Service-gateway access enables external clients that are not on the same foundation as a service instance to connect to the service instance. This is also referred to as off-platform access because the external clients, which are not hosted on the foundation, or platform, can access MySQL service instances that are on the platform.
The external clients are typically apps or management tools such as MySQL Workbench. They can be on another foundation or hosted outside of the foundation.
For related procedures, see:
Use cases for service-gateway access in VMware SQL with MySQL for Tanzu Application Service (VMware Tanzu for MySQL) are:
-
Accessing a MySQL service instance from apps deployed in a different foundation
-
Using MySQL as a service for apps that are not deployed to VMware Tanzu Application Service for VMs (TAS for VMs)
Architecture
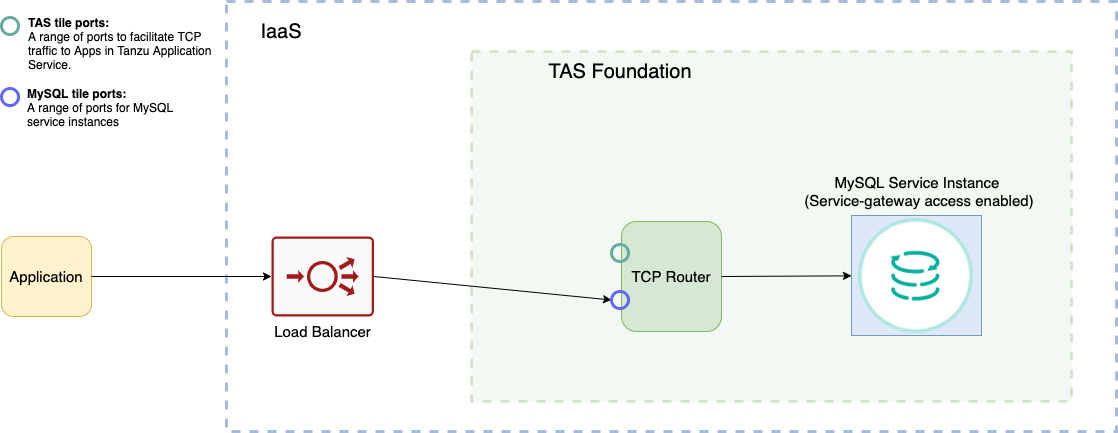
Service-gateway access to MySQL service instances leverages the TCP router in TAS for VMs.
Any database requests that an app makes are forwarded through DNS to a load balancer that can route traffic from outside to inside the foundation. The load balancer opens a range of ports that are reserved for MySQL database traffic. When an app developer creates a service instance with service-gateway access enabled, a port from the range is provisioned for that service instance. The load balancer then forwards the requests for this MySQL service instance to the TCP router. The TCP router internally load balances between the MySQL service instance nodes.
The following diagram shows how the traffic is routed from apps to the MySQL service instance nodes in this case. Apps that are hosted outside the foundation and apps that are hosted on different foundations, use this same route to access the service instance. Apps running on the same foundation connect directly to the service instance without going through the load balancer or router.