As indicated in SNMP-polling and CLI-polling configuration and operation, Network Protocol Manager uses SNMP polling and CLI polling to monitor the managed network. The monitoring is controlled by polling-related and threshold-related objects that are created for Network Protocol Manager through the Polling and Thresholds Console.
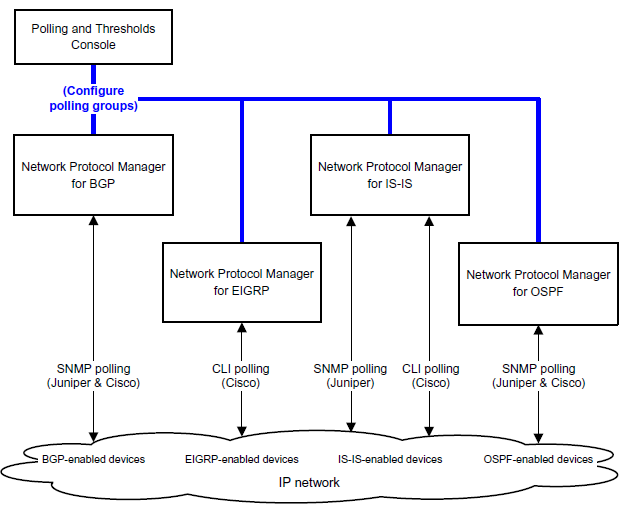
Network Protocol Manager monitors the health of the network by periodically sending SNMP polls or CLI polls to the routing-enabled devices to gather status information. The polled status information, in addition to the received BGP and OSPF trap messages, received BGP and OSPF syslog messages, and received IP Availability Manager status updates, serves as input to the correlation analysis function of Network Protocol Manager.
Appendix E, SNMP Poller, describes SNMP polling for correlation analysis.
The execution of SNMP polling requires SNMP read credentials, and the execution of CLI polling requires CLI login credentials. The SNMPv1, v2c, or v3 read credentials for a discovered device are stored in the attributes of the SNMPAgent object that is created for the device’s SNMP agent. The CLI login credentials for a discovered device are stored in a CLI device-access object. Network Protocol Manager imports SNMPAgent and CLI device-access objects from IP Availability Manager.