VMware allows the Enterprise users to define and configure a Non SD-WAN Destination instance and establish a secure IPsec tunnel to a Non SD-WAN Destination through a SD-WAN Gateway.
The Orchestrator selects the nearest Gateway for the Non SD-WAN Destination with its configured IP address, using geolocation service.
You can configure Non SD-WAN Destination via Gateway only at the Profile Level and cannot override at the SD-WAN Edge level.
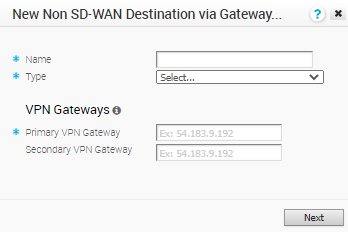
To configure a Non SD-WAN Destination via Gateway:
Procedure
What to do next
- Configure tunnel settings for your Non SD-WAN Destination. For more information about configuring tunnel settings for various IPsec tunnel types, see the following sections:
- Associate your Non SD-WAN Destination to a Profile. For more information, see:
- Configure Business Policy. (Configuring Business Policy is not mandatory for this feature, but if you are going to configure it and would like information, see Create Business Policy Rules.