A Firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules. SD-WAN Orchestrator supports configuration of stateless and stateful Firewalls for Profiles and Edges.
For more information on Firewall, see Firewall Overview.
Configure Profile Firewall
- In the Enterprise portal, go to . The Profiles page displays the existing Profiles.
- To configure a Profile, click the link to the Profile or click the View link in the Firewall column of the Profile.
- Click the Firewall tab.
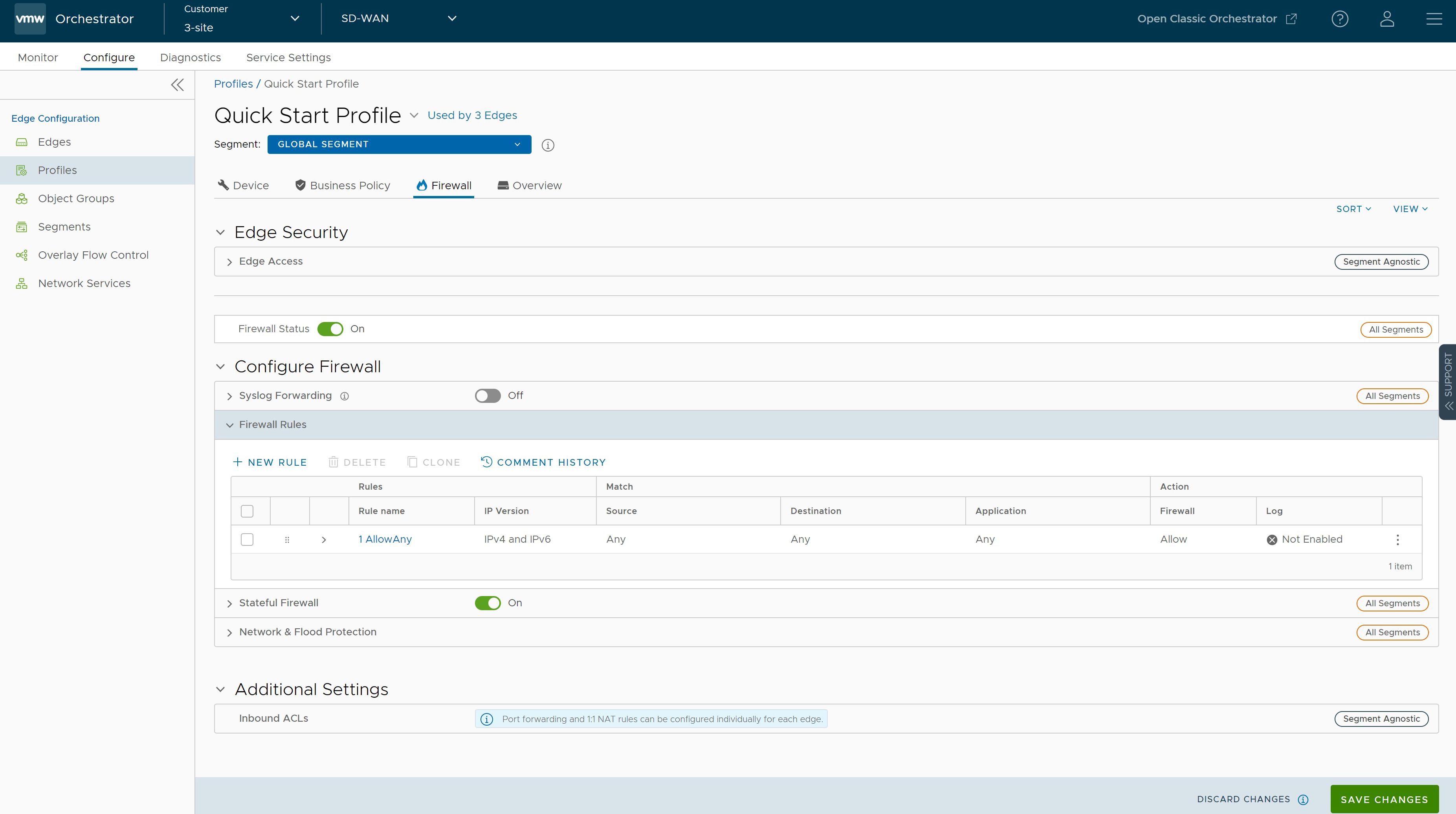
- From the Firewall tab, you can configure the following Edge Security and Firewall capabilities:
Field Description Edge Access Allows you to configure a Profile for Edge access. You must make sure to select the appropriate option for Support access, Console access, USB port access, SNMP access, and Local Web UI access under Firewall settings to make the Edge more secure. This will prevent any malicious user from accessing the Edge. By default, Support access, Console access, SNMP access, and Local Web UI access are deactivated for security reasons. For more information, see Configure Edge Access. Firewall Status Allows you to turn ON or OFF the Firewall rules, configure Firewall settings, and in-bound ACLs for all Edges associated with the Profile. Note: By default, this feature is activated. You can deactivate the Firewall function for Profiles by turning the Firewall Status to OFF.Syslog Forwarding By default, the Syslog Forwarding feature is deactivated for an Enterprise. To collect SD-WAN Orchestrator bound events and Firewall logs originating from Enterprise SD-WAN Edge to one or more centralized remote Syslog collectors (Servers), an Enterprise user must activate this feature at the Enterprise level. To configure Syslog collector details per segment in the SD-WAN Orchestrator, see Configure Syslog Settings for Profiles with New Orchestrator UI. Note: You can view both IPv4 and IPv6 Firewall logging details in a IPv4-based Syslog Server.Firewall Rules The existing pre-defined Firewall rules are displayed. You can click + NEW RULE to create a new Firewall rule. For more information, see Configure Firewall Rule with New Orchestrator UI. To delete existing Firewall rules, select the checkboxes prior to the rules and click DELETE. To duplicate a Firewall rule, select the rule and click CLONE. Stateful Firewall By default, the Stateful Firewall feature is deactivated for an Enterprise. SD-WAN Orchestrator allows you to set session timeout for established and non-established TCP flows, UDP flows, and other flows at the Profile level. Optionally, you can also override the Stateful firewall settings at the Edge level. For more information, see Configure Stateful Firewall Settings. Network & Flood Protection To secure all connection attempts in an Enterprise network, VMware SD-WAN Orchestrator allows you to configure Network and Flood Protection settings at the Profile and Edge levels, to protect against the various types of attacks. For more information, see Configure Network & Flood Protection Settings.
Configure Edge Access
- From the SD-WAN Orchestrator, go to Configure > Profiles > Firewall.
- Under Edge Security, click the Edge Access expand icon.
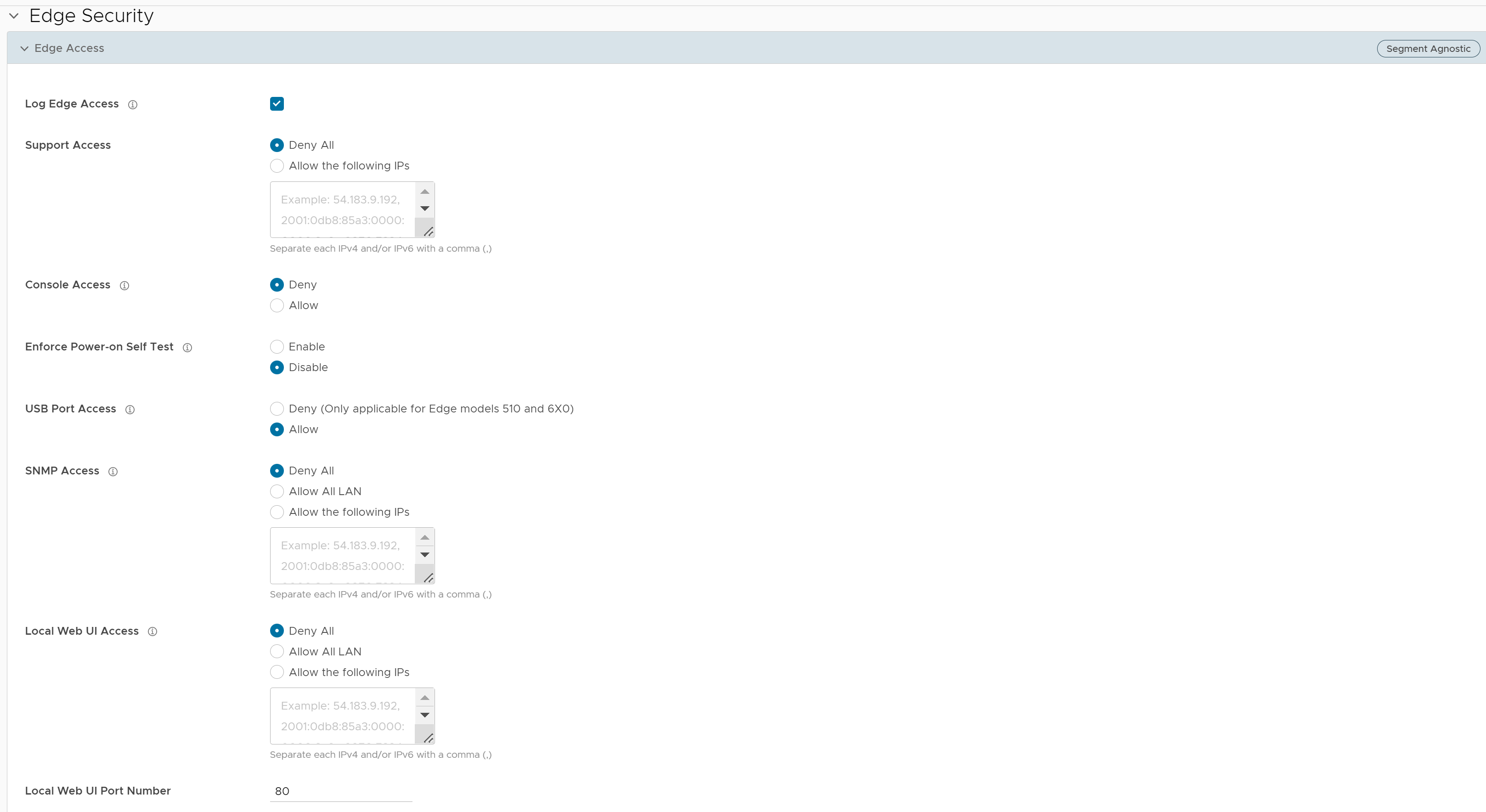
- You can configure one or more of the following Edge Access options, and click Save Changes:
Field Description Log Edge Access When activated, all access to the Edge is logged, including successful and failed attempts. Support Access Select Allow the following IPs if you want to explicitly specify the IP addresses from where you can SSH into this Edge. You can enter both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses separated by comma (,).
By default, Deny All is selected.
Console Access Select Allow to activate Edge access through Physical Console (Serial Port or Video Graphics Array (VGA) Port). By default, Deny is selected and Console login is deactivated after Edge activation. Note: Whenever the console access setting is changed from Allow to Deny or vice-versa, the Edge must be rebooted manually.Enforce Power-on Self Test When activated, a failed Power-on Self Test will deactivate the Edge. You can recover the Edge by running factory reset and then reactivate the Edge. USB Port Access Select Allow to activate and select Deny to deactivate the USB port access on Edges.
This option is available only for Edge models 510 and 6x0.
Note: Whenever the USB port access setting is changed from Allow to Deny or vice-versa, you must reboot the Edge manually if you have access to the Edge and if the Edge is in a remote site, restart the Edge using SD-WAN Orchestrator. For instructions, refer to Remote Actions with New Orchestrator UI.SNMP Access Allows Edge access from routed interfaces/WAN through SNMP. Select one of the following options: - Deny All - By default, SNMP access is deactivated for all devices connected to an Edge.
- Allow All LAN - Allows SNMP access for all devices connected to the Edge through a LAN network.
- Allow the following IPs - Allows you to explicitly specify the IP addresses from where you can access the Edge through SNMP. Separate each IPv4 or IPv6 addresses with a comma (,).
Local Web UI Access Allows Edge access from routed interfaces/WAN through a Local Web UI. Select one of the following options: - Deny All - By default, Local Web UI access is deactivated for all devices connected to an Edge.
- Allow All LAN - Allows Local Web UI access for all devices connected to the Edge through a LAN network.
- Allow the following IPs - Allows you to explicitly specify the IP addresses from where you can access the Edge through Local Web UI. Separate each IPv4 or IPv6 addresses with a comma (,).
Local Web UI Port Number Enter the port number of the local Web UI from where you can access the Edge. The default value is 80.
Configure Stateful Firewall Settings
- From the SD-WAN Orchestrator, go to Configure > Profiles > Firewall.
- Under Configure Firewall, turn on the Stateful Firewall toggle button and then click the expand icon. By default, the timeout sessions are applied for IPv4 addresses.
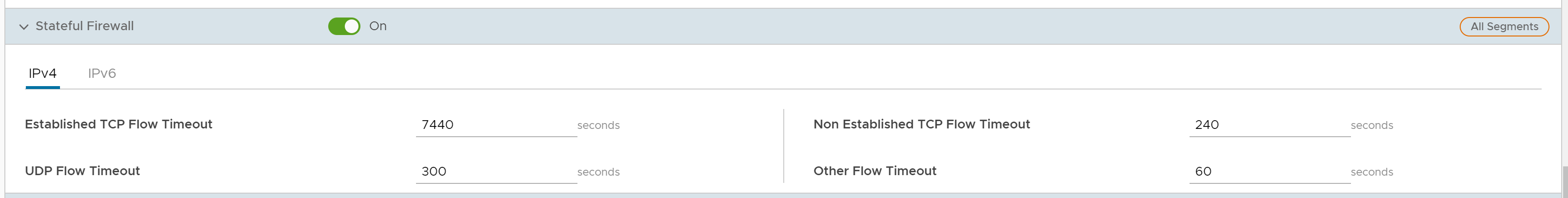
- You can configure the following Stateful Firewall settings, and click Save Changes:
Field Description Established TCP Flow Timeout (seconds) Sets the inactivity timeout period (in seconds) for established TCP flows, after which they are no longer valid. The allowable value ranges from 60 seconds through 15999999 seconds. The default value is 7440 seconds. Non Established TCP Flow Timeout (seconds) Sets the inactivity timeout period (in seconds) for non-established TCP flows, after which they are no longer valid. The allowable value ranges from 60 seconds through 604800 seconds. The default value is 240 seconds. UDP Flow Timeout (seconds) Sets the inactivity timeout period (in seconds) for UDP flows, after which they are no longer valid. The allowable value ranges from 60 seconds through 15999999 seconds. The default value is 300 seconds. Other Flow Timeout (seconds) Sets the inactivity timeout period (in seconds) for other flows such as ICMP, after which they are no longer valid. The allowable value ranges from 60 seconds through 15999999 seconds. The default value is 60 seconds. Note:The configured timeout values apply only when the memory usage is below the soft limit. Soft limit corresponds to anything below 60 percent of the concurrent flows supported by the platform in terms of memory usage.
Configure Network & Flood Protection Settings
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack
- TCP-based attacks - Invalid TCP Flags, TCP Land, and TCP SYN Fragment
- ICMP-based attacks - ICMP Ping of Death and ICMP Fragment
- IP-based attacks - IP Unknown Protocol, IP Options, IPv6 Unknown Protocol, and IPv6 Extension Header.
| Attack Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack | A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is a type of network security attack that overwhelms the targeted device with a tremendous amount of bogus traffic so that the target becomes so preoccupied processing the bogus traffic that legitimate traffic cannot be processed. The target can be a firewall, the network resources to which the firewall controls access, or a specific hardware platform or operating system of an individual host. The DoS attack attempts to exhaust the target device's resources, making the target device unavailable to legitimate users. There are two general methods of DoS attacks: flooding services or crashing services. Flood attacks occur when the system receives too much traffic for the server to buffer, causing them to slow down and eventually stop. Other DoS attacks simply exploit vulnerabilities that cause the target system or service to crash. In these attacks, input is sent that takes advantage of bugs in the target that subsequently crash or severely destabilize the system. |
| Invalid TCP Flags |
Invalid TCP flags attack occurs when a TCP packet has a bad or invalid flag combination. A vulnerable target device will crash due to invalid TCP flag combinations and therefore it is recommended to filter them out. Invalid TCP flags guards against:
|
| TCP Land | A Land attack is a Layer 4 DoS attack in which, a TCP SYN packet is created such that the source IP address and port are set to be the same as the destination IP address and port, which in turn is set to point to an open port on a target device. A vulnerable target device would receive such a message and reply to the destination address effectively sending the packet for reprocessing in an infinite loop. Thus, the device CPU is consumed indefinitely causing the vulnerable target device to crash or freeze. |
| TCP SYN Fragment | The Internet Protocol (IP) encapsulates a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) SYN segment in the IP packet to initiate a TCP connection and invoke a SYN/ACK segment in response. Because the IP packet is small, there is no legitimate reason for it to be fragmented. A fragmented SYN packet is anomalous, and as such suspect. In a TCP SYN fragment attack, a target server or host is flooded with TCP SYN packet fragments. The host catches the fragments and waits for the remaining packets to arrive so it can reassemble them. By flooding a server or host with connections that cannot be completed, the host's memory buffer overflows and therefore no further legitimate connections are possible, causing damage to the target host's operating system. |
| ICMP Ping of Death | An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Ping of Death attack involves the attacker sending multiple malformed or malicious pings to a target device. While ping packets are generally small used for checking reachability of network hosts, they could be crafted larger than the maximum size of 65535 bytes by attackers. When a maliciously large packet is transmitted from the malicious host, the packet gets fragmented in transit and when the target device attempts to reassemble the IP fragments into the complete packet, the total exceeds the maximum size limit. This could overflow memory buffers initially allocated for the packet, causing system crash or freeze or reboot, as they cannot handle such huge packets. |
| ICMP Fragment | An ICMP Fragmentation attack is a common DoS attack which involves the flooding of fraudulent ICMP fragments that cannot be defragmented on the target server. As defragmentation can only take place when all fragments are received, temporary storage of such fake fragments takes up memory and may exhaust the available memory resources of the vulnerable target server, resulting in server unavailability. |
| IP Unknown Protocol | Enabling IP Unknown Protocol protection blocks IP packets with the protocol field containing a protocol ID number of 143 or greater, as it could lead to crash if not handled properly on the end device. A cautious stance would be to block such IP packets from entering the protected network. |
| IP Options | Attackers sometimes configure IP option fields within an IP packet incorrectly, producing either incomplete or malformed fields. Attackers use these malformed packets to compromise vulnerable hosts on the network. Exploitation of the vulnerability may potentially allow for arbitrary code execution. The vulnerability may be exploited after processing a packet containing a specific crafted IP option in the packet's IP header. Enabling IP Insecure Options protection blocks transit IP packets with incorrectly formatted IP option field in the IP packet header. |
| IPv6 Unknown Protocol | Enabling IPv6 Unknown Protocol protection blocks IPv6 packets with the protocol field containing a protocol ID number of 143 or greater, as it could lead to crash if not handled properly on the end device. A cautious stance would be to block such IPv6 packets from entering the protected network. |
| IPv6 Extension Header | IPv6 Extension Header attack is a DoS attack that occurs due to mishandling of extension headers in an IPv6 packet. The mishandling of IPv6 extension headers creates new attack vectors that could lead to DoS, and which can be exploited for different purposes, such as creating covert channels and routing header 0 attacks. Enabling this option would drop IPv6 packet with any extension header except fragmentation headers. |
- From the SD-WAN Orchestrator, go to Configure > Profiles > Firewall.
- Under Configure Firewall, ensure to turn on the Stateful Firewall feature.
- Click the Network & Flood Protection expand icon.
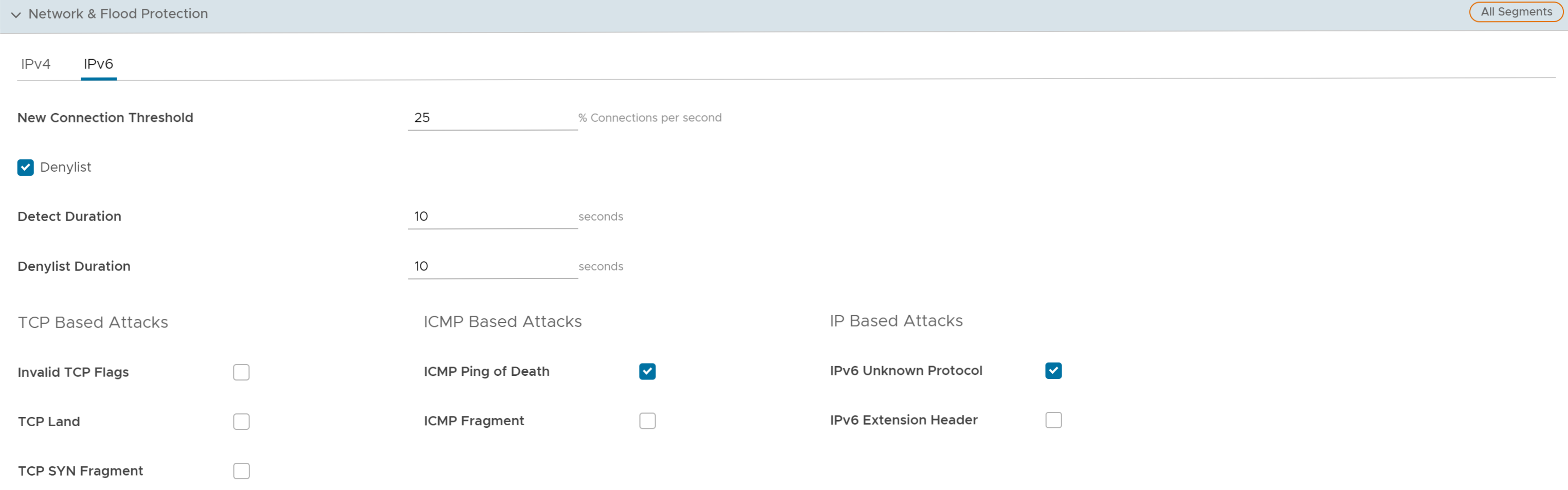
- You can configure the following Network and Flood Protection settings, and click Save Changes:
Note: By default, the network and flood protection settings are applied for IPv4 addresses.
Field Description New Connection Threshold (connections per second) The maximum number of new connections that is allowed from a single source IP per second. The allowable value ranges from 10 percentage through 100 percentage. The default value is 25 percentage. Denylist Select the checkbox to block a source IP address, which is violating the new connection threshold by sending flood traffic either due to misconfiguration of network or malicious user attacks. Note: The New Connection Threshold (connections per second) settings will not work unless Denylist is selected.Detect Duration (seconds) Before blocking a Source IP address, it is the grace time duration for which the violating source IP is allowed to send traffic flows. If a host sends flood traffic of new connection requests (port scan, TCP SYN flood, etc.,) exceeding the maximum allowed connection per second (CPS) for this duration, it will be considered as eligible for denylisting instead of immediately denylisting it as soon as it exceeds the CPS per source once. For example, consider that the maximum allowed CPS is 10 with detect duration of 10 seconds, if the host floods new connection requests greater than 100 requests for 10 seconds, then the host will be denylisted.
The allowable value ranges from 10 seconds through 100 seconds. The default value is 10 seconds.Denylist Duration (seconds) The time duration for which the violated source IP is blocked from sending any packets. The allowable value ranges from 10 seconds through 86400 seconds. The default value is 10 seconds. TCP Based Attacks Supports protection from the following TCP-based attacks by enabling the respective checkboxes: - Invalid TCP Flags
- TCP Land
- TCP SYN Fragment
ICMP Based Attacks Supports protection from the following ICMP-based attacks by enabling the respective checkboxes: - ICMP Ping of Death
- ICMP Fragment
IP Based Attacks Supports protection from the following IP-based attacks by enabling the respective checkboxes: - IP Unknown Protocol
- IP Options
- IPv6 Unknown Protocol
- IPv6 Extension Header