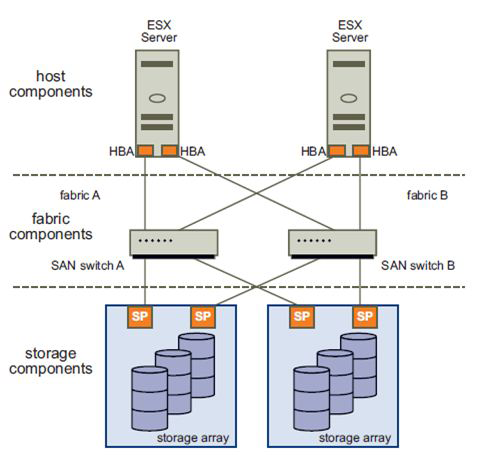
A SAN consists of the following components:
-
SAN switches — SAN switches connect both servers and storage devices. Their functions include:
-
Providing connection points for SAN fabric in the SAN.
-
Providing capabilities to match the number of host SAN connections to the number of connections provided by the storage array.
-
Providing path redundancy, in the event of a path failure, from host server to switch or from storage array to switch.
-
-
SAN fabric — It is the hardware that connects hosts and servers to the storage systems in a SAN using the Fibre Channel protocol.
-
Multiple fabrics may be interconnected in a single SAN, and even a simple SAN may be composed of two fabrics for redundancy.
-
Connections — Host servers and storage systems are connected to the SAN fabric through ports in the fabric.
-
Host Bus Adapter (HBA) — allows a host to connect to a fabric port.
-
Controllers — allows the storage devices to connect to fabric ports.
-
-
PhysicalDisk — A physical disk is a disk in a storage array.
-
SparePhysicalDisk — A spare physical disk in a storage array.
-
RAIDGroup — Logical groups of multiple physical disks.
Depending on your deployment, one or more EMC M&R SolutionPacks are required if you want Server Manager to discovery and monitor storage physical components and to perform detailed SAN correlation. “EMC M&R deployment components” on page 28 provides a list of SolutionPacks. The SolutionPacks associate the physical components with the logical components. If you do not use the SolutionPacks in your deployment, Server Manager discovers and monitors the objects that the vCenter API discovers: The Host bus adapter (HBA), ScsiPath, ScsiLun, and VMware Datastore.
A typical Storage Area Network along with its components are shown in Storage Area Network and its components.
Figure 1. Storage Area Network and its components