Common Criteria (CC) is an international certification accepted by many countries. Obtaining the CC certification is an endorsement that our product has been evaluated by competent and independent licensed laboratories for the fulfilment of certain security properties. This certification is recognized by all the signatories of the Common Criteria Recognition Agreement (CCRA). The CC is the driving force for the widest available mutual recognition of secure IT products. Having this certification is an assurance of security to a standard extent and can provide VMware with the much needed business parity or advantage with its competitors.
Enterprise users can configure the Common Criteria Firewall settings both at the Edge and Profile levels. By default, this feature is deactivated.
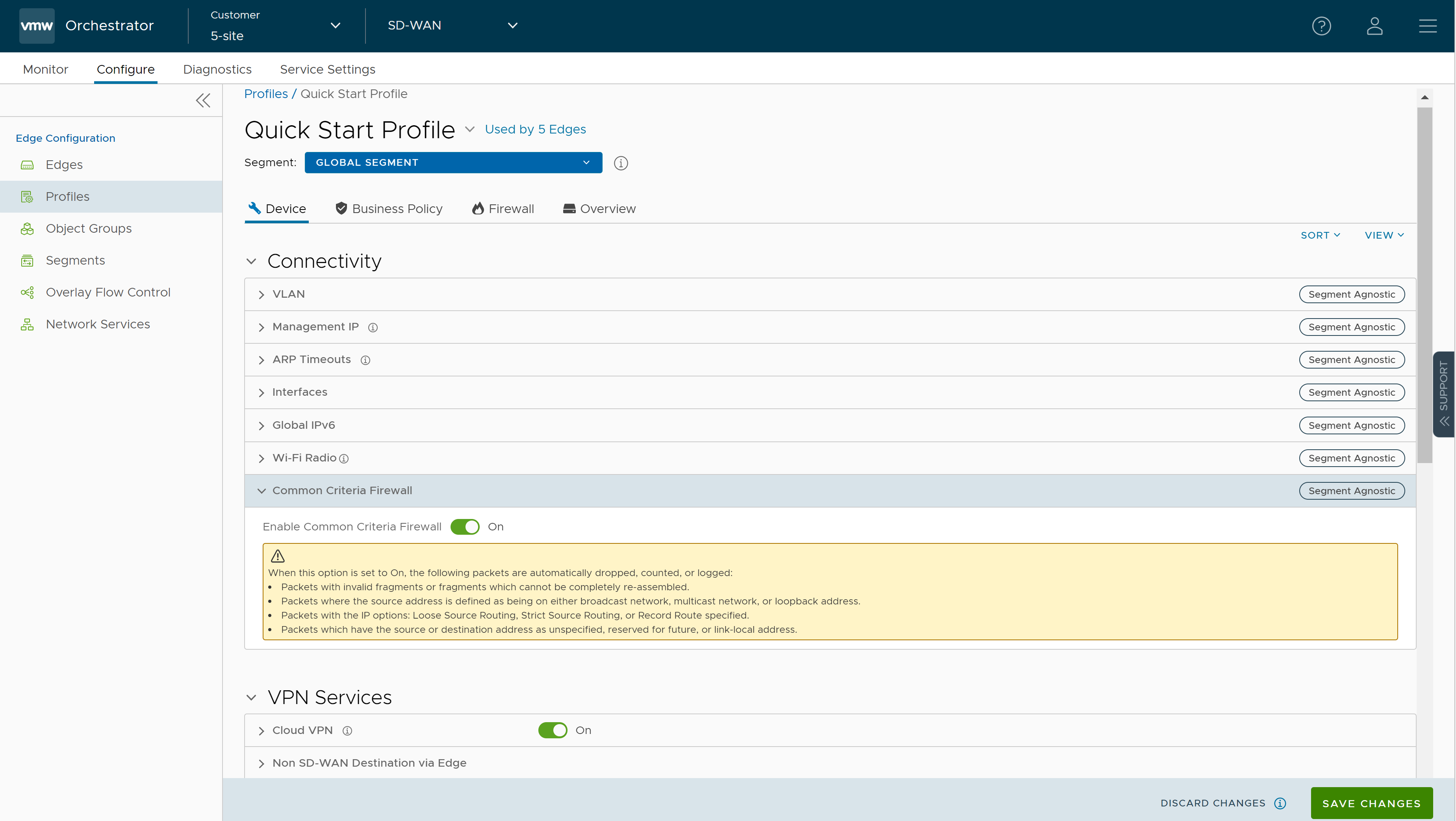
To configure Common Criteria Firewall settings for a Profile, perform the following steps:
Procedure
- In the SD-WAN service of the Enterprise portal, go to .
The
Profiles page displays the existing Profiles.
- Click the link to a Profile or click the View link in the Device column of the Profile. You can also select a Profile and click Modify to configure the Profile.
- The Device tab displays the configuration options for the selected Profile.
- In the Connectivity category, click Common Criteria Firewall.
- Turn on Enable Common Criteria Firewall toggle button.
When the
Enable Common Criteria Firewall option is set to On, the following packets are automatically dropped, counted, or logged:
- Packets with invalid fragments or fragments which cannot be completely re-assembled that are destined to the Edge.
- Packets where the source address is defined as being on either broadcast network, multicast network, or loopback address.
- Packets with the IP options: Loose Source Routing, Strict Source Routing, or Record Route specified.
- Packets which have the source or destination address as unspecified or reserved for future.
- Packets where the source address is equal to the address of the network interface where the network packet was received.
- Packets where the source address does not belong to the networks reachable via the network interface where the network packet was received.
- Packets where the source or destination address of the network packet is defined as being unspecified (i.e. 0.0.0.0) or an address “reserved for future use” (i.e. 240.0.0.0/4) as specified in RFC 5735 for IPv4.
- Packets where the source or destination address of the network packet is defined as an “unspecified address” or an address “reserved for future definition and use” (i.e. unicast addresses not in this address range: 2000::/3) as specified in RFC 3513 for IPv6.