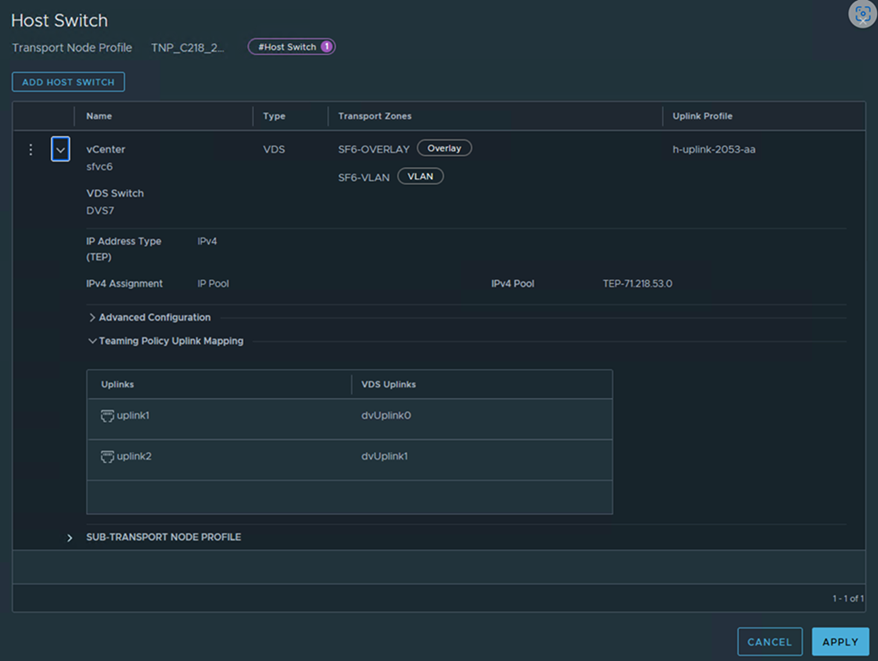
A transport node profile is a template to define configuration that is applied to a group of hosts that are part of a VMware vCenter cluster. It is not applied to prepare standalone hosts. Prepare VMware vCenter cluster hosts as transport nodes by applying a transport node profile. Transport node profiles define transport zones, member hosts, switch configuration including uplink profile, IP assignment, mapping of physical NICs to uplink virtual interfaces and so on.
Transport node creation begins when a transport node profile is applied to a VMware vCenter cluster. NSX Manager prepares the hosts in the cluster and installs the NSX components on all the hosts. Transport nodes for the hosts are created based on the configuration specified in the transport node profile.
On a cluster prepared with a transport node profile, these outcomes are true:
- When you move an unprepared host into a cluster applied with a transport node profile, NSX automatically prepares the host as a transport node using the transport node profile.
- When you move a transport node from the cluster to an unprepared cluster or directly as a standalone host under the data center, first the transport node configuration applied to the node is removed and then NSX VIBs are removed from the host. See Triggering Uninstallation from the vSphere Web Client.
- You can add a maximum of four VDS switches for each configuration: enhanced VDS created for VLAN transport zone, standard VDS created for overlay transport zone, enhanced VDS created for overlay transport zone.
- There is no limit on the number of standard VDS switches created for VLAN transport zones.
- In a single host cluster topology running multiple standard overlay VDS switches and edge VM on the same host, NSX provides traffic isolation such that traffic going through the first VDS is isolated from traffic going through the second VDS and so on. The physical NICs on each VDS must be mapped to the edge VM on the host to allow the north-south traffic connectivity with the external world. Packets moving out of a VM on the first transport zone must be routed through an external router or an external VM to the VM on the second transport zone.
- Each VDS switch name must be unique. NSX does not allow the use of duplicate switch names.
- Each transport zone ID associated with each VDS host in the transport node configuration or transport node profile configuration must be unique.
Prerequisites
- Verify that the hosts are part of a VMware vCenter cluster.
- Verify that cluster hosts are members of VDS version 7.0 or later with at least one uplink on a VDS port group.
- Verify that a transport zone is configured. See Create Transport Zones.
-
Verify that NSX Manager cluster nodes are up and available. To verify cluster status, go to . See Deploy NSX Manager Nodes to Form a Cluster from the UI.
- Verify that an IP pool is configured, or DHCP must be available in the network deployment. See Create an IP Pool for Tunnel Endpoint IP Addresses.
- Verify that a compute manager is configured. See Add a Compute Manager.
- Verify an uplink profile to use for Host configuration is configured. See Create an Uplink Profile.
Procedure
What to do next
Apply the transport node profile to an existing vSphere cluster. See Prepare ESXi Cluster Hosts as Transport Nodes by Using TNP.