Key Concepts for API Auto Registration
This topic explains key concepts you use with API Auto Registration.
API Auto Registration Architecture
You can use the full potential of API Auto Registration by using a distributed environment, like the one in this diagram:
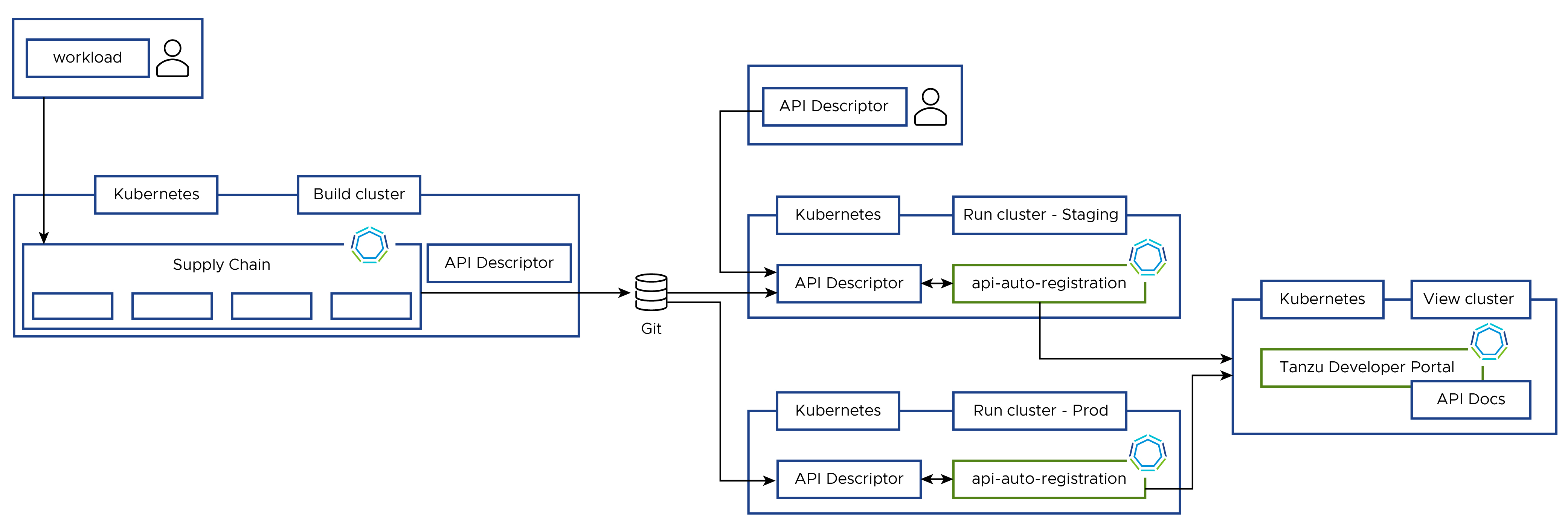
APIDescriptor Custom Resource Explained
To use API Auto Registration, you must create a custom resource of type APIDescriptor. The information from this custom resource is used to construct an API entity in Tanzu Developer Portal (formerly named Tanzu Application Platform GUI).
This custom resource exposes the following text boxes:
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: # name of your APIDescriptor
namespace: # optional namespace of your APIDescriptor
spec:
type: # type of the API spec. oneOf(openapi, grpc, asyncapi, graphql)
description: # description for the API exposed
system: # system that the API is part of
owner: # person/team that owns the API
location:
path: # sub-path where the API spec is available
baseURL: # base URL object where the API spec is available. oneOf(url, ref)
url: # static absolute base URL
ref: # object ref to oneOf(HTTPProxy, Knative Service, Ingress)
apiVersion:
kind:
name:
namespace:
The text boxes cause specific behavior in Tanzu Developer Portal (formerly called Tanzu Application Platform GUI):
- The system and owner are copied to the API entity. You might have to separately create and add the System and Group kind to the catalog.
- Tanzu Developer Portal uses the namespace for the API entity where the APIDescriptor CR is applied. This causes the API entity’s name, system, and owner to all be in that namespace.
- To explicitly use a system or owner in a different namespace, you can specify that in the
system: my-namespace/my-other-systemorowner: my-namespace/my-other-teamtext boxes. - If the system or owner you are trying to link doesn’t have a namespace specified, you can qualify them with the
defaultnamespace. For example,system: default/my-default-system
With an Absolute URL
To create an APIDescriptor with a static baseURL.url, you must apply the following YAML to your cluster.
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: sample-absolute-url
spec:
type: openapi
description: A set of API endpoints to manage the resources within the petclinic app.
system: spring-petclinic
owner: team-petclinic
location:
path: "/v3/api-docs.yaml"
baseURL:
url: https://myservice.com
With an Object Ref
You can use an object reference, instead of hard coding the URL, to point to a HTTPProxy, Knative Service, or Ingress.
With an HTTPPRoxy Object Ref
This section includes an example YAML that points to an HTTPProxy from which the controller extracts the .spec.virtualhost.fqdn as the baseURL.
apiVersion: apis.apps.tanzu.vmware.com/v1alpha1
kind: APIDescriptor
metadata:
name: sample-contour-ref
spec:
type: openapi
description: A set of API endpoints to manage the resources within the petclinic app.
system: spring-petclinic
owner: team-petclinic
location:
path: "/test/openapi"
baseURL:
ref:
apiVersion: projectcontour.io/v1
kind: HTTPProxy
name: my-httpproxy
namespace: my-namespace # optional
With a Knative Service Object Ref
To use a Knative Service, your controller reads the status.url as the baseURL. For example:
# all other fields similar to the above example
baseURL:
ref:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
name: my-knative-service
namespace: my-namespace # optional
With an Ingress Object Ref
To use an Ingress instead, your controller reads the URL from the jsonPath specified. When the jsonPath is left empty, your controller reads the "{.spec.rules[0].host}" as the URL. For example:
# all other fields similar to the above example
baseURL:
ref:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
name: my-ingress
jsonPath: "{.spec.rules[1].host}"
namespace: my-namespace # optional
APIDescriptor Status Fields
When processing an APIDescriptor several fields are added to the status. One of these is conditons, which provide information useful for troubleshooting. The conditions are explained in the Troubleshooting Guide.
In addition to conditions the status contains a couple of other useful fields. The following is a list of these fields with a brief explanation of what they contain.
status:
registeredEntityURL: # Url of the corresponding API Entity in Tanzu Developer Portal
registeredTapUID: # Unique identifier for the corresponding API Entity in Tanzu Developer Portal
resolvedAPISpec: # Full API Spec as retrieved by Api Auto Registration