VoIP Availability Manageruses instances of certain classes modeled to create within its repository data model representations of the discovered VoIP topology.
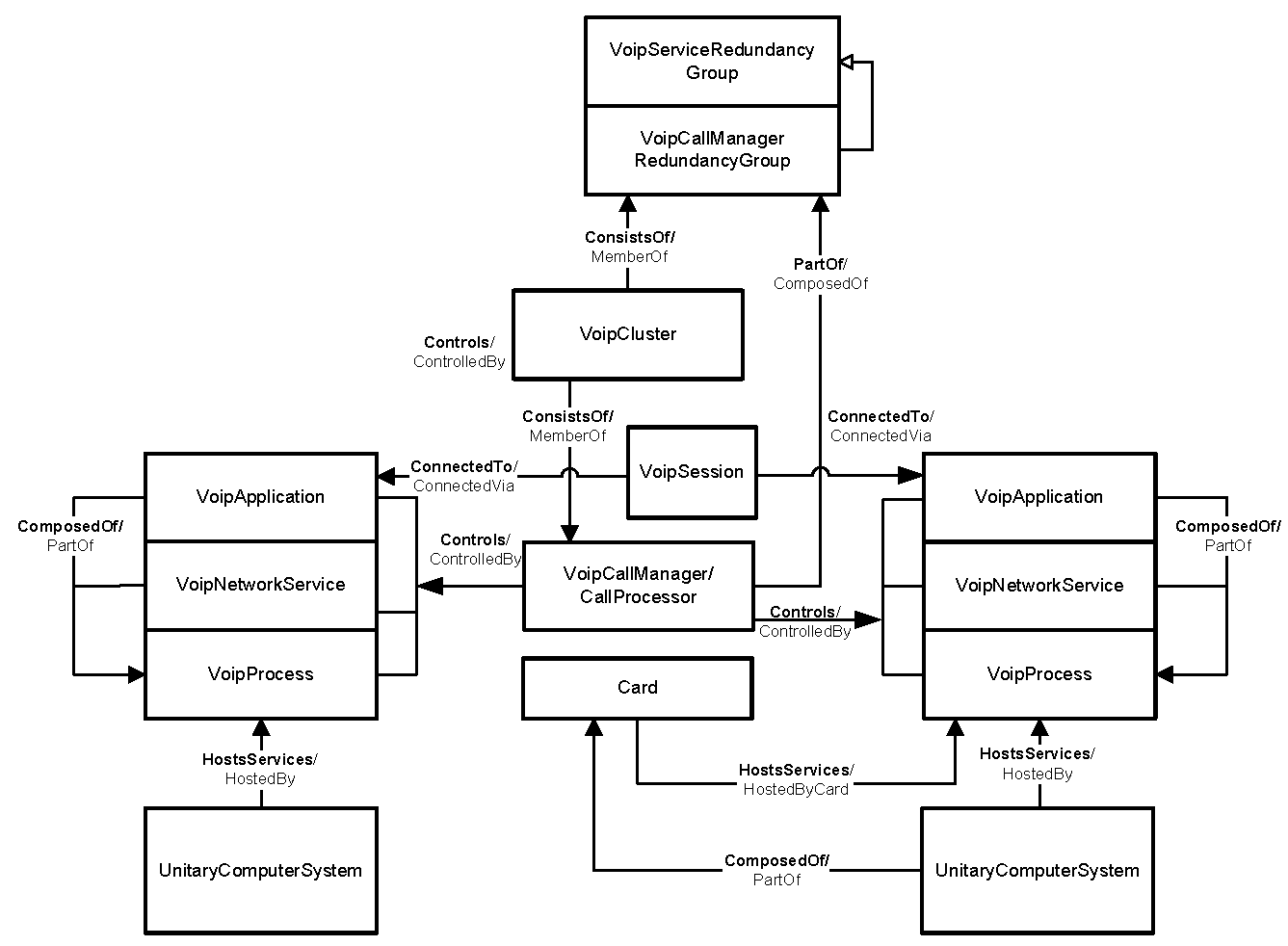
Summary of VoIP Service management modelillustrates a summary of the service management model. In the figure, a VoipSession can be between two call managers, between a ConvergedCallManager and a GatewayService, and so on.
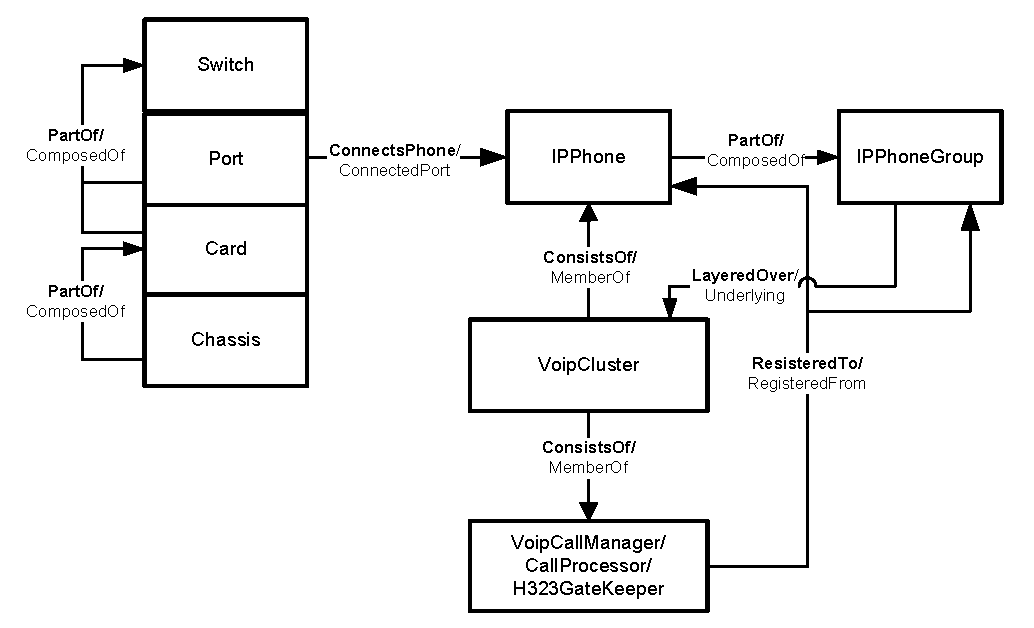
VoIP IP Phone management modelillustrates the IP phone management model. In the figure, an IP phone or an IP phone group can register to an instance of VoipService. A VoipService instance can be: a call manager, call processor, H323Gatekeeper, signaling service, or a gateway service.
These high-level figures represent managed devices, VoIP objects, and their relationships that are significant to the understanding of each respective model.
For class descriptions, consult Complete list of classes in VoIP data model.
VMware Smart Assurance VoIP Availability Manager Discovery Guidedescribes how the topology objects are discovered and provides additional model information.
| Class name |
Description |
Vendor applicability |
|---|---|---|
| Devices |
||
| Host |
A general purpose computer, such as a workstation or server system. |
All |
| CallServer |
A system that hosts the Call Manager application for a VoIP network. |
Avaya, Nortel |
| MediaGateway |
A system that hosts the media server and gateway applications for a VoIP network. |
Avaya |
| Node |
A system that is monitored using generic network management instrumentation. Nodes are probed for standard MIB-II information, but are not probed for enterprise-specific information such as system resources. |
All |
| Router |
A system or, in some cases, software in a computer that determines the next network point to which a packet should be forwarded as it travels toward its destination. |
All |
| Switch |
A system that switches packets, typically at wire speeds, between physically separate network segments. |
All |
| Collections |
||
| PortNetwork |
A collection of media-gateway port cards that terminate phones and trunks. |
Avaya |
| VoipCluster |
A collection of Call Managers that share a common database and provide the VoIP application and network services for an enterprise VoIP system. |
All |
| Physical elements |
||
| Card |
A physical container that typically resides in a chassis. VoIP Availability Manageris able to discover cards related to IP phones. VoIP Availability Manageralso imports Avaya cards that are discovered by IP Availability Manager. |
All |
| IPPhone |
A physical instrument that acts as a telephone using Voice over IP technology. An IP phone can transmit audio-only information or video and audio information. |
All |
| Port |
A place for being physically connected to some other device, usually with a socket and plug. Examples are: switch port or VLAN. VoIP Availability Manageris able to discover cards related to IP phones. |
All |
| VoiceMailbox |
A personal voice mailbox that stores messages for an individual owner or a general delivery mailbox that distributes broadcast messages to a list of individuals. |
Cisco |
| Logical elements |
||
| CallManagerData |
A list of data, provided to a Call Manager, that contains information about the registered, rejected, and unregistered devices for the Call Manager. |
Cisco |
| IPPhoneGroup |
A group of IP phones. IP phone groups correspond to topological objects that are vendor-specific:
|
All |
| MediaResourceAggregate (available only if VoIP Performance Manageris integrated with VoIP Availability Manager) |
A summary of performance data for a specific type of registered media device, where type is one of the following values:
VMware Smart Assurance VoIP Management Suite Overview and Integration Guideprovides complete information about the MediaResourceAggregate class. |
Cisco |
| VoipEndpoint |
A logical VoIP endpoint. |
Cisco |
| Applications |
||
| CTIService |
A Computer Telephony Integrated application that integrates voice and data between the Call Manager and the business application environment. Examples include the delivery of Caller ID information using a Personal Computer, and the ability to access voice mail using the Personal Computer. |
Cisco |
| VoiceMailApplication |
An application that provides a voice mail service for Cisco Unity, Cisco Unity Express, and Cisco Unity Connection devices. |
All |
| VoiceMailService |
An application that answers calls and stores and manages voice messages for individual users. |
Cisco |
| VoipApplication |
An application that provides an end-user service, such as a service represented by the one of the classes that follow. A discovered application other than CTI or voice mail is represented as an instance of the VoipApplication class. An application may run as multiple processes on its host. For a multiple-process application, VoIP Availability Managerdiscovers the application by discovering its processes, and then creates a ComposedOf relationship between the application and each of the discovered processes. |
All |
| Network services |
||
| CallProcessor |
A service that provides light weight call processing, call control, transfer, and call routing functions to local media gateways during a primary Call Manager server failover.
Note:
For example, a discovered instance of the network service provided by the Cisco Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) or Cisco CallManager Express (CCME) is modeled as an instance of the CallProcessor class. |
Cisco |
| CallManager |
A Call Manager application representing a Cisco CallManager, a Cisco Unified CallManager, a Cisco Unified Communications Manager, or a Nortel Call Server. |
Cisco, Nortel |
| ConvergedCallManager |
A Call Manager application representing an Avaya Communication Manager. |
Avaya |
| DS1Service |
A Digital Signal 1 (DS1) card-service application that provides digital connectivity to the PSTN to enable long distance and local telephone service. |
Avaya |
| GatewayService |
An application that converts voice and fax calls between the PSTN and an IP network.
Note:
For example, a discovered instance of the network service provided by the Nortel Voice Gateway Media Card (VGMC) is modeled as an instance of the GatewayService class. |
All |
| H323GateKeeper |
A Control LAN (CLAN) card-service application that provides services such as address translation and network access control for H.323 endpoints. |
Avaya |
| H323Service |
An application that provides signaling using the open industry standard H.323 signaling protocol. |
Cisco |
| IPConnector |
An IP Server Interface (IPSI) card-service application that handles gateway-control and call-control messages between a port network (in a G250/350/700 Media Gateway) and the Call Manager. |
Avaya |
| MediaService |
An application that handles functions such as decoding DTMF tones; transmitting dial tones, busy signals, and announcements; and bridging multiple media streams into a conference. |
Cisco, Nortel |
| MediaProcessor |
A Media Processor (MedPro) card-service application that provides digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital processing services for VoIP calls. |
Avaya |
| SignalingService |
An application that provides an enterprise or industry standard signaling protocol, such as the H.323 protocol represented by the H323Service that follows. A discovered signaling service other than H.323 is represented as an instance of SignalingService. |
Nortel |
| VoiceAnnounceService |
A Voice Announcements over LAN (VAL) card-service that distributes recorded voice announcements over the LAN for scheduled broadcasts. |
Avaya |
| VoipNetworkService |
An application that provides an essential network-connection service, such as a Cisco Publisher or a service. |
Cisco |
| VoipPerformanceManager |
A VoIP Management Suiteproduct that ensures that Avaya, Cisco, and Nortel VoIP networks are delivering an acceptable level of telephony services to the service subscribers. All discovered VoIP Performance Managerapplications are represented as instances of the VoipPerformanceManager class. |
All |
| Software service |
||
| VoipSolution |
A software package providing miscellaneous end-user functionality. For example, contact center applications, etc. |
Cisco |
| Processes |
||
| VoipElement |
A process that is part of a VoIP application or VoIP network service. |
Cisco |
| VoipProcess |
A process that is part of a VoIP application or VoIP network service. All discovered VoIP processes are represented as instances of the VoipProcess class. |
All |
| Service connections |
||
| CallManagerPeerSession |
A logical connection between a Call Manager and a peer Call Manager. This session is established between two Call Managers belonging to the same Call Manager group (redundancy group) as soon as both Call Managers are up and running. |
Cisco |
| H248RegistrationSession |
A logical connection between the Call Manager (ConvergedCallManager) and a gateway (GatewayService) that has registered with the Call Manager, or between an H.323 gatekeeper (H323GateKeeper) and a gateway (GatewayService) that has registered with the H.323 gatekeeper (residing on a CLAN card). This session is established when the gateway registers with the Call Manager or the H.323 gatekeeper. |
Avaya |
| VoIP redundancy groups |
||
| CardServiceRedundancyGroup |
A redundancy group composed of IPConnectors (Avaya IPSI cards) or MediaProcessors (Avaya MedPro cards). Either redundancy group can have only two cards. |
Avaya |
| CallManagerRedundancyGroup |
A redundancy group composed of Call Managers, where:
|
Cisco, Nortel |
| ConvergedCallManagerRedundancyGroup |
A redundancy group composed of Call Managers, where a Call Manager is the Avaya Communication Manager. |
Avaya |
| SignalingRedundancyGroup |
A redundancy group composed of Signaling Servers, each running on its own server system. |
Nortel |
| Business Impact Manager (BIM) (available only if BIM is integrated with VoIP Availability Manager) |
||
| ServiceOffering |
A business service delivered to a set of subscribers (consumers). |
All |
| BusinessProcess |
A service offering that represents functions and operations that support internal business activities and/or other processes (for example, Order Processing and Production Planning in the manufacturing sector). |
All |
| ServiceSubscriber |
A consumer of services provided through a ServiceOffering. |
All |
| Customer |
A service subscriber that represents one or more business enterprises or individuals that maintain a business relationship with an Organization or one of its BusinessUnit elements. |
All |
| Organization |
A service subscriber that represents a business enterprise comprised of one or more business units that engage in one or more lines of business (for example, utilities and service providers). |
All |
| BusinessUnit |
A service subscriber that represents a semi-autonomous division within an organization. A business unit engages in one or more lines of business. |
All |
| LOB |
A service subscriber that represents a division (line of business) within a business unit. A division focuses on specific product markets. |
All |
| Department |
A service subscriber that represents a group within a business unit or LOB. The department engages in business functions which support the business unit or LOB. Examples of a department are Human Resources and Accounting. |
All |