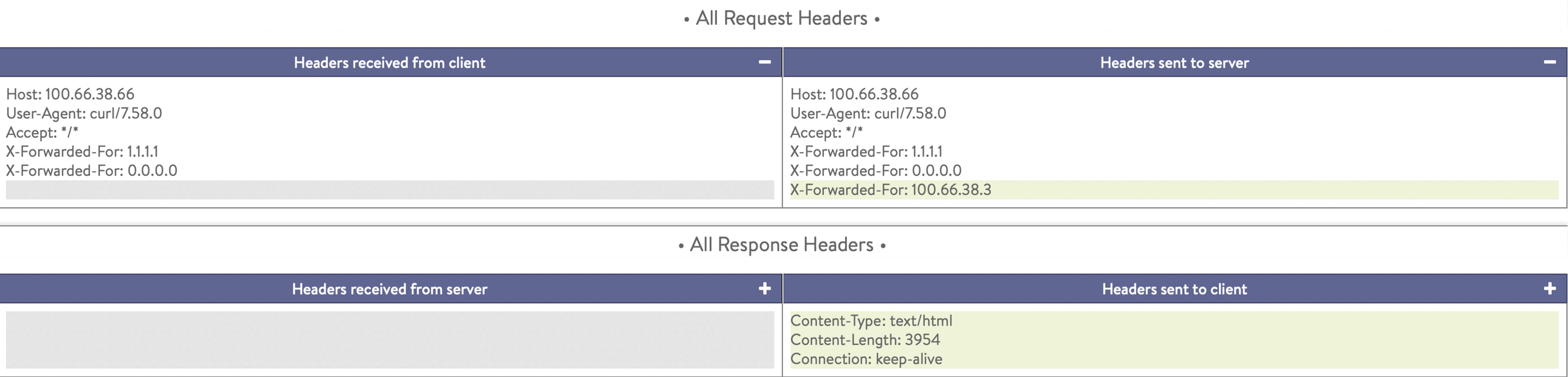
The Application Profile screen is as shown below:
- Preserve Client IP Address
-
Clicking this option causes the NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE to use the client-IP rather than its own as the source-IP for load-balanced connections from the SE to back-end application servers. Enable IP Routing in the SE group is a prerequisite for enabling this option. Preserve Client IP Address is mutually exclusive with SNAT-ting the virtual services. Connection Multiplexing from HTTP(s) Application Profile cannot be used with Preserve Client IP.
- HTTP Session
-
Note: The HTTP Session needs to be enabled in the section.
Available options:
Session Cookie Name
This defines the name of the session cookie that is used by the Avi HTTP session. The default is albsessid.
Session Cookie SameSite Attribute
This option can set the SameSite attitribute to for the HTTP session cookie. Available options are Lax, Strict and None.
Enable Session Cookie Secure
Sets the secure flag on the HTTP session cookie.
Enable Session Cookie HTTP Only
Sets the HTTP only flag on the HTTP session cookie.
- Save
-
Select another tab from the top menu to continue editing or Save to return to the Application Profiles tab.
Multiplex plus Persistence
This table shows the difference in multiplexing behavior depending on persistence.
Mutiplex |
Persistence |
Behavior |
|---|---|---|
Enabled |
Deactivated |
Client connections and their requests are decoupled from the server side of the Service Engine. Requests are load-balanced across the servers in the pool using either new or pre-existing connections to those servers. The connections to the servers may be shared by requests from any clients. |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Client connections and their requests are sent to a single server. These requests may share connections with other clients who are persisted to the same server. HTTP requests are not load balanced. |
Deactivated |
Enabled |
NSX Advanced Load Balancer opens a new TCP connection to the server for each connection received from the client. Connections are not shared with other clients. All requests received through all connections from the same client are sent to one server. HTTP client browsers may open many concurrent connections, and the number of client connections will be the same as the number of server connections. |
Deactivated |
Deactivated |
Connections between the client and server are one-to-one. Requests remain on the same connection they began on. Multiple connections from the same client may be distributed among the available servers. |
Security Configuration
The Security tab of the HTTP application profile controls the security settings for HTTP applications that are associated with the profile.
Security Information
The HTTP security settings affect how a virtual service must handle HTTPS. If a virtual service is configured only for HTTP, the HTTPS settings discussed in this section will not apply. Only if the virtual service is configured for HTTPS, or HTTP and HTTPS, will the settings take effect.
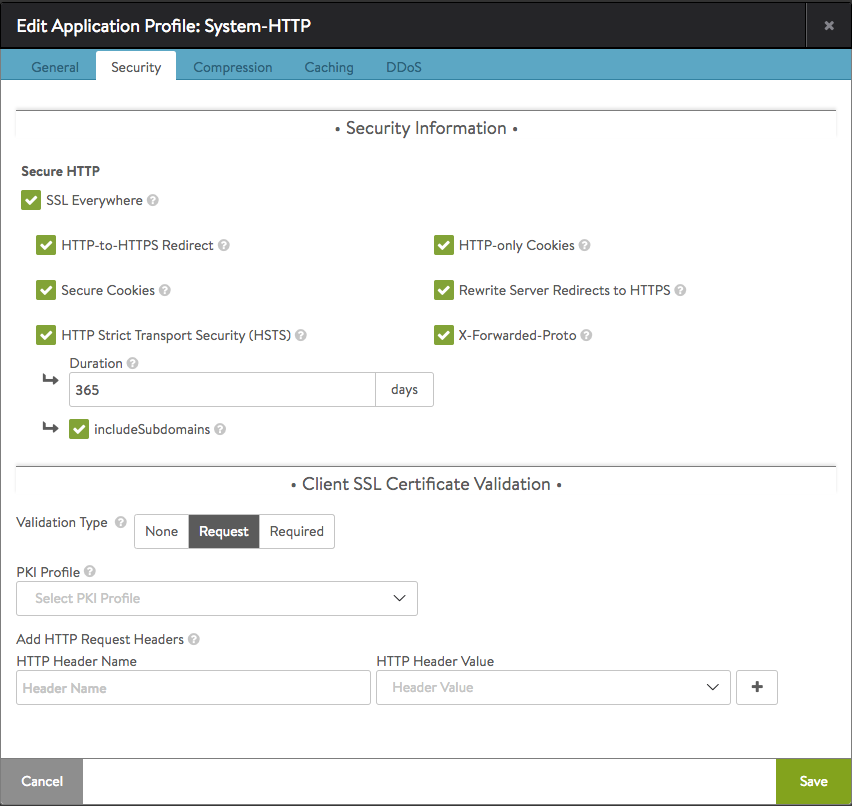
More granular settings also can be configured using policies or DataScripts.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
SSL Everywhere |
This option enables all of the following options, which together provide the recommended security for HTTPS traffic. |
HTTP to HTTPS Redirect |
For a single virtual service configured with both an HTTP service port (SSL disabled) and an HTTPS service port (SSL enabled), this feature will automatically redirect clients from the insecure to the secure port. For instance, clients who type www.avinetworks.com into their browser will automatically be redirected to https://www.avinetworks.com. If the virtual service does not have both an HTTP and HTTPS service port configured, this feature will not activate. For two virtual services (one with HTTP and another on the same IP address listening to HTTPS), an HTTP request policy must be created to manually redirect the protocol and port. |
Secure Cookies |
When NSX Advanced Load Balancer is serving as an SSL proxy for the backend servers in the virtual service’s pool, NSX Advanced Load Balancer communicates with the client over SSL. However, if NSX Advanced Load Balancer communicates with the backend servers over HTTP (not over SSL), the servers will incorrectly return responses as HTTP. As a result, cookies that must be marked as secure will not be so marked. Enabling secure cookies will mark any server cookies with the Secure flag, which tells clients to send only this cookie to the virtual service over HTTPS. This feature will only activate when applied to a virtual service with SSL/TLS termination enabled. |
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) |
Strict Transport Security uses a header to inform client browsers that this site must be accessed only over SSL/TLS. The HSTS header is sent in all HTTP responses, including error responses. This feature mitigates man-in-the-middle attacks that can force a client’s secure SSL/TLS session to connect through insecure HTTP. HSTS has a duration setting that tells clients the SSL/TLS preference must remain in effect for the specified number of days. Insert the include Subdomains directive in the HTTP Strict-Transport-Security header, if required. Doing so, signals the user agent that the HSTS policy applies to this HSTS host as well as to any subdomains of the host’s domain name. This setting will activate only on a virtual service that is configured to terminate SSL/TLS.
Note:
If a virtual service is set temporarily to support SSL/TLS and HSTS has been set, it cannot gracefully be downgraded back to HTTP. Client browsers will refuse to accept the site over HTTP. When HSTS is in effect, clients will not accept a self-signed certificate. |
HTTP-only Cookies |
NSX Advanced Load Balancer supports setting an When a cookie has an To check the CLI command to enable HTTP-Only attribute, see CLI Command to Enable HTTP-Only flag. |
Rewrite Server Redirects to HTTPS |
When a virtual service terminates client SSL/TLS and then passes requests to the server as HTTP, many servers assume that the connection to the client is HTTP. Absolute redirects generated by the server may therefore include the protocol, such as http://www.avinetworks.com. If the server returns a redirect with HTTP in the location header, this feature will rewrite it to HTTPS. Also, if the server returns a redirect for its IP address, this will be rewritten to the hostname requested by the client. If the server returns redirects for hostnames other than what the client requested, they will not be altered.
Note:
Consider creating an HTTP response policy if greater granularity is required when rewriting redirects. This feature will activate only if the virtual service has both HTTP and HTTPS service ports |
X-Forwarded-Proto |
Enabling this option makes NSX Advanced Load Balancer insert the X-Forwarded-Proto header into HTTP requests sent to the server, which informs that server whether the client connected to NSX Advanced Load Balancer over HTTP or HTTPS. This feature activates for any HTTP or HTTPS virtual service. |
CLI Command to Enable HTTP-Only flag
[admin:admin-controller2]: > configure applicationpersistenceprofile System-Persistence-Http-Cookie[admin:admin-controller2]: applicationpersistenceprofile> http_cookie_persistence_profile [admin:admin-controller2]: applicationpersistenceprofile:http_cookie_persistence_profile> http_only [admin:admin-controller2]: applicationpersistenceprofile:http_cookie_persistence_profile> save [admin:admin-controller2]: applicationpersistenceprofile> save
+-------------------------------|---------------------------------------+ |Field |Description | +-------------------------------+---------------------------------------+ |uuid |applicationpersistenceprofile-04ca34e1 | |name |System-Persistence-Http-Cookie | |persistence_type |PERSISTENCE_TYPE_HTTP_COOKIE | |server_hm_down_recovery |HM_DOWN_PICK_NEW_SERVER | |http_cookie_persistence_profile| | | cookie_name |VAJOSFML | | key[1] | | | name |40015eba-ee51-40c6-8f8d-06e2ec0516e9 | | aes_key |b'WX9pow2nYKYTfENMZSdwODZQu8e37Zdraoovt| | always_send_cookie |False | | http_only |True | | is_federated |False | | tenant_ref |admin | +-------------------------------+---------------------------------------+
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
For security, an industry best practice is to ensure all HTTP traffic is SSL-encrypted as HTTPS. Since typical end-users do not specify the HTTPS protocol when entering URLs for requests, the initial requests arrive over HTTP. NSX Advanced Load Balancer can provide SSL termination services, it also must handle redirecting of HTTP users to HTTPS. You can enable HTTP-to-HTTPS redirect in any of the following ways:
In the Application Profile, under Security configuration
Configuring HTTP to HTTPS Redirect in the Application Profile
Configuring Rewrite Server Redirects to HTTPS in the Application Profile
Using the HTTP Request Policy
Configuring HTTP to HTTPS Redirect in the Application Profile
If the virtual service is configured for both HTTP (usually port 80) and HTTPS (usually SSL on port 443), enable HTTP-to-HTTPS redirect using the attached HTTP application profile.
Navigate to , select the desired virtual service, click the edit icon on the right side.
Under Settings, go to the Profiles section.
Select the System-HTTP profile and click the edit icon.
Under Security select HTTP to HTTPS Redirect .
Click Save.
The System-Secure-HTTP profile is similar to the System-HTTP profile except that under SSL Everywhere the HTTP to HTTPS Redirect option, is enabled by default.
Configuring Rewrite Server Redirects to HTTPS in the Application Profile
The Rewrite Server Redirects to HTTPS option is available within the Security tab of the Application Profile. This option will change the location header of redirects from HTTP to HTTPS, and will also remove any hard-coded ports.
Relative redirects are not altered, only absolute. Therefore it is encouraged to have both the options enabled.
This profile setting will have no impact for virtual services that does not have HTTPS configured.
The following example shows a Location header sent from a server:
http://www.test.com:5000/index.htm
NSX Advanced Load Balancer rewrites the Location header, sending the following to the client:
https://www.test.com/index.htm
Using the HTTP Request Policy
For more granularity, use an HTTP Request Policy.
Navigate to , select the desired virtual service, click the edit icon on the right side.
Under the Policies tab, select HTTP Request.
Click the create (+) icon.
Select Service Port from the dropdown-list for Matching Rules, select is and enter 80 in the Ports field.
Save the rule. Optionally, the required criteria can be added to determine when to perform the redirect.
In the Action section, select Redirect from the drop-down menu. Then set the protocol to HTTPS. This will set the redirect port to 443 and the redirect response code to 302 (temporary redirect).
HTTP Request Policies are quick and easy to set up, and impact only a single virtual service at a time.
Adding a Query
Use add_stringfor adding a redirect action in the HTTP Request policy.
The keep_query field when enabled, uses the incoming request’s query parameters to the final redirect URI.
The add_string field, appends the query string to the Redirect URI.
To understand how keep_query and add_string work, consider the example http://test.example.com/images?name=animals as an incoming request and the request is to be redirected to http://google.com.
|
|
Redirect Link |
|---|---|---|
Enabled |
Not configured |
http://google.com/images?name=animals |
Disabled |
Not configured |
http://google.com/images?name=animals |
Enabled |
Set to ` |
http://google.com/images?name=animals&type=cats&color=black |
Disabled |
Set to ` |
http://google.com/images?name=animals&type=cats&color=black |
The CLI configuration is as shown below:
[admin:abc-controller]: > configure httppolicyset vs1-Default-Cloud-HTTP-Policy-Set-0 [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset> http_request_policy [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy> [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy> rules index 1 [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules>[admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules> redirect_action [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> add_string images=cat keep_query [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> status_code http_redirect_status_code_302 [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> port 80 [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> host [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action:host> type uri_param_type_tokenized [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action:host> tokens [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action:host:tokens> type uri_token_type_string str_value www.google.com [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action:host> save [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules:redirect_action> save [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy:rules> save [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset:http_request_policy> save [admin:abc-controller]: httppolicyset> save +------------------------+----------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +------------------------+----------------------------------------------+ | uuid | httppolicyset-2ee5<truncated> | | | | | name | vs1-Default-Cloud-HTTP-Policy-Set-0 | | http_request_policy | | | rules[1] | | | name | Rule 1 | | index | 1 | | enable | True | | match | | | method | | | match_criteria | IS_IN | | methods[1] | HTTP_METHOD_GET | | redirect_action | | | protocol | HTTP | | host | | | type | URI_PARAM_TYPE_TOKENIZED | | tokens[1] | | | type | URI_TOKEN_TYPE_STRING | | str_value | www.vmware.com | | tokens[2] | | | type | URI_TOKEN_TYPE_STRING | | str_value | www.google.com | | port | 80 | | keep_query | True | | status_code | HTTP_REDIRECT_STATUS_CODE_302 | | add_string | images=cat | | is_internal_policy | False | | tenant_ref | admin | +------------------------+----------------------------------------------+
Redirect Using DataScript
For maximum granularity and reusability, use a DataScript to configure the redirect behavior.
To add a DataScript,
Navigate to , select the desired virtual service, and click the edit option.
Navigate to .
Click Add DataScript.
Click the Script To Execute.
Click Create DataScript.
In the New DataScript Set screen, under Events, click Add.
From the Add drop-down menu, select HTTP Request.
Enter the following script in the HTTP Request Event Script text box and save.
if avi.vs.port() ~= "443" then avi.http.redirect("https://" .. avi.http.hostname() .. avi.http.get_uri()) end
Client SSL Certificate Validation
NSX Advanced Load Balancer can validate SSL certificates presented by clients against a trusted certificate authority (CA) and a configured certificate revocation list (CRL). Further options allow passing certificate information to the server through HTTP headers.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Validation Type |
Enables client validation based on their SSL certificates. Select one of the following:
|
PKI Profile |
The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) profile contains configured certificate authority (CA) and the CRL. A PKI profile is not necessary if validation is set to Request, but is mandatory if validation is set to Require. |
HTTP Header Name |
Optionally, NSX Advanced Load Balancer may insert the client’s certificate, or parts of it, into a new HTTP header to be sent to the server. To insert a header, this field is used to determine the name of the header. |
HTTP Header Value |
Used with the HTTP Header Name field, the Value field is used to determine the portion of the client certificate to insert into the HTTP header sent to the server. Using the plus icon, more headers may be inserted. This action may be in addition to any performed by HTTP policies or DataScripts, which could also be used to insert headers in requests sent to the destination servers. |
Compression
Compression is an HTTP 1.1 standard for reducing the size of text-based data using the gzip algorithm. The typical compression ratio for HTML, JavaScript, CSS, and similar text content types is about 75%, meaning that a 20-KB file may be compressed to 5kb before being sent across the Internet, thus reducing the transmission time by a similar percentage.
Compression enables HTTP gzip compression for responses from NSX Advanced Load Balancer to the client.
Use the Compression tab to view or edit the application profile’s HTTP compression settings.
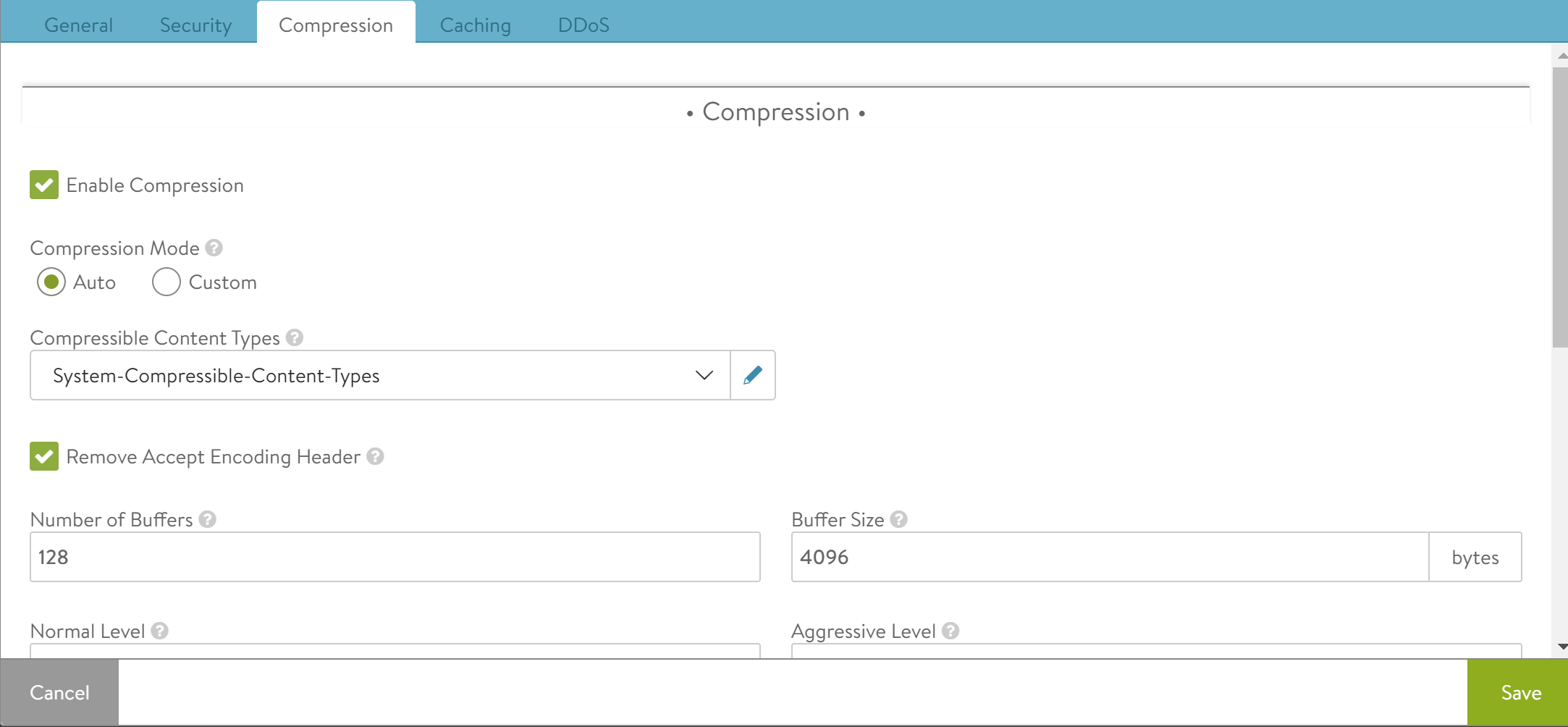
The compression percentage achieved can be viewed using the Client Logs tab of the virtual service. This may require enabling full client logs on the virtual service’s Analytics tab to log some or all client requests. The logs will include a field showing the compression percentage with each HTTP response.
It is highly recommended to enable compression with caching, which together can dramatically reduce the CPU costs of compressing content. When both compression and caching are enabled, an object such as the index.html file will need to be compressed only one time. After an object is compressed, the compressed object is served out of the cache for subsequent requests. NSX Advanced Load Balancer does not needlessly re-compress the object for every client request. For clients that do not support compression, NSX Advanced Load Balancer also will cache an uncompressed version of the object.
Configure the compression settings as discussed in the table.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Enable Compression |
Select this option to enable compression. Enabling this option displays the other settings for compression. |
Compression Mode |
The compression modes enable different levels of compression for different clients. For instance, filters can be created to provide aggressive compression levels for slow mobile clients while deactivating compression for fast clients from the local intranet. Auto is recommended, to dynamically tune the settings based on clients and available Service Engine CPU resources.
|
Compressible Content Types |
This field determines which HTTP content-types are eligible to be compressed. Select a string group which contains the compressible type list from the dropdown menu. |
Remove Accept Encoding Header |
This field removes the Accept Encoding header, which is sent by HTTP 1.1 clients to indicate they are able to accept compressed content. Removing the header from the request prior to sending the request to the server allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to ensure the server will not compress the responses. Only NSX Advanced Load Balancer will perform compression. |
Number of Buffers |
Specify the number of buffers to use for compression output. |
Buffer Size |
Specify the size of each buffer used for compression output, this must ideally be a multiple of page size. |
Normal Level |
Specify the level of compression to apply on content selected for normal compression. |
Aggressive Level |
Specify the level of compression to apply on content selected for aggressive compression. |
Window Size |
Specify the window size used by compression, rounded to the last power of 2. |
Hash Size |
Specify the hash size used by compression, rounded to the last power of 2. |
Response Content Length |
Specify the minimum response content length to enable compression. |
Max Low RTT |
If client RTT is higher than this threshold, enable normal compression on the response. |
Min High RTT |
If client RTT is higher than this threshold, enable aggressive compression on the response. |
Mobile Browser Identifier |
Select the values that identify mobile browsers to enable aggressive compression. |
Custom Compression
To create a custom compression filter:
Click +Compression Filter to create a custom filter.
In the Add Compression Filter section, configure the following.
Field
Description
Filter Name
Provide a unique name for the filter (optional).
Matching Rules
Determine if the client (through Client IP or User Agent string) is eligible to be compressed using the associated Action. If both Client IP and User Agent rules are populated, then both must be true for the compression action to take effect.
Client IP Address allows you to use an IP Group to specify eligible client IP addresses. For example, an IP Group called Intranet that contains a list of all internal IP address ranges. Clearing the Is In button reverses this logic, meaning that any client that is not coming from an internal IP network will match the filter.
User Agent matches the client’s User-Agent string against an eligible list contained within a String Group. The User-Agent is a header presented by clients indicating the type of browser or device they may be using. The System-Devices-Mobile Group contains a list of HTTP User-Agent strings for common mobile browsers.
The Action section determines what will happen to clients or requests that meet the match criteria, specifically the level of HTTP compression that will be used.
Field
Description
Aggressive compression
It uses Gzip level 6, which will compress text content by about 80% while requiring more CPU resources from both NSX Advanced Load Balancer and the client.
Normal compression
It uses Gzip level 1, which will compress text content by about 75%, which provides a good mix between compression ratio and the CPU resources consumed by both NSX Advanced Load Balancer and the client.
No Compression
It disables compression. For clients coming from very fast, high bandwidth and low latency connections, such as within the same data center, compression may actually slow down the transmission time and consume unnecessary CPU resources.
HTTP Caching
NSX Advanced Load Balancer can cache HTTP content, thereby enabling faster page load times for clients and reduced workloads for both servers and NSX Advanced Load Balancer. When a server sends a response, such as logo.jpg, NSX Advanced Load Balancer can add the object to its cache and serve it to subsequent clients that request the same object. This can reduce the number of connections and requests sent to the server.
Enabling caching and compression allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to compress text-based objects and store both the compressed and original uncompressed versions in the cache. Subsequent requests from clients that support compression will be served from the cache, meaning that NSX Advanced Load Balancer will need not compress every object every time, which greatly reduces the compression workload.
Regardless of the configured caching policy, an object can be cached only if it is eligible for caching. Some objects may not be eligible for caching.
By default, caching is deactivated. Click Enable Caching to configure options specific to caching.
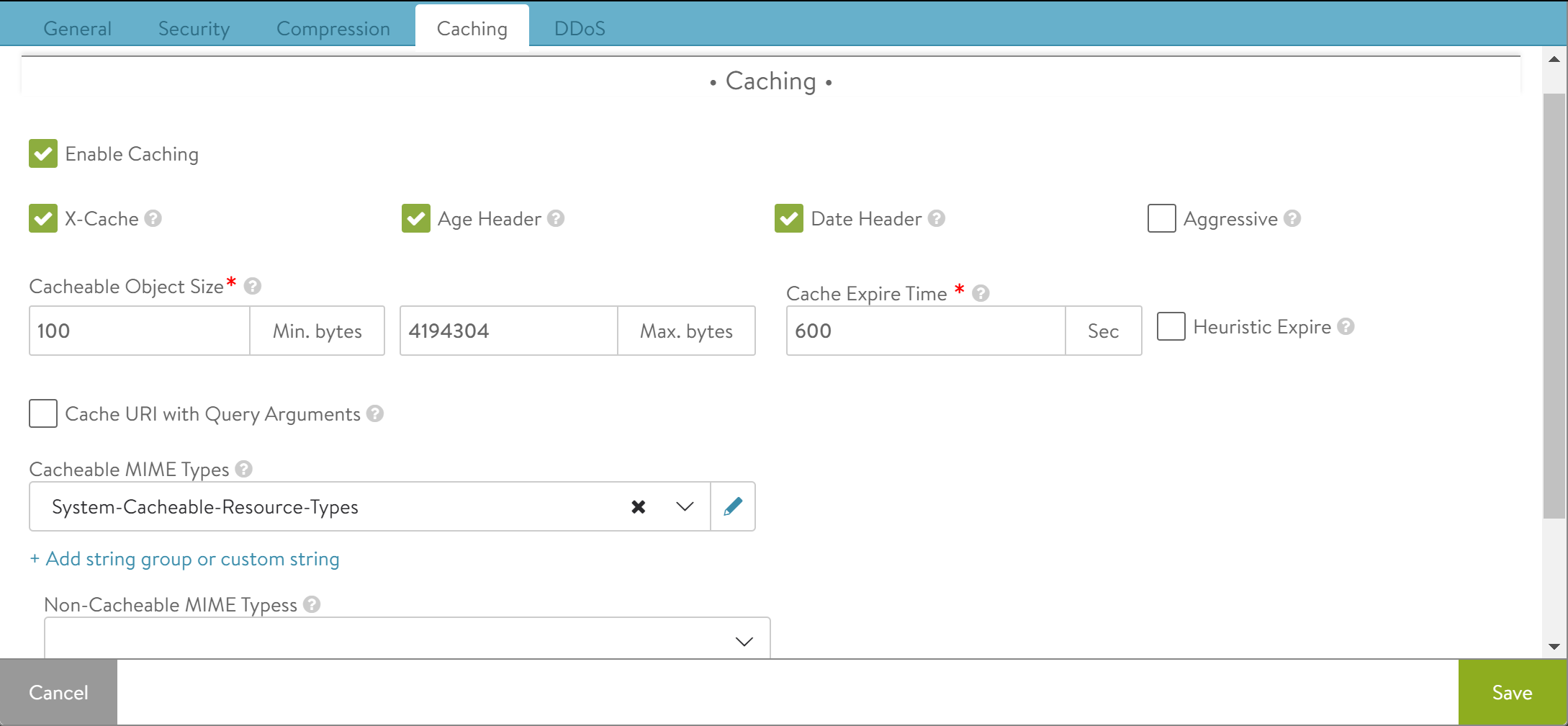
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
X-Cache |
NSX Advanced Load Balancer will add an HTTP header labeled X-Cache for any response sent to the client that was served from the cache. This header is informational only and will indicate the object was served from an intermediary cache. |
Age Header |
NSX Advanced Load Balancer will add a header to the content served from the cache that indicates to the client the number of seconds that the object has been in an intermediate cache. For example, if the originating server declared that the object must expire after 10 minutes and it has been in the NSX Advanced Load Balancer cache for 5 minutes, then the client will know that it must only cache the object locally for 5 more minutes. |
Date Header |
If a date header was not added by the server, then NSX Advanced Load Balancer will add a date header to the object served from its HTTP cache. This header indicates to the client when the object was originally sent by the server to the HTTP cache in NSX Advanced Load Balancer. |
Cacheable Object Size |
The minimum and maximum size of an object (image, script, and more) that can be stored in the NSX Advanced Load Balancer HTTP cache, in bytes. Most objects smaller than 100 bytes are web beacons and must not be cached despite being image objects. |
Cache Expire Time |
An intermediate cache must be able to guarantee that it is not serving stale content. If the server sends headers indicating how long the content can be cached (such as cache control), then NSX Advanced Load Balancer will use those values. If the server does not send expiration timeouts and NSX Advanced Load Balancer is unable to make a strong determination of freshness, then NSX Advanced Load Balancer will store the object for no longer than the duration of time specified by the Cache Expire Time. |
Heuristic Expire |
If a response object from the server does not include the Cache-Control header but does include an If-Modified-Since header, then NSX Advanced Load Balancer will use this time to calculate the cache-control expiration, which will supersede the Cache Expire Time setting for this object. |
Cache URL with Query Arguments |
This option allows caching of objects whose URI includes a query argument. Disabling this option prevents caching these objects. When enabled, the request must match the URI query to be considered a hit. Below are two examples of URI that include queries. The first example may be a legitimate use case for caching a generic search, while the second may be a unique request posing a security liability to the cache.
|
Cacheable MIME Types |
This option statically defines a list of cacheable objects. This may be a string group, such as System-Cacheable-Resource-Types, or a custom comma-separated list of MIME types that NSX Advanced Load Balancer must cache. If no MIME types are listed in this field, then NSX Advanced Load Balancer will by default assume that any object is eligible for caching. |
Non-Cacheable MIME Types |
Statically define a list of objects that are not cacheable. This creates a denylist that is the opposite of the cacheable list. |
HTTP DDoS
The Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) section allows the configuration of mitigation controls for HTTP and the underlying TCP protocols. By default, NSX Advanced Load Balancer is configured to protect itself from many types of attacks. For instance, if a virtual service is targeted by a SYN flood attack, NSX Advanced Load Balancer will activate SYN cookies to validate clients before opening connections. Many of the options listed below are not quite as straightforward, as bursts of data may be normal for the application. NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides knobs to modify the default behavior to ensure optimal protection.
In addition to the DDoS settings described below, NSX Advanced Load Balancer also can implement connection limits to a virtual service and a pool, configured through the Advanced properties page. Virtual services also may be configured with connection rate limits and burst limits in the Network Security Policies section. Because these settings apply to individual virtual services and pools, they are not configured within the profile.
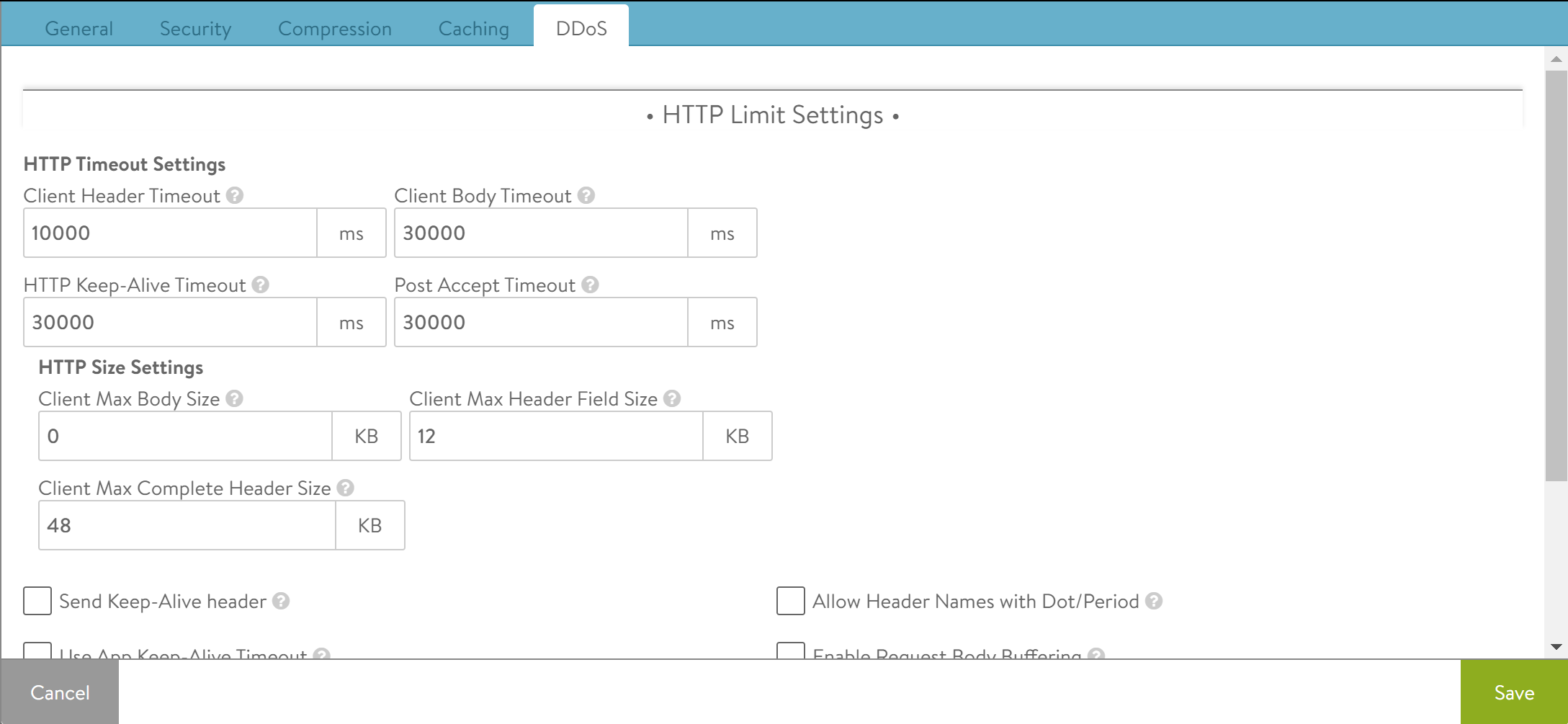
HTTP Limits
The first step in mitigating HTTP-based denial of service attacks is to set parameters for the transfer of headers and requests from clients. Many of these settings protect against variations of HTTP SlowLoris and SlowPOST attacks, in which a client opens a valid connection then very slowly streams the request headers or POSTs a file. This type of attack is intended to overwhelm the server (in this case the SE) by tying up buffers and connections.
Clients that exceed the limits defined below will have that TCP connection reset and a log generated. This does not prevent the client from initiating a new connection and does not interrupt other connections the same client might have open.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Client Header Timeout |
Set the maximum length of time the client is allowed for successfully transmitting the complete headers of a request. The default is 10 seconds. |
HTTP Keep-alive Timeout |
Set the maximum length of time an HTTP 1.0 or 1.1 connection may be idle. This affects only client-to-NSX Advanced Load Balancer interaction. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer-to-server keep-alive is governed through the Connection Multiplex feature. |
Client Body Timeout |
Set the maximum length of time for the client to send a message body. This usually affects only clients that are POSTing (uploading) objects. The default value of 0 disables this timeout |
Post Accept Timeout |
Once a TCP three-way handshake has been completed, the client has this much time to send the first byte of the request header. Once the first byte has been received, this timer is satisfied and the client header timeout (described above) kicks in. |
Send Keep-Alive header |
Select this to send the HTTP keep-alive header to the client. |
Use App Keep-Alive Timeout |
When the above parameter is checked such that keep-alive headers are sent to the client, a timeout value needs to be specified therein. If this box is unchecked, NSX Advanced Load Balancer will use the value specified in the HTTP Keep-Alive Timeout field. If it is checked, the timeout sent by the application will be honored. |
Client Post Body Size |
Set the maximum size of the body of a client request. This generally limits the size of a client POST. Setting this value to 0 disables this size limit. |
Client Request Size |
Set the maximum combined size of all the headers in a client request. |
Client Header Size |
Set the maximum size of a single header in a client request. |
Rate Limits
This section controls the rate at which clients may interact with the site. Each enabled rate limit has three settings:
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Threshold |
The client has violated the rate limit when the defined threshold of connections, packets, or HTTP requests has occurred within the specified time period. |
Time Period |
The client has violated the rate limit when the defined threshold of connections, packets, or HTTP requests have occurred within the specified time period. |
Action |
Select the action to perform when a client has exceeded the rate limit. The options will depend on whether the limit is a TCP limit or an HTTP limit.
|
Rate Limit Connections from a Client |
Rate limit all connections made from any single client IP address to the virtual service. |
Rate Limit Requests from a Client to all URLs |
Rate limit all HTTP requests from any single client IP address to all URLs of the virtual service. |
Rate Limit Requests from all Clients to a URL |
Rate limit all HTTP requests from all client IP addresses to any single URL. |
Rate Limit Requests from a Client to a URL |
Rate limit all HTTP requests from any single client IP address to any single URL. |
Rate Limit Failed Requests from a Client to all URLs |
Rate limit all requests from a client for a specified period of time once the count of failed requests from that client, crosses a threshold for that period. Clients are tracked based on their IP address. Requests are deemed failed based on client or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and how metrics subsystems mark failed requests. |
Rate Limit Failed Requests from all Clients to a URL |
Rate limit all requests to a URI for a specified period of time once the count of failed requests to that URI, crosses a threshold for that period. Requests are deemed failed based on client- or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and metrics subsystems mark failed requests. |
Rate Limit Failed Requests from a Client to a URL |
Rate limit all requests from a client to a URI for a specified period of time once the count of failed requests from that client to the URI crosses a threshold for that period. Requests are deemed failed based on client- or server-side error status codes, consistent with how NSX Advanced Load Balancer logs and metrics subsystems mark failed requests. |
Rate Limit Scans from a Client to all URLs |
Automatically track clients and classify them into three groups: Good, Bad, and Unknown. Clients are tracked based on their IP address. Clients are added to the Good group when the NSX Advanced Load Balancer scan detection system builds a history of requests from the clients that complete successfully. Clients are added to the Unknown group when there is insufficient history about them. Clients with a history of failed requests are added to the Bad group and their requests are rate limited with stricter thresholds than the Unknown client's group. The NSX Advanced Load Balancer scan detection system automatically tunes itself so that the Good, Bad, and Unknown client-IP group members change dynamically with changes in traffic patterns through NSX Advanced Load Balancer. In other words, if a change to the website causes mass failures (such as 404 errors) for most customers, NSX Advanced Load Balancer adapts and does not mark all clients as attempting to scan the site. |
Rate Limit Scans from all Clients to all URLs |
Similar to the previous limit, but restricts the scanning from all clients as a single entity rather than individually. Once a limit is collectively reached by all clients, any client that sends the next failed request will be reset. |
You can upload any type of file as a local response. It is recommended to configure a local file using the UI. To update the local file using API, encode the base64 file out of band and use the encoded format in the API.
DNS Profile
A DNS application profile specifies settings dictating the request-response handling by NSX Advanced Load Balancer.
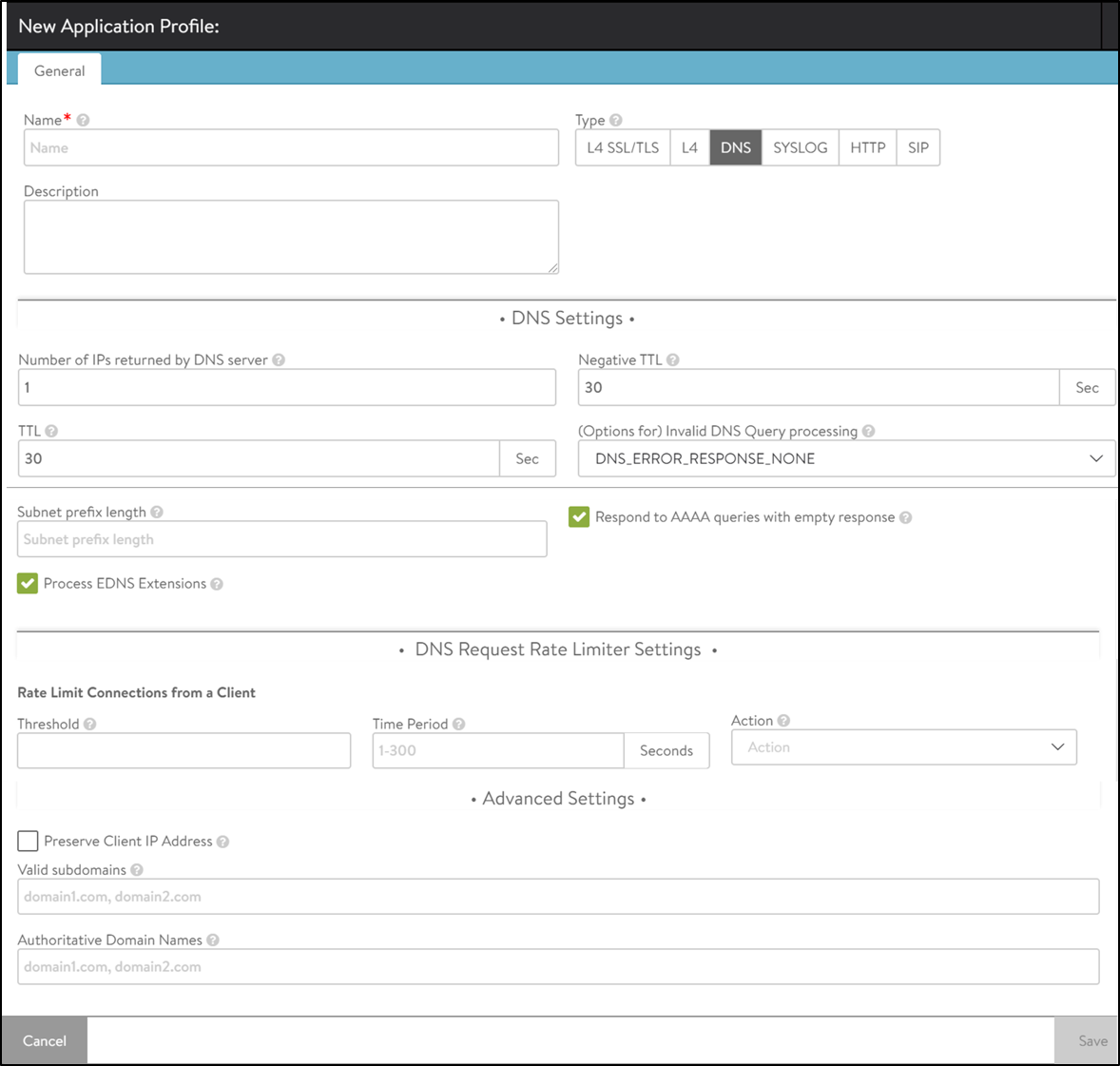
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Number of IPs returned by DNS server |
This option specifies the number of IP addresses returned by the DNS service. Default is 1. Enter 0 to return all IP addresses. Otherwise, the valid range is 1-20. |
TTL |
The time in seconds (default = 30) a served DNS response is considered to be valid by requestors of the DNS service. The valid range is 1-86400 seconds. |
Subnet prefix length |
This length is used in concert with the DNS client subnet (ECS) option. When the incoming request does not have any ECS and the prefix length is specified, NSX Advanced Load Balancer inserts an ECS option in the request to upstream servers. A valid length ranges from 1-32. |
Process EDNS Extensions |
This option makes the DNS service aware of the Extension mechanism for DNS (EDNS). EDNS extensions are parsed and shown in logs. For GSLB services, the EDNS subnet option can be used to influence load balancing. EDNS is supported. |
Negative TTL |
This option specifies the TTL value (in seconds) for SOA (Start of Authority) (corresponding to an authoritative domain owned by this DNS Virtual Service) record’s minimum TTL served by the DNS Virtual Service. Negative TTL is a value in the range 0-86400. |
(Options for) Invalid DNS Query processing |
Specifies whether the DNS service must drop or respond to a client when processing its request results in an error. By default, such a request is dropped without any response, or passed through to a passthrough pool, if configured. When set to respond, an appropriate response is sent to the client, for example, NXDOMAIN response for non-existent records, empty NOERROR response for unsupported queries, and more. |
Respond to AAAA queries with the empty response |
Enable this option to have the DNS service respond to AAAA queries with an empty response when there are only IPv4 records. |
Rate Limit Connections from a Client |
Limits connections made from any single client IP address to the DNS virtual service for which this profile applies. The default (=0) is interpreted as no rate limiting. |
Threshold |
Specifies the maximum number of connections or requests or packets that will be processed in the time value specified in the Time Period field (a legitimate value range is 10-2500). A higher number will result in rate-limiting. Specifying a number higher than 0 makes the Time Periodfield mandatory. |
Time Period |
The span of time, in seconds, during which NSX Advanced Load Balancer monitors for exceeded threshold. The allowed range is 1-300. NSX Advanced Load Balancer calculates and takes specified action if the inbound request rate is exceeded. This rate is the ratio of the maximum number to the time span. |
Action |
Choose one of three actions from the pulldown to be performed when rate limiting is required: Report Only, Drop SYN Packets, or Send TCP RST. |
Preserve Client IP Address |
Enable this option to have the client IP address pass through to the back end. Be sure you understand what the back-end DNS servers expect and what they will do when offered the client IP address. This option is not compatible with connection multiplexing. |
Valid subdomains |
A comma-delimited allowlist of subdomain names. Identifies the subdomains serviced by the DNS virtual service with which this profile is associated; all others will not be processed. This option’s best use is in the context of GSLB, in which the GSLB DNS’ sole purpose is to return IP addresses corresponding to the global applications being served. Valid subdomains are configured with ends-with semantics. |
Authoritative Domain Names |
A comma-delimited set of domain names for which the GSLB DNS’ SEs can provide authoritative translation of FQDNs to IP addresses. Queries for FQDNs that are subdomains of these domains and do not have any DNS record in NSX Advanced Load Balancer are either dropped or an NXDOMAIN response is sent (depending on the option set for invalid DNS queries, described above). Authoritative domain names are configured with ends-with semantics. |
All labels in a subdomain and authoritative domain names must be complete. To illustrate by example, suppose alpha.beta.com, delta.beta.com, delta.eta.com, and gamma.eta.com are valid FQDNs. If we intend the GSLB DNS to return authoritative responses to queries for each of the four FQDNSs, two authoritative domains could be identified, beta.com and eta.com. It is not sufficient to stipulate eta.com alone because “eta” is not a complete label, and therefore doesn’t match either alpha.beta.com or delta.beta.com.
The EDNS option is enabled by default for the System-DNS profile. If NSX Advanced Load Balancer is upgraded from an older version to a newer version, EDNS is not enabled by default in the existing DNS profile. However, if a new DNS profile is created on the same NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller, EDNS is enabled by default.
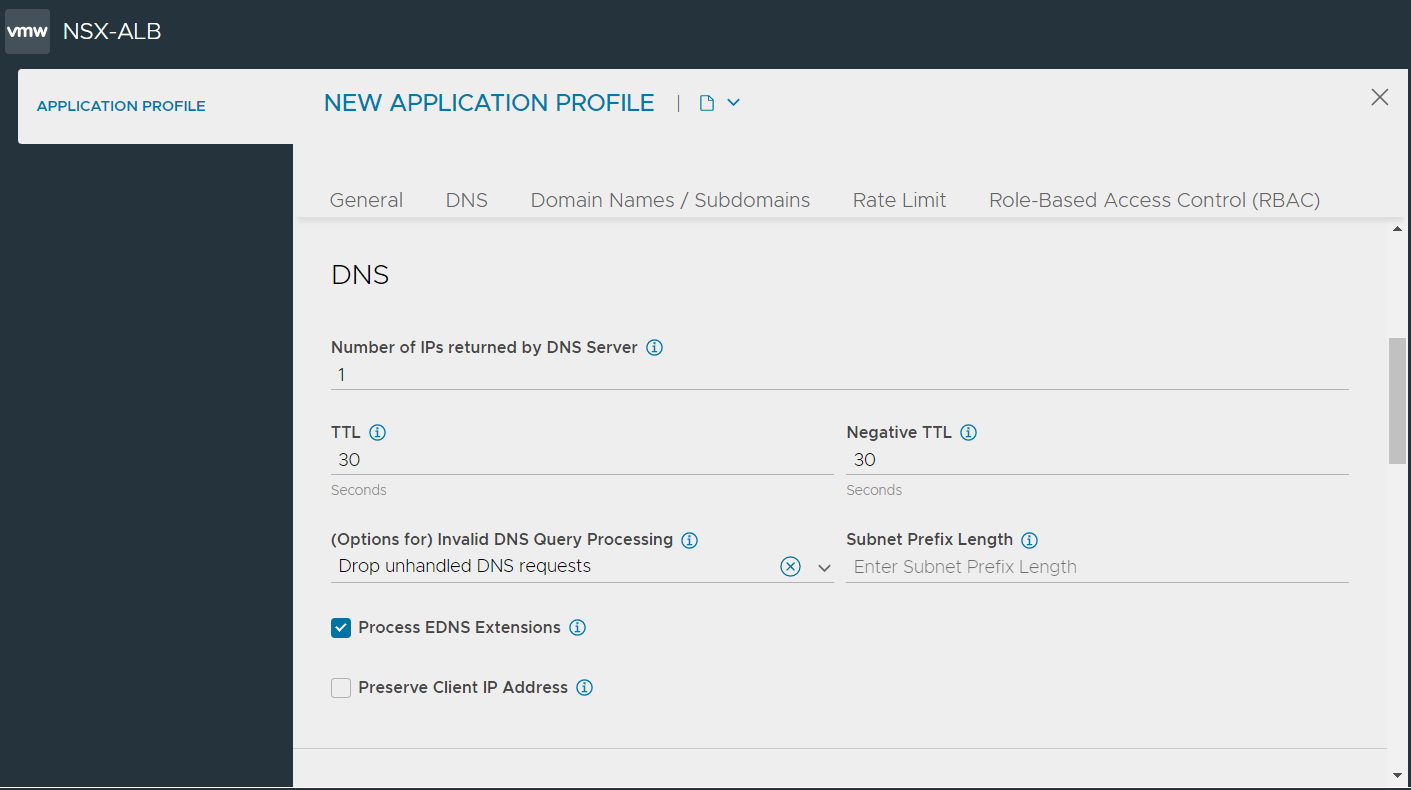
Closing TCP Connection Post Response Proactively for DNS Pass-through
Starting with NSX Advanced Load Balancer version 22.1, user can configure the DNS profile with the option to close TCP connections proactively in case of pass-through. NSX Advanced Load Balancer now supports an optional close_tcp_connection_post_response configuration knob for the DNS profile. If this configuration knob is enabled for the DNS profile, the Service Engine initiates closure of client TCP connections after the first DNS response for pass-through or proxy cases.
Log in to the NSX Advanced Load Balancer Controller and use the configure applicationprofile System-DNS mode to set the value of the close_tcp_connection_post_response parameter to true. The default value of the close_tcp_connection_post_response configuration knob is false.
[admin:controller-1-site-a]: > configure applicationprofile System-DNS Updating an existing object. Currently, the object is: +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | uuid | applicationprofile-76884b09-000000-6ac58b471948 | | name | System-DNS | | type | APPLICATION_PROFILE_TYPE_DNS | | dns_service_profile | | | num_dns_ip | 1 | | ttl | 30 sec | | error_response | DNS_ERROR_RESPONSE_NONE | | edns | True | | dns_over_tcp_enabled | True | | aaaa_empty_response | True | | negative_caching_ttl | 30 sec | | admin_email | hostmaster | | close_tcp_connection_post_response | False | | ecs_stripping_enabled | True | | preserve_client_ip | False | | preserve_client_port | False | | preserve_dest_ip_port | False | | tenant_ref | admin | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile> dns_service_profile [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile:dns_service_profile> close_tcp_connection_post_response Overwriting the previously entered value for close_tcp_connection_post_response [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile:dns_service_profile> save [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile> save +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | uuid | applicationprofile-76884b09-9c06-000000-6ac58b471948 | | name | System-DNS | | type | APPLICATION_PROFILE_TYPE_DNS | | dns_service_profile | | | num_dns_ip | 1 | | ttl | 30 sec | | error_response | DNS_ERROR_RESPONSE_NONE | | edns | True | | dns_over_tcp_enabled | True | | aaaa_empty_response | True | | negative_caching_ttl | 30 sec | | admin_email | hostmaster | | close_tcp_connection_post_response | True | | ecs_stripping_enabled | True | | preserve_client_ip | False | | preserve_client_port | False | | preserve_dest_ip_port | False | | tenant_ref | admin | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ [admin:controller-1-site-a]: >
Use the no close_tcp_connection_post_response command to set the value of the close_tcp_connection_post_response parameter to false as required.
[admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile> dns_service_profile [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile:dns_service_profile> no close_tcp_connection_post_response +------------------------------------+-------------------------+ | Field | Value | +------------------------------------+-------------------------+ | num_dns_ip | 1 | | ttl | 30 sec | | error_response | DNS_ERROR_RESPONSE_NONE | | edns | True | | dns_over_tcp_enabled | True | | aaaa_empty_response | True | | negative_caching_ttl | 30 sec | | admin_email | hostmaster | | close_tcp_connection_post_response | False | | ecs_stripping_enabled | True | +------------------------------------+-------------------------+ [admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile:dns_service_profile> save s[admin:controller-1-site-a]: applicationprofile> save +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | uuid | applicationprofile-76884b09-000000-ae4c-6ac58b471948 | | name | System-DNS | | type | APPLICATION_PROFILE_TYPE_DNS | | dns_service_profile | | | num_dns_ip | 1 | | ttl | 30 sec | | error_response | DNS_ERROR_RESPONSE_NONE | | edns | True | | dns_over_tcp_enabled | True | | aaaa_empty_response | True | | negative_caching_ttl | 30 sec | | admin_email | hostmaster | | close_tcp_connection_post_response | False | | ecs_stripping_enabled | True | | preserve_client_ip | False | | preserve_client_port | False | | preserve_dest_ip_port | False | | tenant_ref | admin | +--------------------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------+ [admin:controller-1-site-a]: >
L4 Profile
An L4 Profile is used for any virtual service that does not require application-layer proxying.
Using an L4 profile is equivalent to setting the virtual service’s application profile to none.
Rate limits may be placed on the number of TCP connections or UDP packets that may be made to the virtual service from a single client IP address.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Threshold |
The client has violated the rate limit when the defined threshold of connections (TCP) or packets (UDP) is reached within the specified time period. |
Time Period |
The client has violated the rate limit when the defined threshold of connections (TCP) or packets (UDP) is reached within the specified time period. |
Action |
Select the action to perform when a client has exceeded the rate limit.
|
Syslog Profile
The Syslog Application Profile type supports UDP applications - typically, but not limited to, Syslog - with unidirectional client to server traffic flow only. With this Application Profile type, the NSX Advanced Load Balancer does not maintain flow table entries and load balances each received UDP datagram individually according to the configured load balancing algorithm in the Pool.
The Syslog Application Profile type supports the System-UDP-No-SNAT network profile, which disables SNAT for the load balanced traffic and preserves the client’s IP address and source port. Since there is no flow tracking and no reply traffic from the servers, this configuration is compatible with all Service Engine H/A models.
The usual limitations and requirements associated with preserving the client IP do not apply to this configuration. See UDP Fast Path.
Refrain from using the Least Connections load balancing alogorithm with the Syslog Application Profile type, since there is no tracking of connections.
SIP Profile
SIP profile allows NSX Advanced Load Balancer to process traffic for SIP applications. This profile defines the transaction timeout allowed for SIP traffic through NSX Advanced Load Balancer. Configure the timeout within the range of 16-512 seconds.