The services that comprise a GSLB pool (for example, VS-B3 and VS-B4 as shown in the following figures) are called GSLB pool members.
The following parameters can be used to specify members:
The virtual service.
An IP address, to specify standalone servers or VIPs defined by third-party load balancers
FQDN (NSX Advanced Load Balancer resolves the name to an IP for health-checks, and responds with a CNAME).
GSLB Pool Member Weights
There are different GSLB algorithms that can be configured to load balance the traffic to GSLB pool members. For more information, see Load Balancing Algorithms for GSLB.
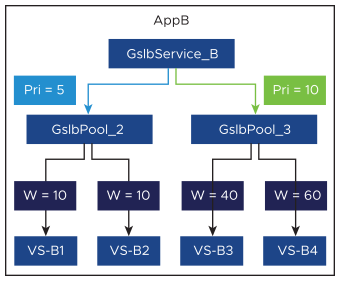
Two-level GSLB Pool Member Service Selection
Selection of a GSLB pool member service is a two-level process:
Select the pool.
Select the service.
Within a GSLB service, each GSLB pool is given a distinct priority. A GSLB service allows for the assignment of the same priority to multiple GSLB pools. If a set of pools share a priority that exceeds the priorities of the other pools, the NSX Advanced Load Balancer selects from that set in a round-robin fashion, for the time, the minimum member logic is satisfied. The valid priority range includes a priority of zero. Setting a pool’s priority to zero disqualifies it from the selection. This might be done temporarily, for example, to perform maintenance on the services comprising the pool.
Setting pool priority to zero is not equivalent to deactivating it. A zero-priority pool will continue to be health monitored and its state will be displayed as UP, DOWN, or NOT DISABLED.