A GSLB service can comprise multiple GSLB pools. A GSLB service can switch load across multiple GSLB pools based on the priority of the pools as explained in the example below or based on the geolocation.
A GSLB pool is different from a server pool. The former aggregates back-end services, while the latter aggregates servers.
- GSLB_SERVICE_ALGORITHM_GEO
-
A GSLB pool is selected based on the geolocation. When
GSLB_SERVICE_ALGORITHM_GEOis selected for GSLB service, pool priority holds no significance.For more information, see Geolocation-based Load Balancing Algorithm for GSLB Members.
- GSLB_SERVICE_ALGORITHM_PRIORITY
-
A GSLB pool is selected based on its priority.
The valid priority range defined is 0-100. Setting a pool’s priority to zero disqualifies it from the selection. This can be done temporarily, for example, to perform maintenance on the services comprising the pool.
Note:Setting pool priority to 0 is not the same as disabling it. A zero-priority pool will continue to be health-monitored; its state will be displayed as
UPorDOWN, and notDISABLED.
Refer to the diagrams shown below:
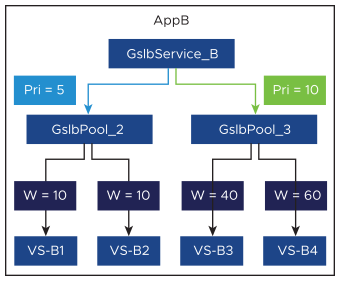
AppB, which corresponds to the GslbService_B, is comprised of two pools, with priorities 5 and 10. As long as the pool of highest priority (GslbPool_3) is up and not at its connection limit, all traffic will be directed to it. GslbPool_2 will remain idle. However, if a pool is inaccessible, down, or at maximum capacity, a lower priority pool will be chosen instead.
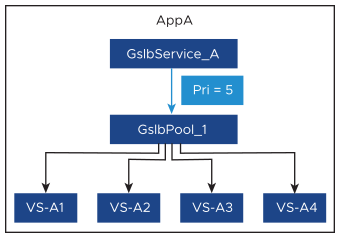
GslbPool_1 aggregates services VS-A1 through VS-A4 across which load will be balanced.
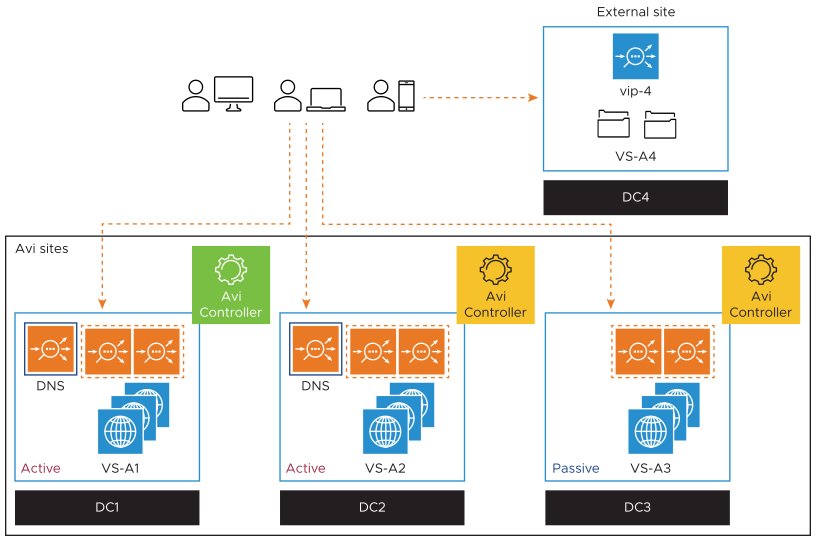
For more information, see Load Balancing Algorithms for GSLB.
Manual Resume option for GSLB Service with Priority Algorithm
Starting with NSX Advanced Load Balancer 22.1.3, a manual resume option is available for GSLB Service with priority algorithm. For more information, see Manual Resume Option for GSLB Service with Priority Algorithm.