This topic describes how to install and configure VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition (TKGI) on Azure as a VMware Tanzu Operations Manager (Ops Manager) tile.
Prerequisites
Before performing the procedures in this topic, you must have deployed and configured Ops Manager. For more information, see Azure Prerequisites and Resource Requirements.
If you use an instance of Ops Manager that you configured previously to install other runtimes, perform the following steps before you install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition:
- Navigate to Ops Manager.
- Open the Director Config pane.
- Select the Enable Post Deploy Scripts check box.
- Click the Installation Dashboard link to return to the Installation Dashboard.
- Click Review Pending Changes. Select all products you intend to deploy and review the changes. For more information, see Reviewing Pending Product Changes.
- Click Apply Changes.
Overview
To install and configure TKGI:
- Install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
- Configure Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
- Apply Changes
- Retrieve the TKGI API Endpoint
- Configure an Azure Load Balancer for the TKGI API
- Install the TKGI and Kubernetes CLIs
- Configure Authentication for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
Step 1: Install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
To install Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition, do the following:
- Download the product file from Broadcom Support.
- Navigate to
https://YOUR-OPS-MANAGER-FQDN/in a browser to log in to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard. - Click Import a Product to upload the product file.
- Under Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition in the left column, click the plus sign to add this product to your staging area.
Step 2: Configure Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
To configure TKGI:
-
Click the orange Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile to start the configuration process.

WARNING: When you configure the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile, do not use spaces in any field entries. This includes spaces between characters as well as leading and trailing spaces. If you use a space in any field entry, the deployment of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition fails.
- TKGI API
- Plans
- Kubernetes Cloud Provider
- Networking
- UAA
- (Optional) Host Monitoring
- (Optional) In-Cluster Monitoring
- Tanzu Mission Control
- VMware CEIP
- Errands
- Resource Config
Assign Networks
To configure the networks used by the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition control plane:
-
Click Assign Networks.
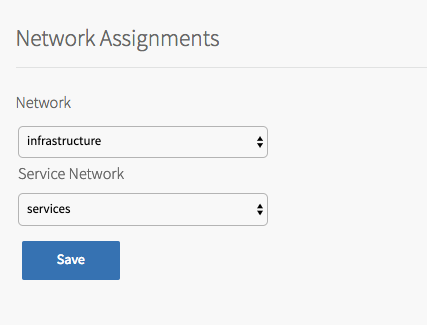
-
Under Network, select the infrastructure subnet that you created for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition component VMs, such as the TKGI API and TKGI Database VMs. For example,
infrastructure. - Under Service Network, select the services subnet that you created for Kubernetes cluster VMs. For example,
services. - Click Save.
TKGI API
Perform the following steps:
-
Click TKGI API.
-
Under Certificate to secure the TKGI API, provide a certificate and private key pair.
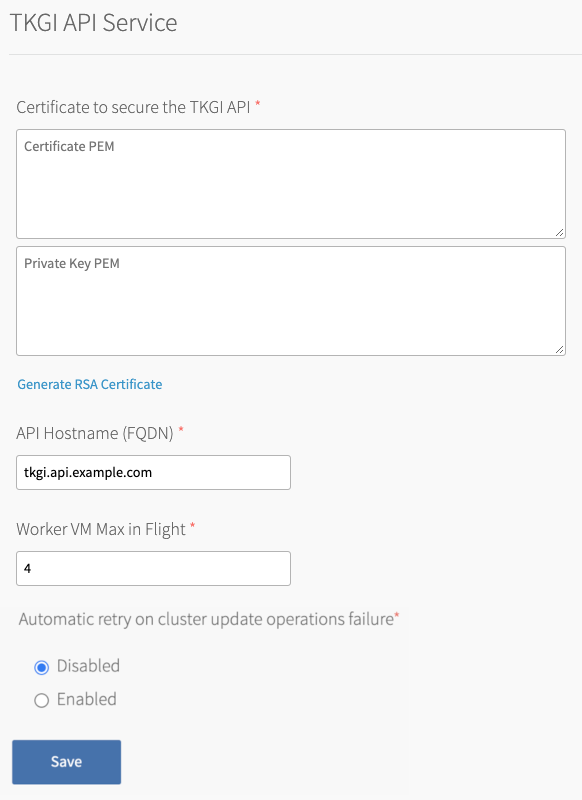
The certificate that you supply must cover the specific subdomain that routes to the TKGI API VM with TLS termination on the ingress. If you use UAA as your OIDC provider, this certificate must be a proper certificate chain and have a SAN field.
Warning: TLS certificates generated for wildcard DNS records only work for a single domain level. For example, a certificate generated for
You can enter your own certificate and private key pair, or have Ops Manager generate one for you.*.tkgi.EXAMPLE.comdoes not permit communication to*.api.tkgi.EXAMPLE.com. If the certificate does not contain the correct FQDN for the TKGI API, calls to the API will fail.
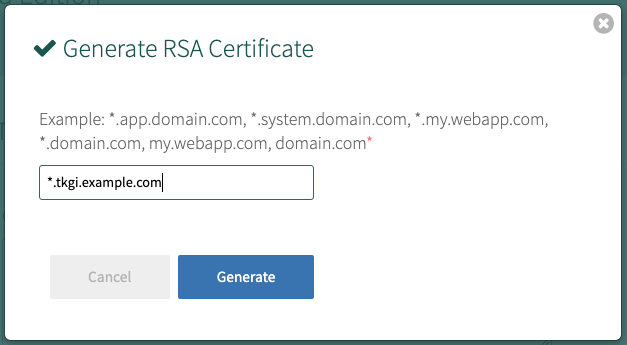
To generate a certificate using Ops Manager:- Click Generate RSA Certificate for a new install or Change to update a previously-generated certificate.
- Enter the domain for your API hostname. This must match the domain you configure under TKGI API > API Hostname (FQDN) below, in the same pane. It can be a standard FQDN or a wildcard domain.
- Click Generate.
- Under API Hostname (FQDN), enter the FQDN that you registered to point to the TKGI API load balancer, such as
api.tkgi.example.com. To retrieve the public IP address or FQDN of the TKGI API load balancer, log in to your IaaS console.Note: The FQDN for the TKGI API must not contain uppercase letters or trailing whitespace.
- Under Worker VM Max in Flight, enter the maximum number of non-canary worker instances to create, update or upgrade in parallel within an availability zone.
This field sets themax_in_flightvariable value. Themax_in_flightsetting limits the number of component instances the TKGI CLI creates or starts simultaneously when runningtkgi create-clusterortkgi update-cluster. By default,max_in_flightis set to4, limiting the TKGI CLI to creating or starting a maximum of four component instances in parallel. - Enable the Automatic retry on cluster update operations failure option to make
tkgi update-clusterretry the cluster update process up to three times if it fails. - Disable the Configure clusters to use private registries option to disable the
--private-registriesoption of thetkgi create-clusterandtkgi update-clustercommands described in Configuring Cluster Access to Private Registries. By default, the ability to configure clusters to use private registries is enabled. - Click Save.
Plans
A plan defines a set of resource types used for deploying a cluster.
Activate a Plan
You must first activate and configure Plan 1, and afterwards you can optionally activate Plan 2 through Plan 10.
To activate and configure a plan, perform the following steps:
- Click the plan that you want to activate.
Note: Plans 11, 12, and 13 support Windows worker-based Kubernetes clusters on vSphere with NSX, and are a beta feature on vSphere with Antrea.
- Select Active to activate the plan and make it available to developers deploying clusters.
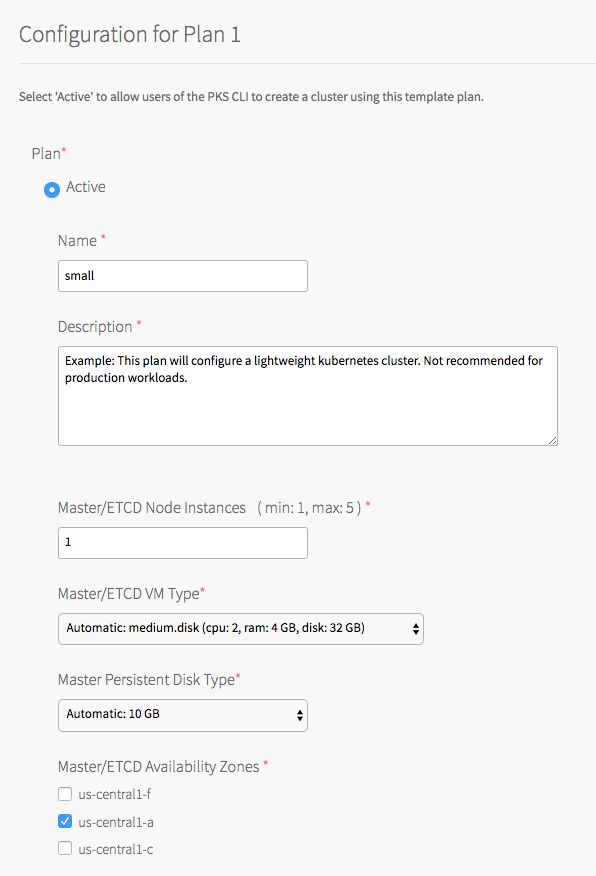
- Under Name, provide a unique name for the plan.
- Under Description, edit the description as needed. The plan description appears in the Services Marketplace, which developers can access by using the TKGI CLI.
- Under Master/ETCD Node Instances, select the default number of Kubernetes control plane/etcd nodes to provision for each cluster. You can enter
1,3, or5.Note: If you deploy a cluster with multiple control plane/etcd node VMs, confirm that you have sufficient hardware to handle the increased load on disk write and network traffic. For more information, see Hardware recommendations in the etcd documentation.
In addition to meeting the hardware requirements for a multi-control plane node cluster, we recommend configuring monitoring for etcd to monitor disk latency, network latency, and other indicators for the health of the cluster. For more information, see Configuring Telegraf in TKGI.WARNING: To change the number of control plane/etcd nodes for a plan, you must ensure that no existing clusters use the plan. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition does not support changing the number of control plane/etcd nodes for plans with existing clusters.
-
Under Master/ETCD VM Type, select the type of VM to use for Kubernetes control plane/etcd nodes. For more information, including control plane node VM customization options, see the Control Plane Node VM Size section of VM Sizing for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Clusters.
-
Under Master Persistent Disk Type, select the size of the persistent disk for the Kubernetes control plane node VM.
-
Under Master/ETCD Availability Zones, select one or more AZs for the Kubernetes clusters deployed by Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition. If you select more than one AZ, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition deploys the control plane VM in the first AZ and the worker VMs across the remaining AZs. If you are using multiple control plane nodes, deploys the control plane and worker VMs across the AZs in round-robin fashion.
Note: Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition does not support changing the AZs of existing control plane nodes.
- Under Maximum number of workers on a cluster, set the maximum number of Kubernetes worker node VMs that Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition can deploy for each cluster. Enter any whole number in this field.
- Under Worker Node Instances, specify the default number of Kubernetes worker nodes the TKGI CLI provisions for each cluster. The Worker Node Instances setting must be less than, or equal to, the Maximum number of workers on a cluster setting.
For high availability, create clusters with a minimum of three worker nodes, or two per AZ if you intend to use PersistentVolumes (PVs). For example, if you deploy across three AZs, you must have six worker nodes. For more information about PVs, see PersistentVolumes in Maintaining Workload Uptime. Provisioning a minimum of three worker nodes, or two nodes per AZ is also recommended for stateless workloads.
For more information about creating clusters, see Creating Clusters.Note: Changing a plan’s Worker Node Instances setting does not alter the number of worker nodes on existing clusters. For information about scaling an existing cluster, see Scale Horizontally by Changing the Number of Worker Nodes Using the TKGI CLI in Scaling Existing Clusters.
- Under Worker VM Type, select the type of VM to use for Kubernetes worker node VMs. For more information, including worker node VM customization options, see Worker Node VM Number and Size in VM Sizing for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Clusters.
Note: Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition requires a Worker VM Type with an ephemeral disk size of 32 GB or more.
-
Under Worker Persistent Disk Type, select the size of the persistent disk for the Kubernetes worker node VMs.
-
Under Worker Availability Zones, select one or more AZs for the Kubernetes worker nodes. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition deploys worker nodes equally across the AZs you select.
-
Under Kubelet customization - system-reserved, enter resource values that Kubelet can use to reserve resources for system daemons. For example,
memory=250Mi, cpu=150m. For more information about system-reserved values, see the Kubernetes documentation.
- Under Kubelet customization - eviction-hard, enter threshold limits that Kubelet can use to evict pods when they exceed the limit. Enter limits in the format
EVICTION-SIGNAL=QUANTITY. For example,memory.available=100Mi, nodefs.available=10%, nodefs.inodesFree=5%. For more information about eviction thresholds, see the Kubernetes documentation.WARNING: Use the Kubelet customization fields with caution. If you enter values that are invalid or that exceed the limits the system supports, Kubelet might fail to start. If Kubelet fails to start, you cannot create clusters.
- Under Errand VM Type, select the size of the VM that contains the errand. The smallest instance possible is sufficient, as the only errand running on this VM is the one that applies the Default Cluster App YAML configuration.
- (Optional) Under (Optional) Add-ons - Use with caution, enter additional YAML configuration to add custom workloads to each cluster in this plan. You can specify multiple files using
---as a separator. For more information, see Adding Custom Linux Workloads. - (Optional) To allow users to create pods with privileged containers, select the Allow Privileged option. For more information, see Pods in the Kubernetes documentation.
- (Optional) Under Node Drain Timeout(mins), enter the timeout in minutes for the node to drain pods. If you set this value to
0, the node drain does not terminate.

-
(Optional) Under Pod Shutdown Grace Period (seconds), enter a timeout in seconds for the node to wait before it forces the pod to terminate. If you set this value to
-1, the default timeout is set to the one specified by the pod. -
(Optional) To configure when the node drains, activate the following:
- Force node to drain even if it has running pods not managed by a ReplicationController, ReplicaSet, Job, DaemonSet or StatefulSet.
- Force node to drain even if it has running DaemonSet-managed pods.
- Force node to drain even if it has running running pods using emptyDir.
- Force node to drain even if pods are still running after timeout.
Warning: If you select Force node to drain even if pods are still running after timeout, the node halts all running workloads on pods. Before enabling this configuration, set Node Drain Timeout to a value greater than
0.For more information about configuring default node drain behavior, see Worker Node Hangs Indefinitely in Troubleshooting.
-
Click Save.
Deactivate a Plan
To deactivate a plan, perform the following steps:
- Click the plan that you want to deactivate.
- Select Inactive.
- Click Save.
Kubernetes Cloud Provider
To configure your Kubernetes cloud provider settings, follow the procedures below:
-
Click Kubernetes Cloud Provider.
-
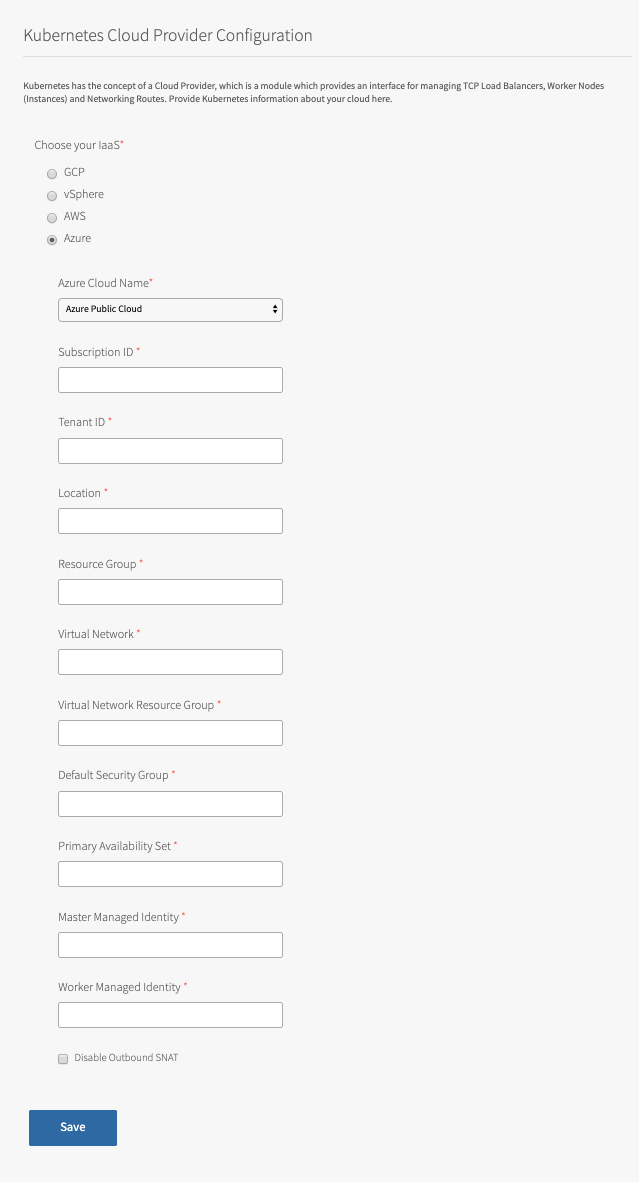
Under Choose your IaaS, select Azure.
-
Under Azure Cloud Name, select the identifier of your Azure environment.
-
Enter Subscription ID. This is the ID of the Azure subscription that the cluster is deployed in.
-
Enter Tenant ID. This is the Azure Active Directory (AAD) tenant ID for the subscription that the cluster is deployed in.
-
Enter Location. This is the location of the resource group that the cluster is deployed in.
-
If you do not already know the valid location value for your resource group, determine it:
- You set the location name in Step 1: Create Network Resources in Deploying Ops Manager on Azure Manually.
- The location name property is a lower-case string without spaces. For example, if your resource group location is
Central US, the location name property value iscentralus. -
To determine the valid location value for your resource group location, list the valid locations:
az account list-locations
-
Enter Location. Enter the valid location value for your resource group location into the Location field.
-
-
Enter Resource Group. This is the name of the resource group that the cluster is deployed in.
-
Enter Virtual Network. This is the name of the virtual network that the cluster is deployed in.
-
Enter Virtual Network Resource Group. This is the name of the resource group that the virtual network is deployed in.
-
Enter Default Security Group. This is the name of the security group attached to the cluster’s subnet.
Note: Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition automatically assigns the default security group to each VM when you create a Kubernetes cluster.
However, on Azure this automatic assignment might not occur. For more information, see Azure Default Security Group Is Not Automatically Assigned to Cluster VMs in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Release Notes.
-
Enter Primary Availability Set. This is the name of the availability set that will be used as the load balancer back end. Locate the name of the availability set within the Azure console.
-
For Master Managed Identity, enter
tkgi-master. You created the managed identity for the control plane nodes in Create the Control Plane Nodes Managed Identity in Creating Managed Identities in Azure for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition. -
For Worker Managed Identity, enter
tkgi-worker. You created the managed identity for the worker nodes in Create the Worker Nodes Managed Identity in Creating Managed Identities in Azure for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition. -
Select Disable Outbound SNAT to deactivate the default outbound SNAT rule for Azure.
-
Click Save.
Networking
To configure networking, do the following:
- Click Networking.
- Under Container Networking Interface, select Antrea.
 Antrea is the Container Networking Interface (CNI) for TKGI v1.20. Flannel CNI is no longer supported. For more information about Flannel CNI removal, see About Switching from the Flannel CNI to the Antrea CNI in the TKGI 1.18 documentation.
Antrea is the Container Networking Interface (CNI) for TKGI v1.20. Flannel CNI is no longer supported. For more information about Flannel CNI removal, see About Switching from the Flannel CNI to the Antrea CNI in the TKGI 1.18 documentation. - (Optional) Enter values for Kubernetes Pod Network CIDR Range and Kubernetes Service Network CIDR Range.
- Ensure that the CIDR ranges do not overlap and have sufficient space for your deployed services.
- Ensure that the CIDR range for the Kubernetes Pod Network CIDR Range is large enough to accommodate the expected maximum number of pods.
-
Under Allow outbound internet access from Kubernetes cluster vms (IaaS-dependent), leave the Enable outbound internet access check box unselected. You must leave this check box unselected due to an incompatibility between the public dynamic IPs provided by BOSH and load balancers on Azure.
-
Click Save.
UAA
To configure the UAA server:
- Click UAA.
-
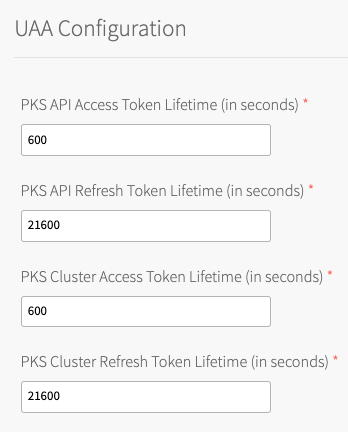
Under TKGI API Access Token Lifetime, enter a time in seconds for the TKGI API access token lifetime. This field defaults to
600.
-
Under TKGI API Refresh Token Lifetime, enter a time in seconds for the TKGI API refresh token lifetime. This field defaults to
21600. - Under TKGI Cluster Access Token Lifetime, enter a time in seconds for the cluster access token lifetime. This field defaults to
600. - Under TKGI Cluster Refresh Token Lifetime, enter a time in seconds for the cluster refresh token lifetime. This field defaults to
21600.Note: VMware recommends using the default UAA token timeout values. By default, access tokens expire after ten minutes and refresh tokens expire after six hours.
- Under Configure created clusters to use UAA as the OIDC provider, select Enabled or Disabled. This is a global default setting for TKGI-provisioned clusters. For more information, see OIDC Provider for Kubernetes Clusters.
To configure Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition to use UAA as the OIDC provider:- Under Configure created clusters to use UAA as the OIDC provider, select Enabled.
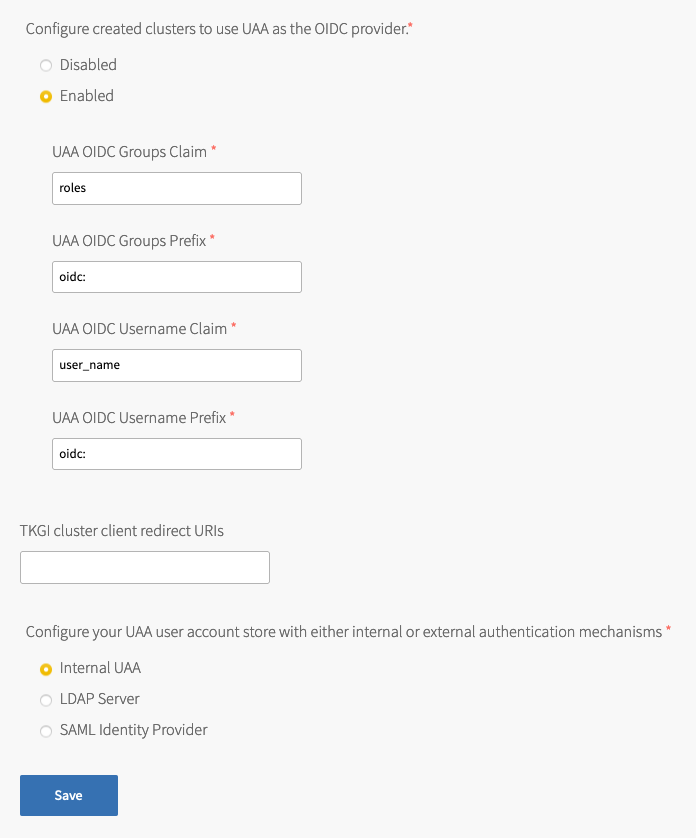
- For UAA OIDC Groups Claim, enter the name of your groups claim. This is used to set a user’s group in the JSON Web Token (JWT) claim. The default value is
roles. - For UAA OIDC Groups Prefix, enter a prefix for your groups claim. This prevents conflicts with existing names. For example, if you enter the prefix
oidc:, UAA creates a group name likeoidc:developers. The default value isoidc:. - For UAA OIDC Username Claim, enter the name of your user name claim. This is used to set a user’s user name in the JWT claim. The default value is
user_name. Depending on your provider, you can enter claims besidesuser_name, likeemailorname. - For UAA OIDC Username Prefix, enter a prefix for your user name claim. This prevents conflicts with existing names. For example, if you enter the prefix
oidc:, UAA creates a user name likeoidc:admin. The default value isoidc:.Warning: VMware recommends adding OIDC prefixes to prevent users and groups from gaining unintended cluster privileges. If you change the above values for a pre-existing Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition installation, you must change any existing role bindings that bind to a user name or group. If you do not change your role bindings, developers cannot access Kubernetes clusters. For instructions, see Managing Cluster Access and Permissions.
- Under Configure created clusters to use UAA as the OIDC provider, select Enabled.
- (Optional) For TKGI cluster client redirect URIs, enter one or more comma-delimited UAA redirect URIs. Configure TKGI cluster client redirect URIs to assign persistent UAA
cluster_clientredirect_uriURIs to your clusters. UAA redirect URIs configured in the TKGI cluster client redirect URIs field persist through cluster updates and TKGI upgrades. - Select one of the following options:
- To use an internal user account store for UAA, select Internal UAA. Click Save and continue to (Optional) Host Monitoring.
- To use LDAP for UAA, select LDAP Server and continue to Connecting Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition to an LDAP Server.
- To use SAML for UAA, select SAML Identity Provider and continue to Connecting Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition to a SAML Identity Provider.
(Optional) Host Monitoring
In Host Monitoring, you can configure monitoring of nodes and VMs using Syslog, or Telegraf.
You can configure one or more of the following:
- Syslog: To configure Syslog, see Syslog below. Syslog forwards log messages from all BOSH-deployed VMs to a syslog endpoint.
- Telegraf: To configure Telegraf, see Configuring Telegraf in TKGI. The Telegraf agent sends metrics from TKGI API, control plane node, and worker node VMs to a monitoring service, such as Wavefront or Datadog.
For more information about these components, see Monitoring TKGI and TKGI-Provisioned Clusters.
Syslog
To configure Syslog for all BOSH-deployed VMs in Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition:
- Click Host Monitoring.
- Under Enable Syslog for TKGI, select Yes.
- Under Address, enter the destination syslog endpoint.
- Under Port, enter the destination syslog port.
- Under Transport Protocol, select a transport protocol for log forwarding.
- (Optional) To enable TLS encryption during log forwarding, complete the following steps:
- Ensure Enable TLS is selected.
Note: Logs might contain sensitive information, such as cloud provider credentials. VMware recommends that you enable TLS encryption for log forwarding.
- Under Permitted Peer, provide the accepted fingerprint (SHA1) or name of remote peer. For example,
*.YOUR-LOGGING-SYSTEM.com. - Under TLS Certificate, provide a TLS certificate for the destination syslog endpoint.
Note: You do not need to provide a new certificate if the TLS certificate for the destination syslog endpoint is signed by a Certificate Authority (CA) in your BOSH certificate store.
- Ensure Enable TLS is selected.
- (Optional) Under Max Message Size, enter a maximum message size for logs that are forwarded to a syslog endpoint. By default, the Max Message Size field is 10,000 characters.
- (Optional) Under Custom Rsyslog Configuration, enter your RSyslog rules configuration using RainerScript syntax. For more information, see RainerScript in the RSyslog documentation. For example RSyslog rule configurations, see Example Custom Rules in the Syslog BOSH GitHub repository.
- Click Save.
(Optional) In-Cluster Monitoring
In In-Cluster Monitoring, you can configure one or more observability components and integrations that run in Kubernetes clusters and capture logs and metrics about your workloads. For more information, see Monitoring Workers and Workloads.
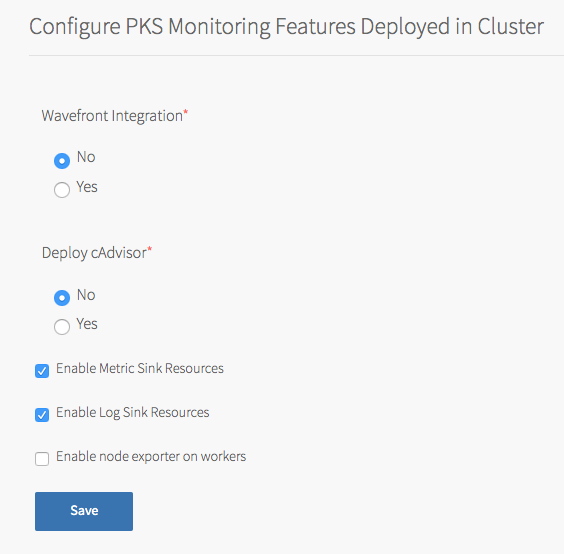
To configure in-cluster monitoring:
- To configure Wavefront, see Wavefront.
- To configure cAdvisor, see cAdvisor.
-
To configure sink resources, see:
You can enable both log and metric sink resources or only one of them.
Wavefront
You can monitor Kubernetes clusters and pods metrics externally using the integration with Wavefront by VMware.
NoteWavefront integration in TKGI has been deprecated.
Prerequisites
Before you configure Wavefront integration, you must have an active Wavefront account and access to a Wavefront instance. You provide your Wavefront access token during configuration. For additional information, see the Wavefront documentation.
To use Wavefront with Windows worker-based clusters, developers must install Wavefront to their clusters manually, using Helm.
Procedure
To enable and configure Wavefront monitoring:
- In the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile, select In-Cluster Monitoring.
- Under Wavefront Integration, select Yes.
- Under Wavefront URL, enter the URL of your Wavefront subscription. For example:
https://try.wavefront.com/api - Under Wavefront Access Token, enter the API token for your Wavefront subscription.
- (Optional) For installations that require a proxy server for outbound Internet access, enable access by entering values for HTTP Proxy Host, HTTP Proxy Port, Proxy username, and Proxy password.
- Click Save.
The Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile does not validate your Wavefront configuration settings. To verify your setup, look for cluster and pod metrics in Wavefront.
cAdvisor
cAdvisor is an open source tool for monitoring, analyzing, and exposing Kubernetes container resource usage and performance statistics.
To deploy a cAdvisor container:
- Select In-Cluster Monitoring.
- Under Deploy cAdvisor, select Yes.
- Click Save.
Note: For information about configuring cAdvisor to monitor your running Kubernetes containers, see cAdvisor in the cAdvisor GitHub repository. For general information about Kubernetes cluster monitoring, see Tools for Monitoring Resources in the Kubernetes documentation.
Metric Sink Resources
You can configure TKGI-provisioned clusters to send Kubernetes node metrics and pod metrics to metric sinks. For more information about metric sink resources and what to do after you enable them in the tile, see Sink Resources in Monitoring Workers and Workloads.
To enable clusters to send Kubernetes node metrics and pod metrics to metric sinks:
- In In-Cluster Monitoring, select Enable Metric Sink Resources. If you enable this check box, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition deploys Telegraf as a
DaemonSet, a pod that runs on each worker node in all your Kubernetes clusters. -
(Optional) To enable Node Exporter to send worker node metrics to metric sinks of kind
ClusterMetricSink, select Enable node exporter on workers. If you enable this check box, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition deploys Node Exporter as aDaemonSet, a pod that runs on each worker node in all your Kubernetes clusters.For instructions on how to create a metric sink of kind
ClusterMetricSinkfor Node Exporter metrics, see Create a ClusterMetricSink Resource for Node Exporter Metrics in Creating and Managing Sink Resources. - Click Save.
Log Sink Resources
You can configure TKGI-provisioned clusters to send Kubernetes API events and pod logs to log sinks. For more information about log sink resources and what to do after you enable them in the tile, see Sink Resources in Monitoring Workers and Workloads.
To enable clusters to send Kubernetes API events and pod logs to log sinks:
- Select Enable Log Sink Resources. If you enable this check box, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition deploys Fluent Bit as a
DaemonSet, a pod that runs on each worker node in all your Kubernetes clusters. -
(Optional) To increase the Fluent Bit Pod memory limit, enter a value greater than 100 in the Fluent-bit container memory limit(Mi) field.
-
Click Save.
Tanzu Mission Control
Tanzu Mission Control integration lets you monitor and manage Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition clusters from the Tanzu Mission Control console, which makes the Tanzu Mission Control console a single point of control for all Kubernetes clusters. For more information about Tanzu Mission Control, see the VMware Tanzu Mission Control home page.
To integrate Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition with Tanzu Mission Control:
-
Confirm that the TKGI API VM has internet access and can connect to
cna.tmc.cloud.vmware.comand the other outbound URLs listed in the What Happens When You Attach a Cluster section of the Tanzu Mission Control Product documentation. -
Navigate to the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile > the Tanzu Mission Control pane and select Yes under Tanzu Mission Control Integration.
-
Configure the fields below:
- Tanzu Mission Control URL: Enter the Org URL of your Tanzu Mission Control subscription, without a trailing slash (
/). For example,YOUR-ORG.tmc.cloud.vmware.com. - VMware Cloud Services API token: Enter your API token to authenticate with VMware Cloud Services APIs. You can retrieve this token by logging in to VMware Cloud Services and viewing your account information.
-
Tanzu Mission Control Cluster Group: Enter the name of a Tanzu Mission Control cluster group.
The name can bedefaultor another value, depending on your role and access policy:Org Memberusers in VMware cloud services have aservice.adminrole in Tanzu Mission Control. These users:- By default, can create and attach clusters only in the
defaultcluster group. - Can create and attach clusters to other cluster groups after an
organization.adminuser grants them theclustergroup.adminorclustergroup.editrole for those groups.
- By default, can create and attach clusters only in the
-
Org Ownerusers in VMware cloud services haveorganization.adminpermissions in Tanzu Mission Control. These users:- Can create cluster groups.
- Can grant
clustergrouproles toservice.adminusers through the Tanzu Mission Control Access Policy view.
For more information about role and access policy, see Access Control in the VMware Tanzu Mission Control Product documentation.
- Tanzu Mission Control Cluster Name Prefix: Enter a name prefix for identifying the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition clusters in Tanzu Mission Control.
- Tanzu Mission Control URL: Enter the Org URL of your Tanzu Mission Control subscription, without a trailing slash (
- Click Save.
Warning: After the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile is deployed with a configured cluster group, the cluster group cannot be updated.
Note: When you upgrade your Kubernetes clusters and have Tanzu Mission Control integration enabled, existing clusters will be attached to Tanzu Mission Control.
VMware CEIP
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition-provisioned clusters send usage data to the TKGI control plane for storage. The VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) provides the option to also send the cluster usage data to VMware to improve customer experience.
To configure Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition CEIP Program settings:
- Click CEIP.
- Review the information about the CEIP.
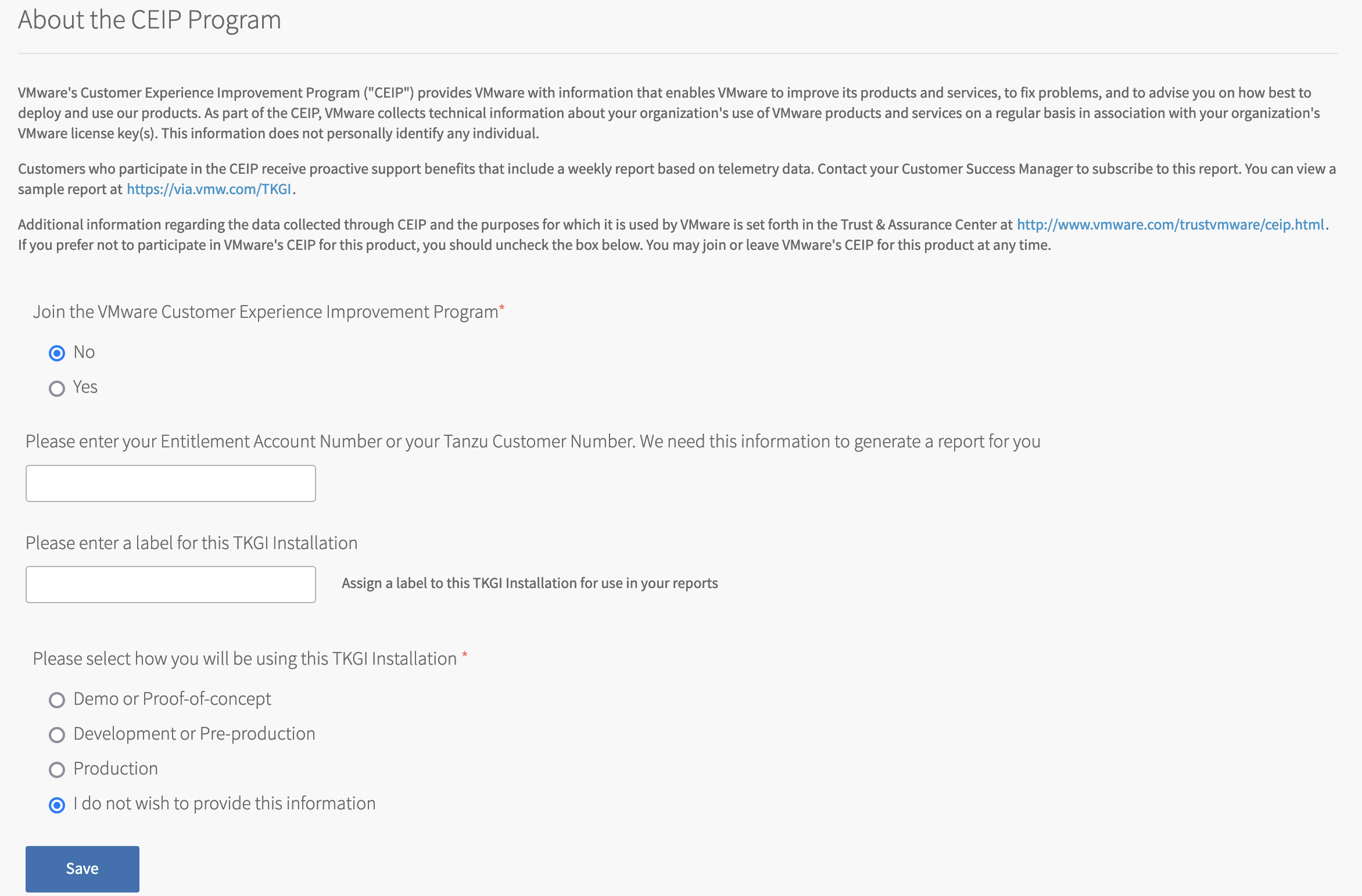
View a larger version of this image. - If you wish to participate in CEIP, select Yes. Otherwise, select No.
- If you selected the Yes, complete the following:
- (Optional) Enter your entitlement account number or Tanzu customer number. If you are a VMware customer, you can find your entitlement account number in your Account Summary on my.vmware.com. If you are a Pivotal customer, you can find your Pivotal Customer Number in your Pivotal Order Confirmation email.
- (Optional) Enter a descriptive name for your TKGI installation. The label you assign to this installation will be used in CEIP reports to identify the environment.
- To provide information about the purpose for this installation, select an option.

- Click Save.
Errands
Errands are scripts that run at designated points during an installation.
To configure which post-deploy and pre-delete errands run for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition:
- Make a selection in the dropdown next to each errand.
Note: We recommend that you use the default settings for all errands except for the Run smoke tests errand.
-
(Optional) Set the Run smoke tests errand to On.
The Smoke Test errand smoke tests the TKGI upgrade by creating and deleting a test Kubernetes cluster. If test cluster creation or deletion fails, the errand fails, and the installation of the TKGI tile halts.
The errand uses the TKGI CLI to create the test cluster configured using the configuration settings on the TKGI tile.
-
(Optional) To ensure that all of your cluster VMs are patched, configure the Upgrade all clusters errand errand to On.
Updating the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile with a new Linux stemcell and the Upgrade all clusters errand enabled triggers the rolling of every Linux VM in each Kubernetes cluster. Similarly, updating the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile with a new Windows stemcell triggers the rolling of every Windows VM in your Kubernetes clusters.
Note: VMware recommends that you review the Broadcom Support metadata and confirm stemcell version compatibility before using the Broadcom Support APIs to update the stemcells in your automated pipeline. For more information, see the API reference.
Resource Config
To modify the resource configuration of Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition and specify your TKGI API load balancer, follow the steps below:
-
Select Resource Config.
-
For each job, review the Automatic values in the following fields:
- INSTANCES: Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition defaults to the minimum configuration. If you want a highly available configuration (beta), scale the number of VM instances as follows:
- To configure your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition database for high availability (beta), increase the INSTANCES value for TKGI Database to
3. - To configure your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition API and UAA for high availability (beta), increase the INSTANCES value for TKGI API to
2or more.Warning: High availability mode is a beta feature. Do not scale your TKGI API or TKGI Database to more than one instance in production environments.
Note: On Azure, you must reconfigure your TKGI API load balancer backend pool whenever you modify your TKGI API VM group. For more information about configuring your TKGI API load balancer backend pool, see Create a Load Balancer in Configuring an Azure Load Balancer for the TKGI API.
- To configure your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition database for high availability (beta), increase the INSTANCES value for TKGI Database to
- VM TYPE: By default, the TKGI Database and TKGI API jobs are set to the same Automatic VM type. If you want to adjust this value, we recommend that you select the same VM type for both jobs.
Note: The Automatic VM TYPE values match the recommended resource configuration for the TKGI API and TKGI Database jobs.
- PERSISTENT DISK TYPE: By default, the TKGI Database and TKGI API jobs are set to the same persistent disk type. If you want to adjust this value, you can change the persistent disk type for each of the jobs independently. Using the same persistent disk type for both jobs is not required.
- INSTANCES: Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition defaults to the minimum configuration. If you want a highly available configuration (beta), scale the number of VM instances as follows:
-
For the TKGI Database job:
- Leave the LOAD BALANCERS field blank.
- (Optional) If you do not use a NAT instance, select INTERNET CONNECTED. This allows component instances direct access to the internet.
-
For the TKGI API job:
-
Enter the name of your TKGI API load balancer in the LOAD BALANCERS field. For more information on the TKGI API load balancer, see Configuring an Azure Load Balancer for the TKGI API.
Note: After you click Apply Changes for the first time, BOSH assigns the TKGI API VM an IP address. BOSH uses the name you provide in the LOAD BALANCERS field to locate your load balancer and then connect the load balancer to the TKGI API VM using its new IP address.
-
(Optional) If you do not use a NAT instance, select INTERNET CONNECTED. This allows component instances direct access to the internet.
Warning: To avoid workload downtime, use the resource configuration recommended in About Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Upgrades and Maintaining Workload Uptime.
-
Step 3: Apply Changes
- Return to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard.
- Click Review Pending Changes. Select the product that you intend to deploy and review the changes. For more information, see Reviewing Pending Product Changes.
- Click Apply Changes.
Step 4: Retrieve the TKGI API Endpoint
You need to retrieve the TKGI API endpoint to allow your organization to use the API to create, update, and delete Kubernetes clusters.
To retrieve the TKGI API endpoint, do the following:
- Navigate to the Ops Manager Installation Dashboard.
- Click the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition tile.
- Click the Status tab and locate the TKGI API job. The IP address of the TKGI API job is the TKGI API endpoint.
Step 5: Configure an Azure Load Balancer for the TKGI API
Follow the procedures in Configuring an Azure Load Balancer for the TKGI API to configure an Azure load balancer for the TKGI API.
Step 6: Install the TKGI and Kubernetes CLIs
The TKGI CLI and the Kubernetes CLI help you interact with your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition-provisioned Kubernetes clusters and Kubernetes workloads. To install the CLIs, follow the instructions below:
Step 7: Configure Authentication for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition
Follow the procedures in Setting Up Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Admin Users on Azure.
Next Steps
After installing Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition on Azure, you might want to do one or more of the following:
- Create a load balancer for your Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition clusters. For more information, see Creating and Configuring an Azure Load Balancer for Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition Clusters.
- Create your first Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Integrated Edition cluster. For more information, see Creating Clusters.