Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a point-to-multipoint access network that uses passive splitters in a fiber distribution network, enabling one single feeding fiber from the provider to serve multiple homes and small businesses. GPON supports triple-play services, high-bandwidth, and long reach (up to 20km).
GPON has a downstream capacity of 2.488 Gb/s and an upstream capacity of 1.244 Gbps/s that is shared among users. Encryption is used to keep each user’s data private and secure. There are other technologies that could provide fiber to the home; however, passive optical networks (PONs) like GPON are generally considered the strongest candidate for widespread deployments.
GPON Support
- Longer transmission distance: The transmission media of optical fibers covers up to 60 km coverage radius on the access layer, resolving transmission distance and bandwidth issues in a twisted pair transmission.
- Higher bandwidth: Each GPON port can support a maximum transmission rate of 2.5 Gbit/s in the downstream direction and 1.25 Gbit/s in the upstream direction, meeting the usage requirements of high-bandwidth services, such as high definition television (HDTV) and outside broadcast (OB).
- Better user experience on full services: Flexible QoS measures support traffic control based on users and user services, implementing differentiated service provisioning for different users.
- Higher resource usage with lower costs: GPON supports a split ratio up to 1:128. A feeder fiber from the CO equipment room can be split into up to 128 drop fibers. This economizes on fiber resources and O&M costs.
Configuring GPON ONT from the SD-WAN Orchestrator
Click the SFP interface that the specific GPON module is plugged into. When the SFP is plugged in, the slot name will display as SFP1 and SFP2 in the Device Settings area of the SD-WAN Orchestrator.
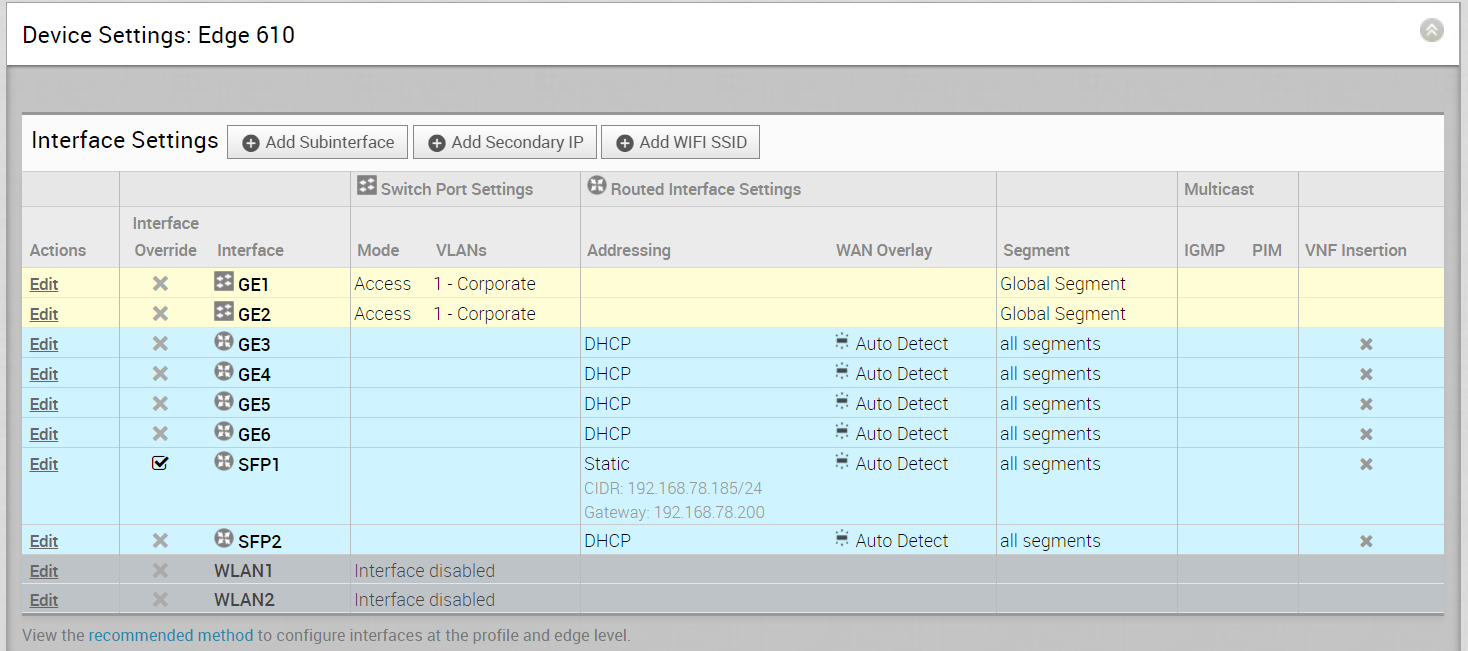
To Configure GPON ONT SFP from the SD-WAN Orchestrator:
- From the SD-WAN Orchestrator, go to Configure > Edges, and then select an 6X0 Edge.
- Click the Device tab, and scroll down to Device Settings for the 6X0 Edge.
- Click the Edit link in the Actions column for the SFP (SFP1 or SFP 2) Interface as shown in the image above.
The 6X0 Edge device Interface dialog box displays.
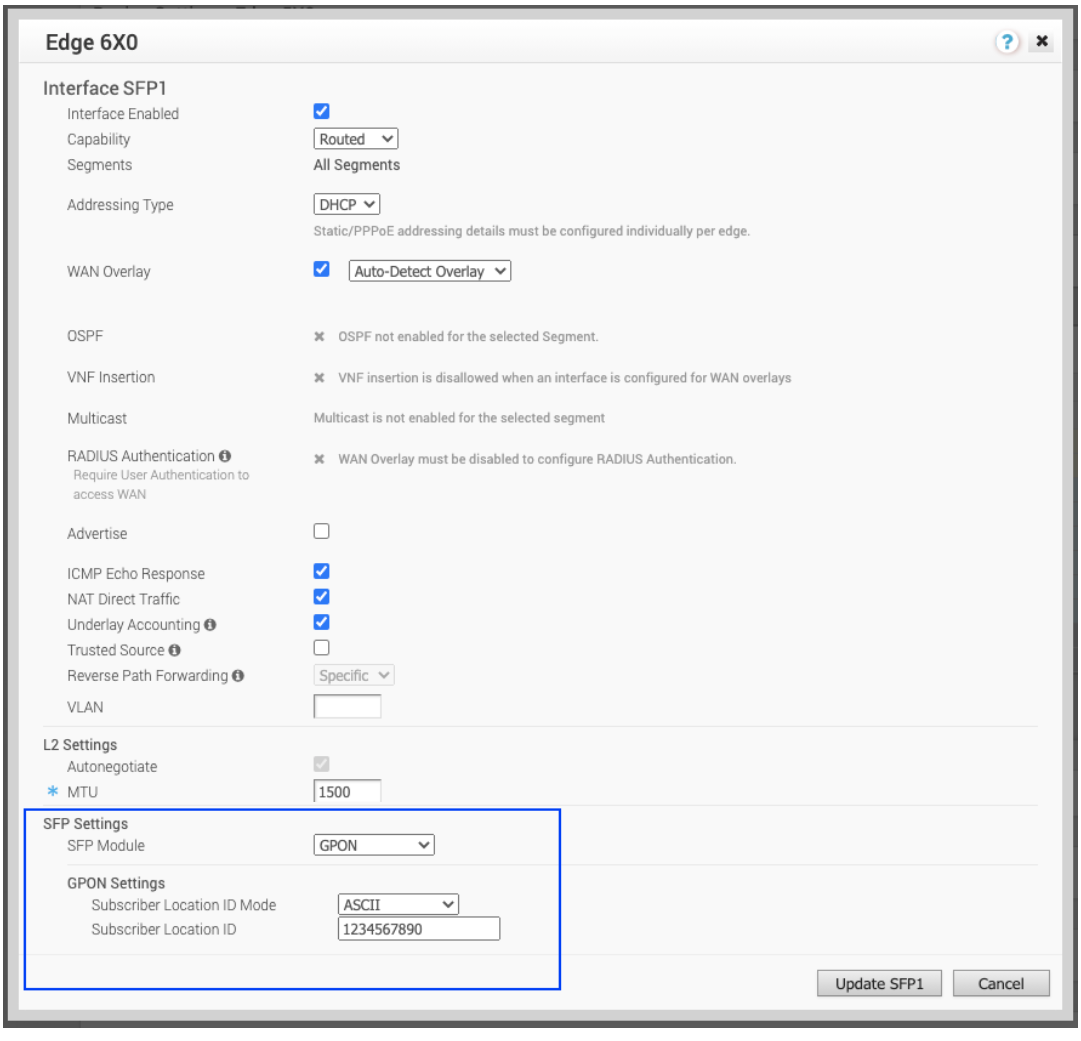
- The Override Interface checkbox must be checked to configure GPON Settings.
- Check the Interface Enabled checkbox.
Note: The steps in this procedure are specifically for configuring GPON. For a complete description of all items in the 6X0 Edge device Interface dialog box, see Configure Interface Settings.
- In the SFP Settings area, choose GPON as the SFP Module as shown in the image below.
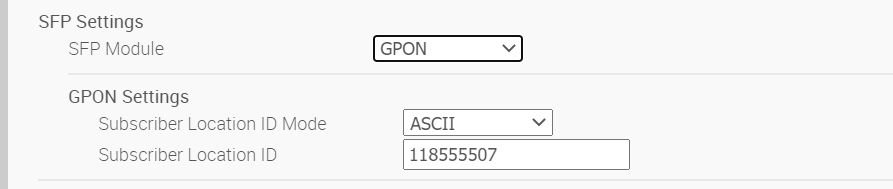
- In the GPON Settings area, enter the Subscriber Location ID Mode. (The Subscriber Location ID can be up to 10 ASCII characters or up to 20 Hex Numbers. The ASCII Subscriber Location ID mode will allow up to 10 ASCII characters. The HEX Subscriber Location ID mode will allow up to 20 Hexadecimal characters).
- In the GPON Settings area, enter the Subscriber Location ID.
- Click the Update SFP1 button.
To Configure GPON ONT SFP from the Local UI:
- From the Local UI, navigate to Details Edge Overview.
The Edge Overview Page displays as shown in the image below.
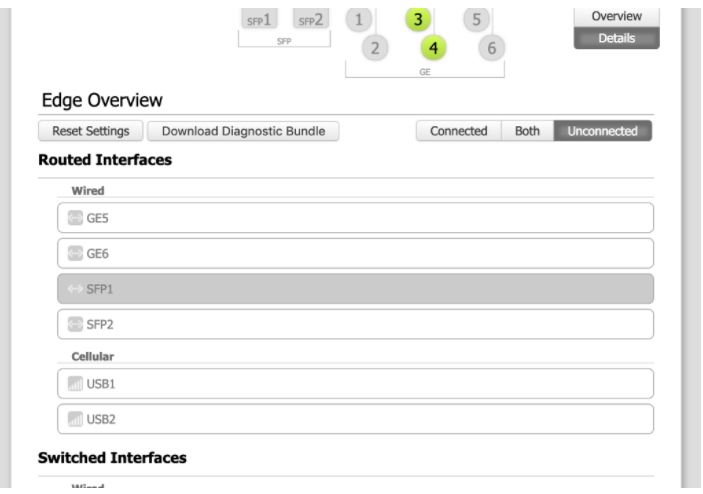
- Select an SFP interface to change its setting.
- In the SFP properties page, select GPON from the SFP Module drop-down menu. (See image below).
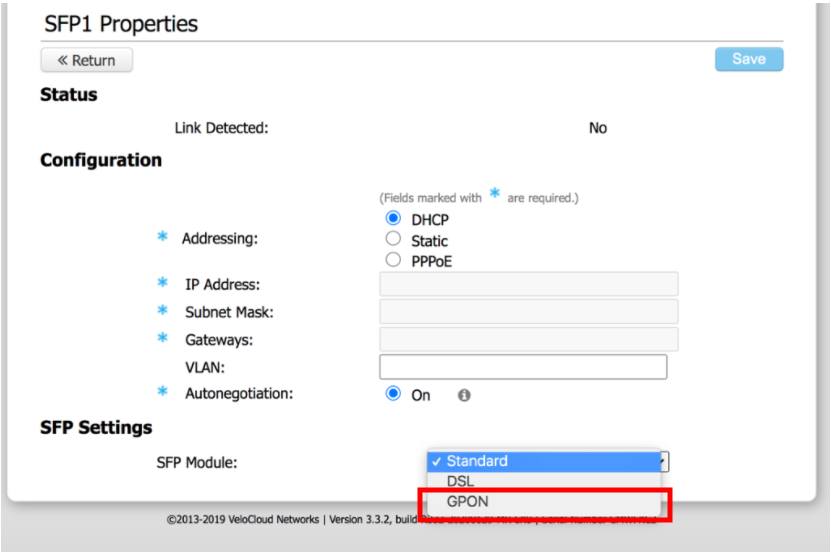
The following GPON Settings, the Subscriber Location ID Mode and Subscriber Location ID, display as shown in the image below.
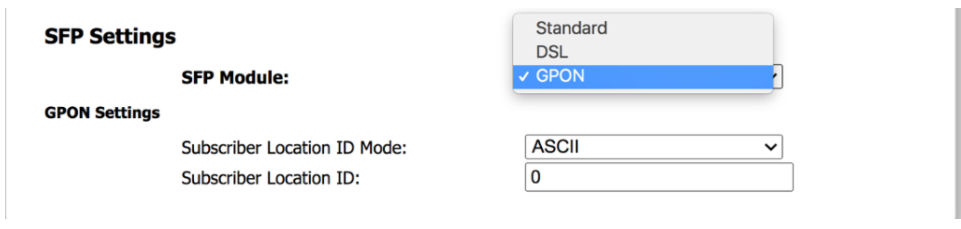
- In the Subscriber Location ID Mode drop-down menu, choose either ACII or HEX (image below).
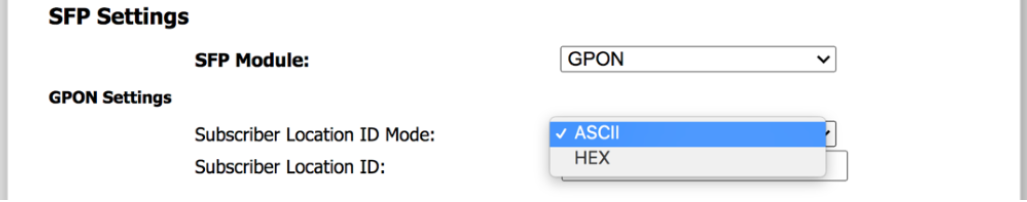
- Enter the Subscriber Location ID in the appropriate text box.
Troubleshooting GPON Settings
The GPON diagnostic test is available only for 6X0 devices. See Performing Remote Diagnostics Tests for more information.