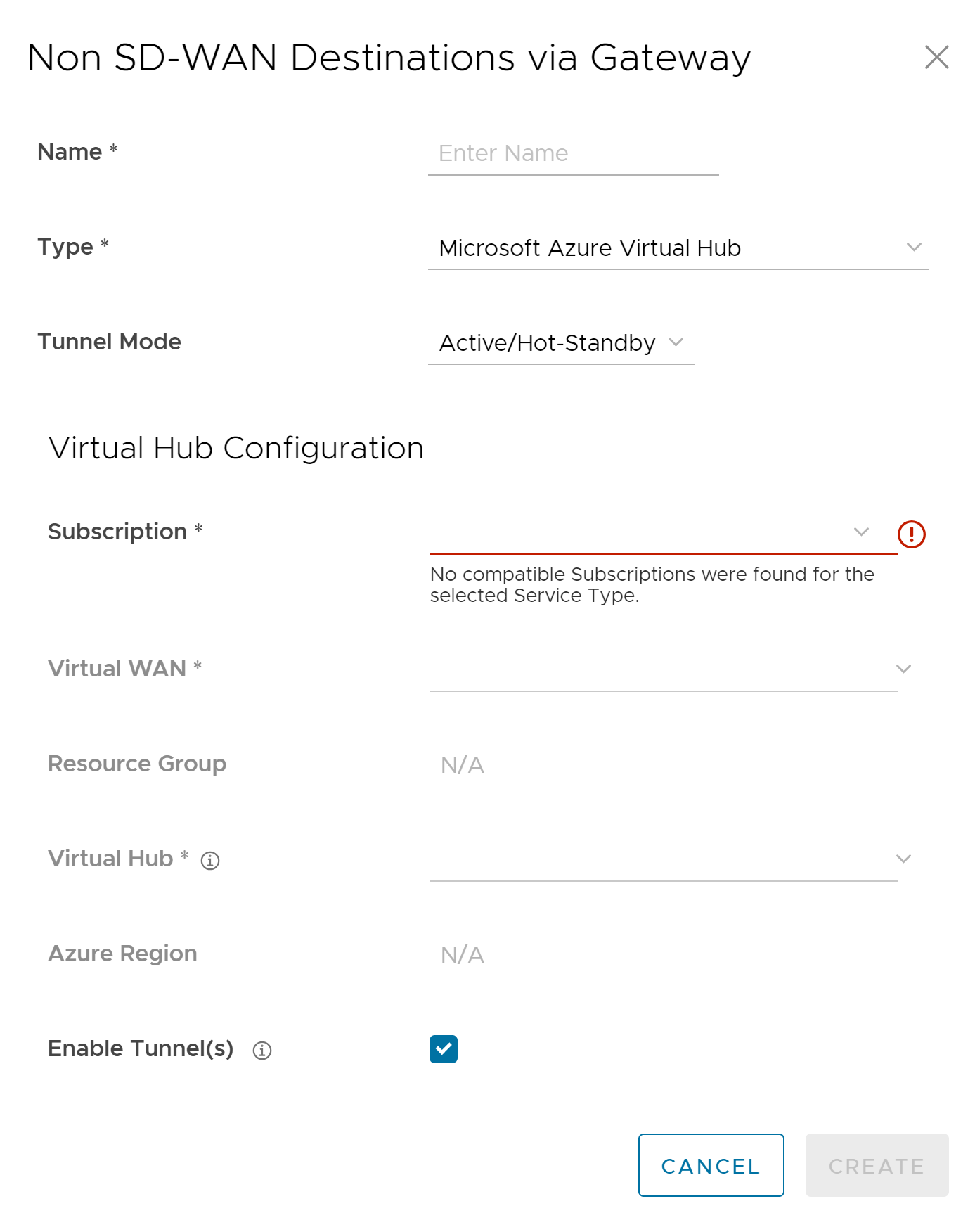
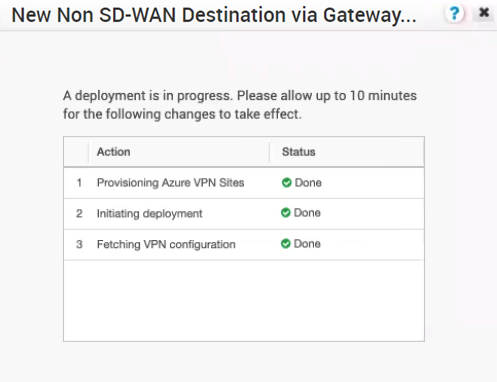
Follow the below steps to configure a Non SD-WAN Destination of type Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub in the SASE Orchestrator.
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have configured a Cloud subscription. For steps, see Configure API Credentials.
- Ensure you have created Virtual WAN and Hubs in Azure. For steps, see Configure Azure Virtual WAN for Branch-to-Azure VPN Connectivity.
Procedure
What to do next
- Associate the Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination to a Profile to establish a tunnel between a branch and Azure Virtual Hub. For more information, see Associate a Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination to an SD-WAN Profile.
- You must add SD-WAN routes into Azure network manually. For more information, see Edit a VPN Site.
- After associating a Profile to the Microsoft Azure Non SD-WAN Destination, you can return to the Non SD-WAN Destinations via Gateway section by navigating to , and then configure the BGP settings for the Non SD-WAN Destination. Scroll to the name of your Non SD-WAN Destination, and then click the Edit link in the BGP column. For more information, see Configure BGP Over IPsec from Gateways.
- In the Non SD-WAN Destinations via Gateway area, click the Edit link in the BFD column for a Non SD-WAN Destination, to configure the BFD settings. For more information, see Configure BFD for Gateways.
For information about Azure Virtual WAN Gateway Automation, see Configure SASE Orchestrator for Azure Virtual WAN IPsec Automation from SD-WAN Gateway.