Follow the below steps to configure a Non SD-WAN Destination of type Generic Firewall (Policy Based VPN) in the SASE Orchestrator.
Procedure
- Once you have created a Non SD-WAN Destination configuration of the type Generic Firewall (Policy Based VPN), you are redirected to an additional configuration options page:
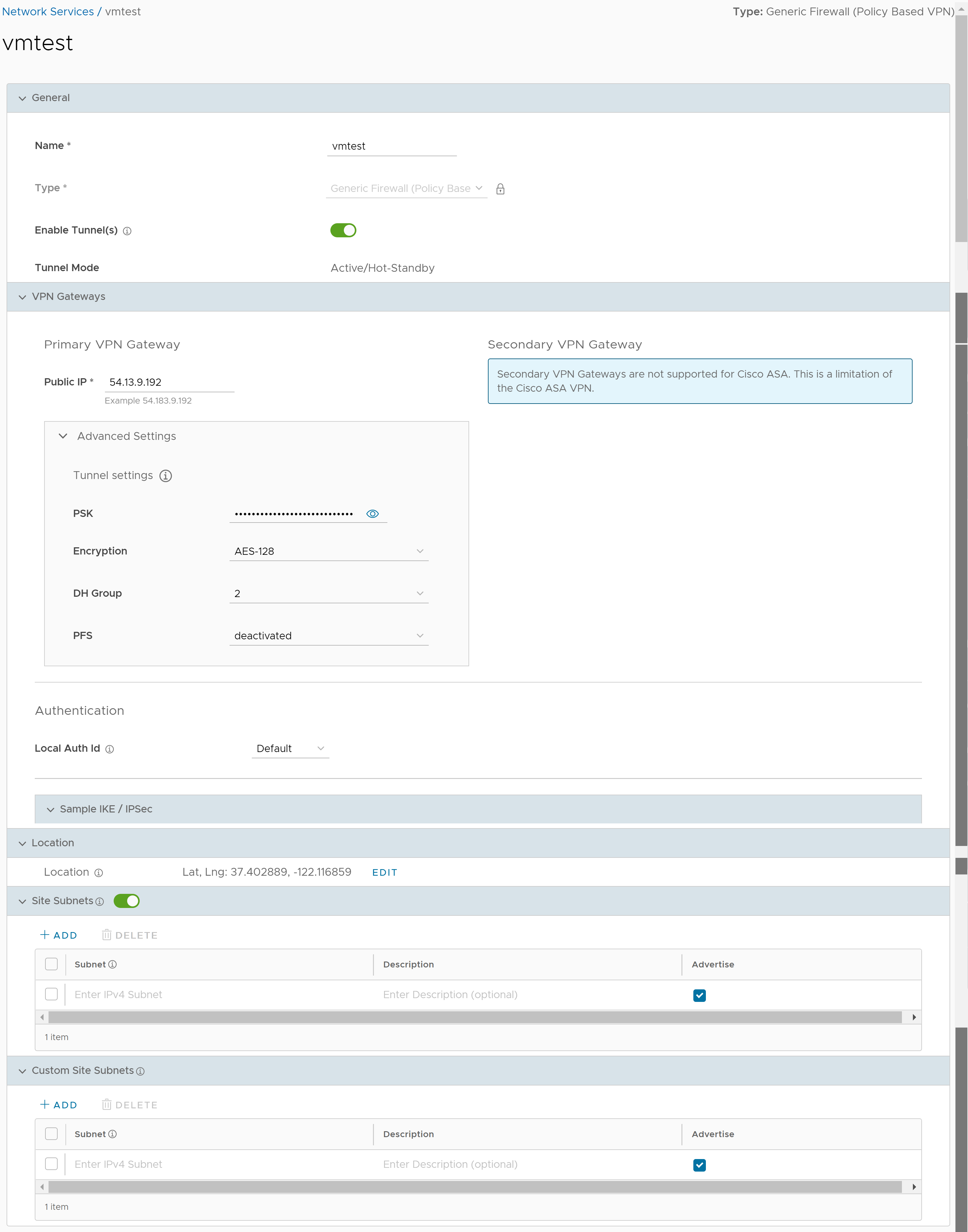 Note: Secondary VPN Gateway is not supported for the Generic Firewall (Policy Based VPN) service type.
Note: Secondary VPN Gateway is not supported for the Generic Firewall (Policy Based VPN) service type. - You can configure the following tunnel settings:
Option Description General Name You can edit the previously entered name for the Non SD-WAN Destination. Type Displays the type as Generic Firewall (Policy Based VPN). You cannot edit this option. Enable Tunnel(s) Click the toggle button to initiate the tunnel(s) from the SD-WAN Gateway to the Generic Firewall VPN Gateway. Tunnel Mode Displays Active/Hot-Standby, indicating that if the Active tunnel goes down, the Standby (Hot-Standby) tunnel takes over and becomes the Active tunnel. Primary VPN Gateway Public IP Displays the IP address of the Primary VPN Gateway. PSK The Pre-Shared Key (PSK) is the security key for authentication across the tunnel. The SASE Orchestrator generates a PSK by default. If you want to use your own PSK or password, enter it in the text box. Note: Starting from the 4.5 release, the use of the special character "<" in the password is no longer supported. In cases where users have already used "<" in their passwords in previous releases, they must remove it to save any changes on the page.Encryption Select either AES-128 or AES-256 as the AES algorithm key size to encrypt data. The default value is AES-128. DH Group Select the Diffie-Hellman (DH) Group algorithm from the drop-down menu. This is used for generating keying material. The DH Group sets the strength of the algorithm in bits. The supported DH Groups are 2, 5, and 14. The default value is 2. PFS Select the Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) level for additional security. The supported PFS levels are deactivated, 2, and 5. The default value is deactivated. Local Auth Id Local authentication ID defines the format and identification of the local gateway. From the drop-down menu, choose from the following types and enter a value: - FQDN - The Fully Qualified Domain Name or hostname. For example: vmware.com
- User FQDN - The User Fully Qualified Domain Name in the form of email address. For example: [email protected]
- IPv4 - The IP address used to communicate with the local gateway.
- IPv6 - The IP address used to communicate with the local gateway.
Note:- If you do not specify a value, Default is used as the local authentication ID.
- The default local authentication ID value is the SD-WAN Gateway Interface Local IP.
Sample IKE / IPsec Click to view the information needed to configure the Non SD-WAN Destination Gateway. The Gateway administrator should use this information to configure the Gateway VPN tunnel(s). Note: Currently, the supported IKE version is IKEv1.Location Click Edit to set the location for the configured Non SD-WAN Destination. The latitude and longitude details are used to determine the best Edge or Gateway to connect to in the network. Site Subnets Use the toggle button to activate or deactivate the Site Subnets. Click Add to add subnets for the Non SD-WAN Destination. If you do not need subnets for the site, select the subnet and click Delete. Note:- To support the datacenter type of Non SD-WAN Destination, besides the IPsec connection, you must configure Non SD-WAN Destination local subnets into the VMware system.
- If there are no site subnets configured, deactivate Site Subnets to activate the tunnel.
Custom Site Subnets Use this section to override the source subnets routed to this VPN device. Normally, source subnets are derived from the Edge LAN subnets routed to this device. - Click Save Changes.