This topic tells you how to enable service-gateway access.
Service-gateway access enables external clients to connect to a MySQL service. The clients are typically apps running external to the foundation, apps on a different foundation, and management tools such as MySQL Workbench.
For a more detailed overview, see About Service-Gateway access.
To enable service-gateway access for an on-demand offering:
- Activate TCP routing using the TAS for VMs tile.
- Configure the firewall to allow incoming traffic to the TCP router.
- Configure the load balancer in the IaaS to redirect traffic to the TCP router.
- Create a DNS record that maps to the load balancer.
- Activate service-gateway access.
VMware recommends that you configure Transport Layer Security (TLS) alongside service-gateway access to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. For instructions on how to configure TLS, see Configure security.
Activate TCP Routing using the TAS for VMs tile
TCP routing is deactivated by default. To activate TCP routing:
- Go to the Networking pane of the TAS for VMs tile.
- Under Enable TCP requests to apps through specific ports on the TCP router, select Enable TCP routing.
- For TCP routing ports, enter one or more ports to which the load balancer forwards requests. For example,
1024for a single port or1024–1123for a range of ports. - Go back to Ops Manager Installation Dashboard > Review Pending Changes.
- Click Apply Changes for the TAS for VMs tile to create the TCP router.
- From the status tab of the TAS for VMs tile, record the cloud identity (CID) of the TCP router.
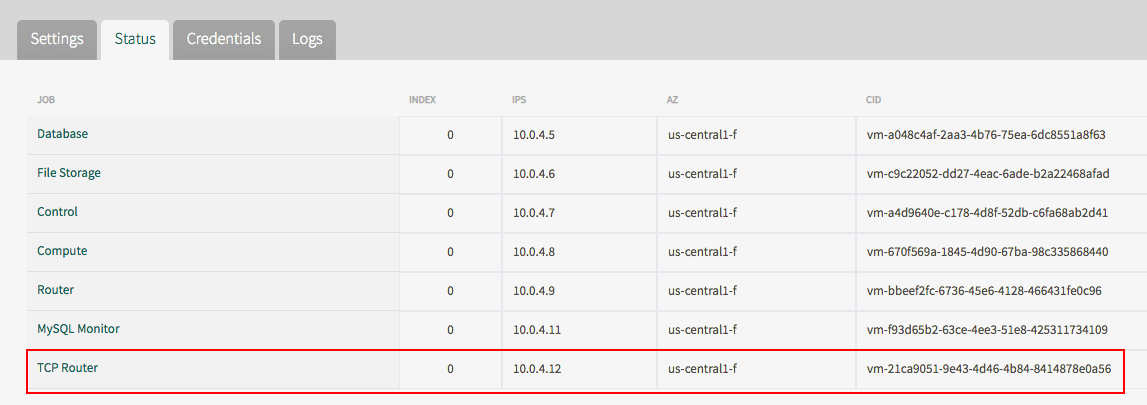
<a href="./images/TCP-router-CID.png" target="_blank" aria-hidden="true">View a larger version of this image</a>
Configure the firewall to allow incoming traffic to the TCP Router
These are the steps you take to allow traffic to the TCP router depend on your IaaS:
-
Allow incoming traffic to the TCP router VM created in Activate TCP Routing using the TAS for VMs tile.
For more detailed information, see the documentation for your IaaS.
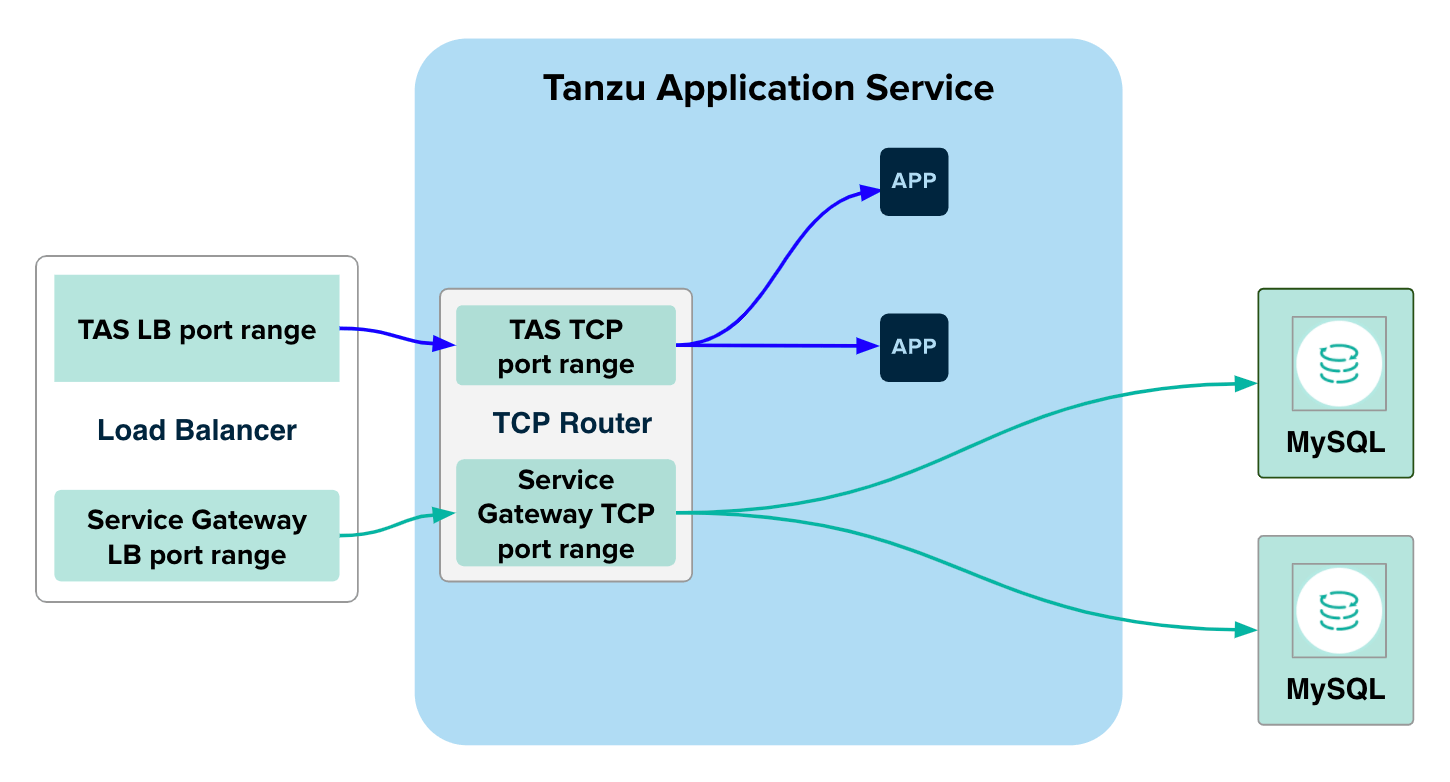
Configure the Load Balancer in the IaaS to redirect traffic to the TCP Router
To configure the load balancer:
- Use the IaaS console and the CID that you recorded earlier to find the VM that runs the TCP router.
- Create an external TCP load balancer that points to the VM running the TCP router.
-
Configure a distinct external port range that does not overlap with any of the following:
- The TCP networking port or port range that you configured in Activate TCP Routing using the TAS for VMs tile.
- The port range configured for service-gateway access for other service tiles, such as VMware Tanzu™ RabbitMQ® for VMs.
For example, if your TCP routing port range is
1024–1123, and ports1124–1223are reserved for Tanzu RabbitMQ service instances, then your load balancer port range for service gateway must not overlap1024-1223.Each VMware Tanzu for MySQL service instance using service-gateway access requires a unique port. Ensure that the port range configured has enough capacity to accommodate all the service instances that you need. The start port and the end port are both inclusive.
-
Record this port range.
Create a DNS record that maps to the Load Balancer
To create a DNS record and prepare to map it:
- Following the documentation for your IaaS, create a new DNS record of type A that maps to the external IP address of the load balancer created in Configure the Load Balancer in the IaaS to redirect traffic to the TCP Router.
- Record the domain used for this DNS record.
Enable Service-Gateway access
When service-gateway access is activated, all developers have the ability to create a service instance that is available to apps outside the foundation.
For VMware Tanzu for MySQL, service-gateway access is enabled globally. Access is not tied to certain service plans as in Tanzu RabbitMQ.
To configure service-gateway access for the foundation:
-
Go to the Settings pane in the VMware Tanzu for MySQL tile.
-
Under Enable off-platform access of MySQL service instances, click Enabled.
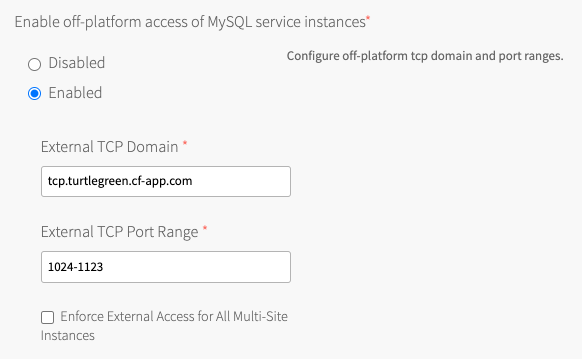
This activates the feature and makes the **External TCP Domain**, **External TCP Port Range**, and **Enable External Access for All Multi-Site Instances** fields visible.
-
Configure the fields as follows:
Field Instructions External TCP Domain Set this to the DNS entry for the external load balancer that you recorded in Create a DNS Record That Maps to the Load Balancer. External TCP Port Range Set this to the range of ports you configured for the external load balancer for MySQL service instances in Configure the Load Balancer in the IaaS to Redirect Traffic to the TCP Router. If service-gateway access is deactivated and then activated again, app developers must create new service keys to obtain a new set of credentials for service-gateway access.
-
Go back to Ops Manager Installation Dashboard > Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply Changes to apply the changes to the VMware Tanzu for MySQL tile.
Deactivate Service-Gateway access
If service-gateway access is deactivated and then activated again, app developers must create new service keys to obtain a new set of credentials for service-gateway access.
To deactivate service-gateway access:
-
Go to the Settings pane in the VMware Tanzu for MySQL tile.
-
Under Enable off-platform access of MySQL service instances, click Disabled.
-
Go back to Ops Manager Installation Dashboard > Review Pending Changes.
-
Click Apply Changes to apply the changes to the VMware Tanzu for MySQL tile.
Developer workflow
For instructions for app developers, see Create a service instance with Service-Gateway access.