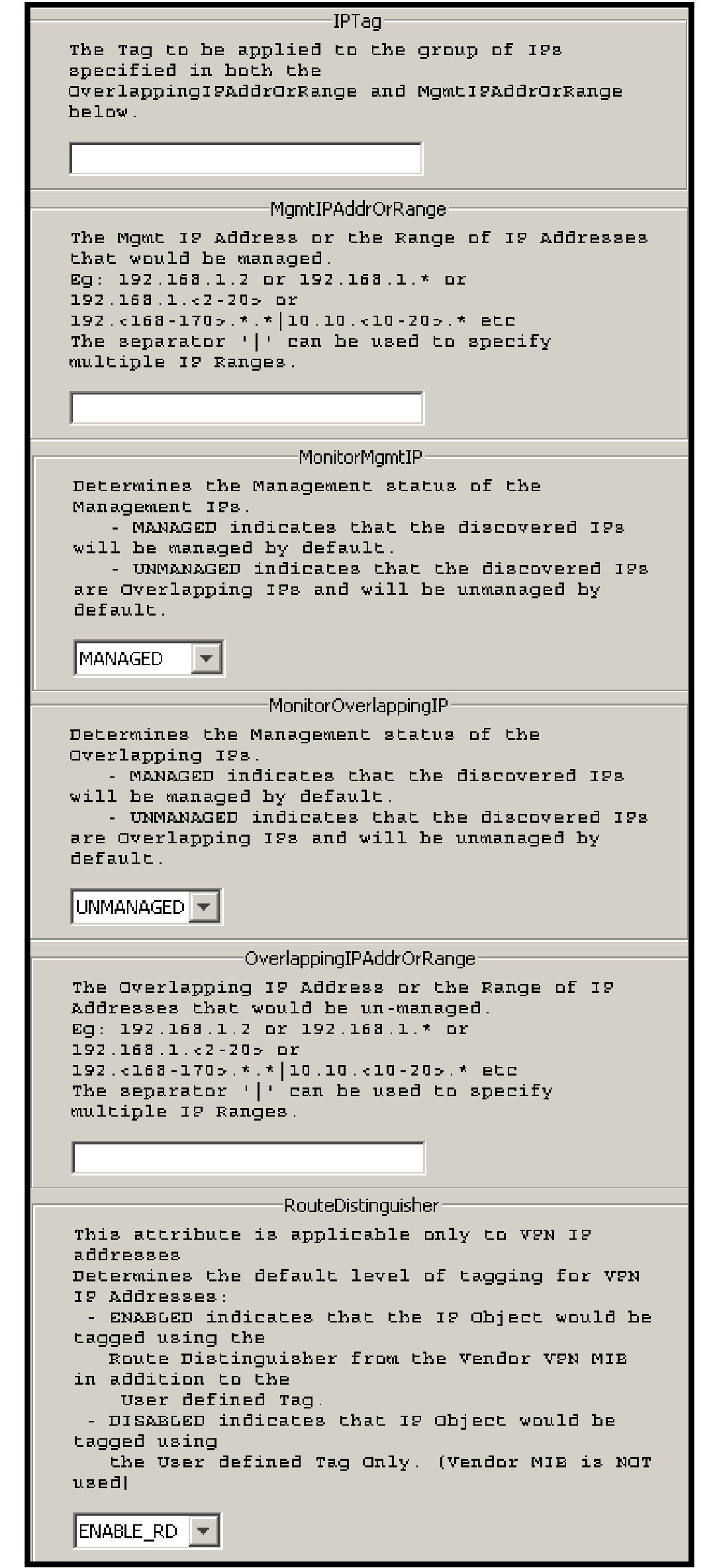
A single default tagging setting named IP Tagging Policy is provided by the IP Availability Manager. The IP Tagging Policy setting configures the IP tagging for a system. Default values for the IP Tagging Policy setting lists the IP Tagging Policy setting parameters, and Parameters of default setting IP Tagging Policy shown in a single view shows all of the parameters in a single view.
| Parameter |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| IPTag |
String of unspecified length Default: Null string (empty) |
Specifies the name to be assigned to this tag. This tag will be applied to the IP addresses falling within the ranges that are specified for the OverlappingIPAddrOrRange and MgmtIPAddrOrRange parameters. |
| MgmtIPAddrOrRange |
String of unspecified length Default: Null string (empty) |
Specifies the IP address or range of IP addresses to be managed by default. Use the pattern matching criteria in Chapter 9, “Wildcard Patterns,” For example:
The pipe ( | ) separator can be used to specify multiple IP ranges. |
| MonitorMgmtIP |
MANAGED,UNMANAGED Default: MANAGED |
Determines the management status to be assigned to the IP addresses falling within the range of the MgmtIPAddrOrRange parameter:
|
| MonitorOverlappingIP |
MANAGED,UNMANAGED Default: UNMANAGED |
Determines the management status to be assigned to the IP addresses falling within the range of the OverlappingIPAddrOrRange parameter:
|
| OverlappingIPAddrOrRange |
String of unspecified length Default: Null string (empty) |
Specifies the IP address or range of IP addresses to be unmanaged by default. Use the pattern matching criteria in Chapter 9, “Wildcard Patterns,” For example:
The pipe ( | ) separator can be used to specify multiple IP ranges. |
| RouteDistinguisher |
ENABLE_RD,DISABLE_RD Default: ENABLE_RD |
Determines the level of tagging for VPN-IP (VRF IP) addresses:
|