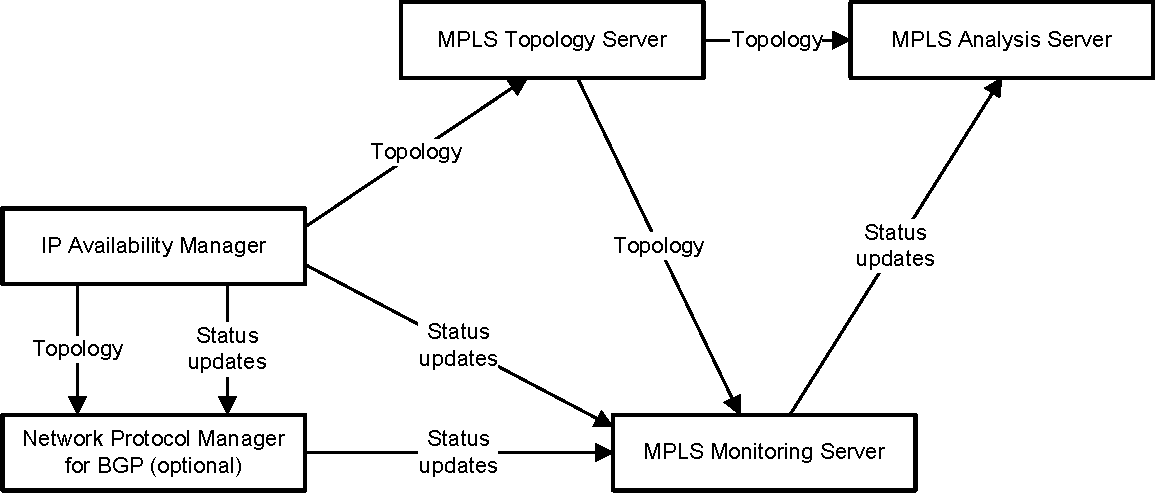
Topology and status transfer between domains in an MPLS Manager deployment shows the communication links between the MPLS component servers, themselves, and between the MPLS component servers and an IP Availability Manager source. Network Protocol Manager for BGP is included in the deployment only if the MPLS-BGP cross-domain correlation feature is enabled.
In general, an VMware Smart Assurance application, such as an MPLS component server, imports topology and status information from another VMware Smart Assurance application by using internal programs called data exchange adapters (DXAs) and remote repository (proxy) accessors. DXA operation and remote repository accessor operation are shown in DXA operation and Remote repository accessor operation.
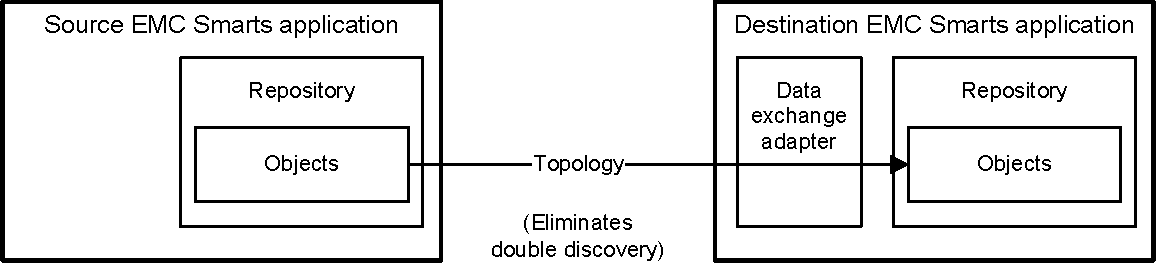
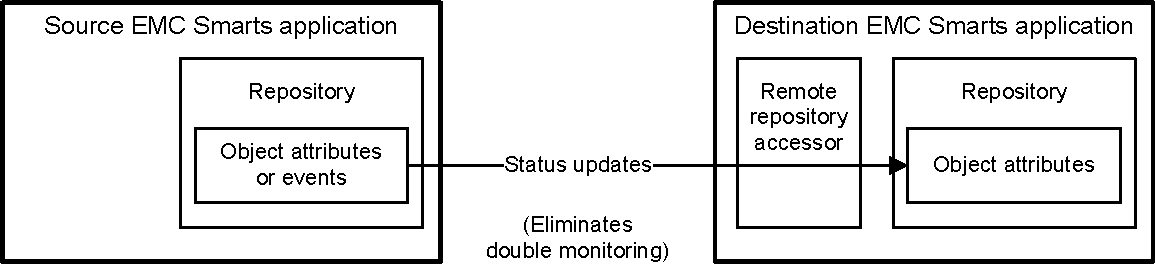
In order for a destination VMware Smart Assurance application to import topology, status, or both from a source VMware Smart Assurance application, all that is required is to send an “add source” request to the destination application to announce the name of the source application.
Three “add source” requests are required to set up the communication links in an MPLS Manager deployment:
-
Send an “add source” request to the MPLS Topology Server to announce the names of the IP Availability Manager sources.
-
Send an “add source” request to the MPLS Monitoring Server to announce the name of the MPLS Topology Server source.
-
Send an “add source” request to the MPLS Analysis Server to announce the name of the MPLS Topology Server source.
Once the MPLS servers know the names of their sources, they consult the VMware Smart Assurance Broker for the deployment and establish connections to their respective sources.