This section describes the resolution to the intermittent connection refusals observed on Service Engines, which correlate to higher traffic volume.
The shared memory pool on an NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE is divided into the following two components:
Connections: Connections consist of the TCP, HTTP, and SSL connection tables. Memory allocated to connections directly impacts the total concurrent connections a Service Engine can maintain.
Buffers: Buffers consist of application layer packet buffers. These buffers are used to queue packets to provide improved network performance.
The connection refusals can be due to the Service Engine running low on packet buffers. When packet buffer usage exceeds the configured value, connection refusals start. This issue can be alleviated by increasing the memory allocated per Service Engine. As the available packet buffers decrease, NSX Advanced Load Balancer Service Engine conserves the remaining memory by refusing a percentage of the connections. As the available buffers reduce, the rate of refused connections increases. This is why the issue is amplified with the higher load on the NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE.
To change memory allocation per SE,
Navigate to .
Select the specific cloud.
Select the desired SE and click the edit (pencil icon) on the right side.
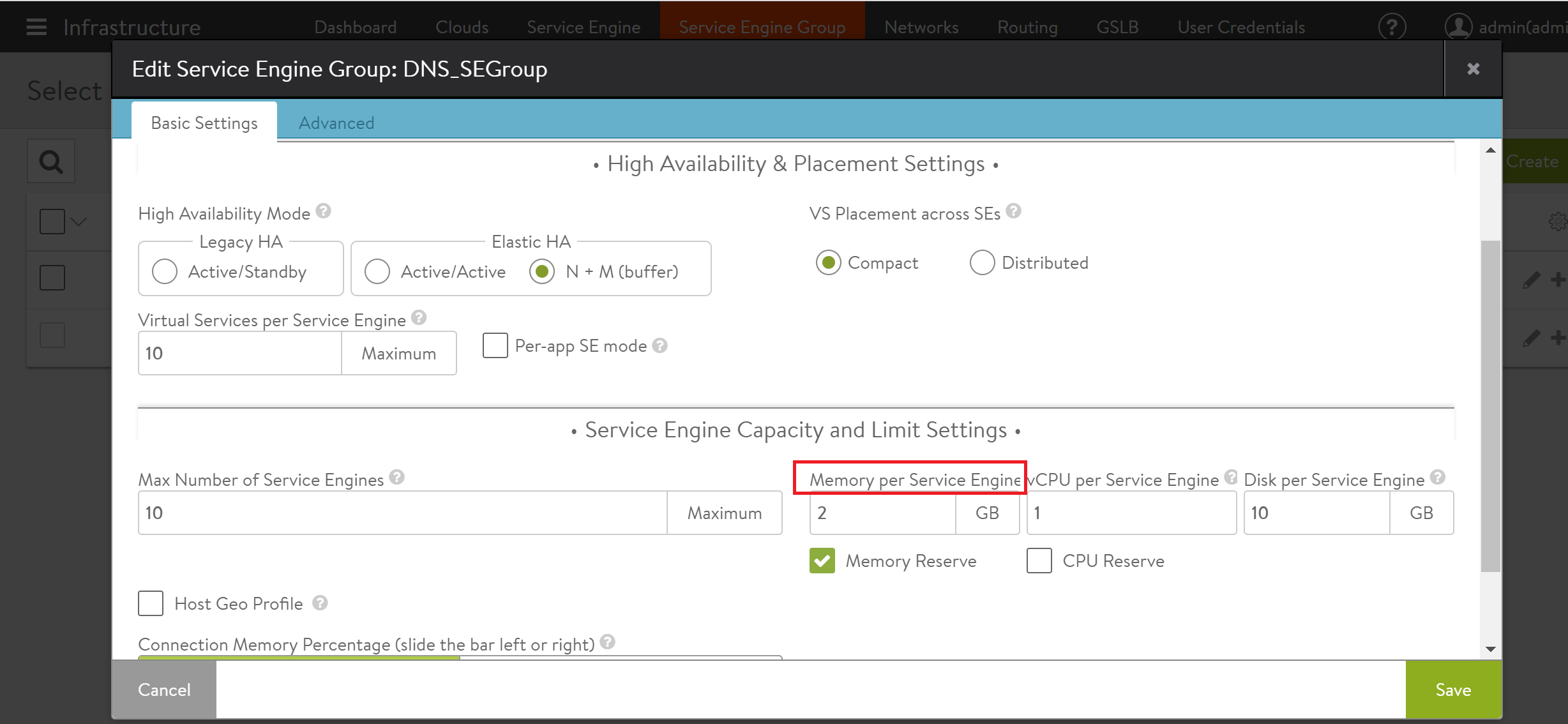
Memory per Service Engine option is available under the Service Engine Capacity and Limit Setting section as shown in the image below:
For more information on memory allocation on an NSX Advanced Load Balancer SE and how to enable per virtual service level admission control SE Memory Consumption, see SE Memory Consumption.