In a networked environment, the same IP addresses can be reused across multiple systems (devices) running in separate networks. These IP addresses, known as overlapping IP addresses, are prominent in MPLS VPN environments and in networks centrally managed by Managed Service Providers, where private IP networks of customers often deploy identically numbered IP address spaces. Example of an overlapping IP in an MPLS VPN network is an example of an overlapping IP address in an MPLS VPN network.
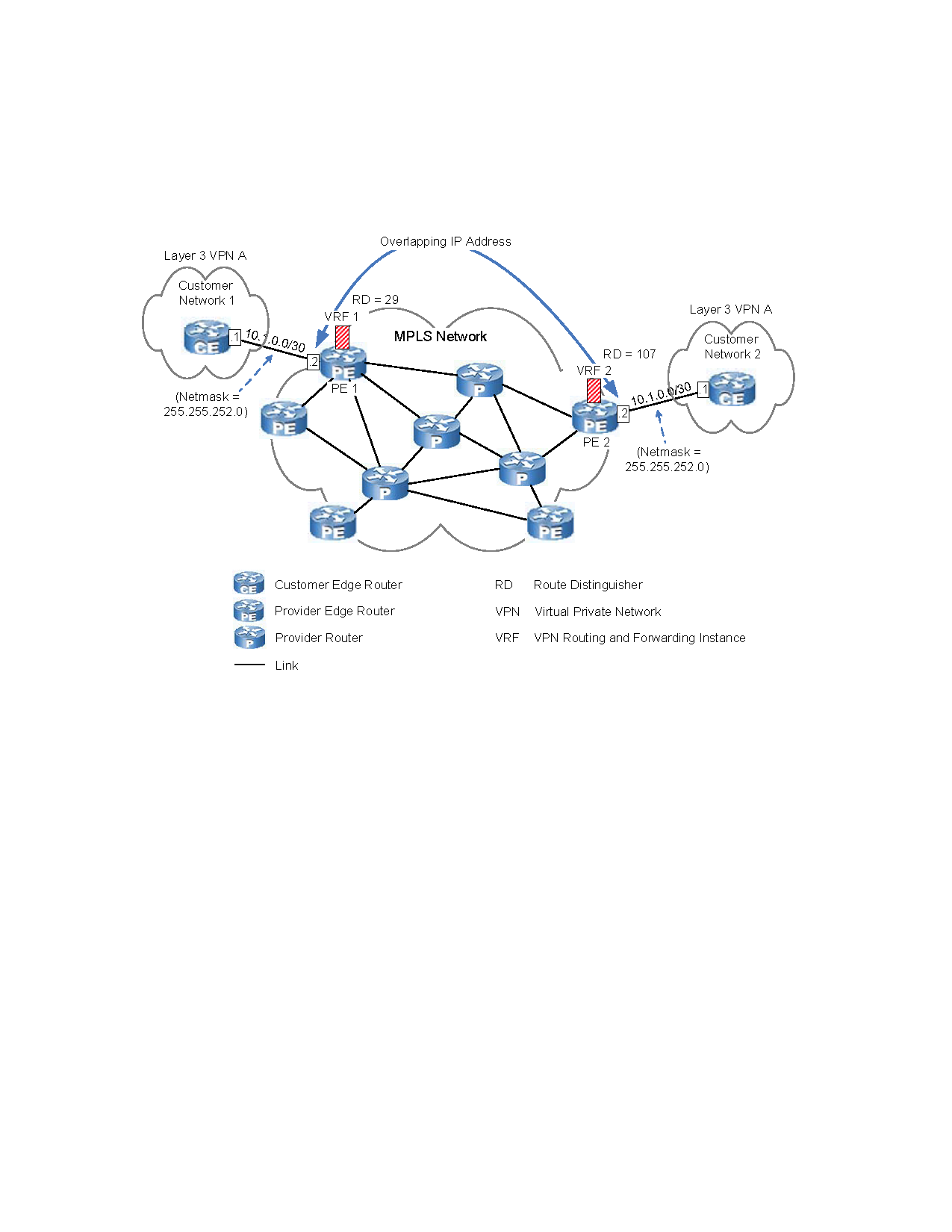
Overlapping IP addresses do not create problems across different networks; however, when a service-assurance application for a centrally managed network attempts to discover the overlapping IP addresses, IP address identity problems arise. For example, without the IP tagging feature, the IP Manager will respond as follows when it discovers an overlapping IP address:
-
Create a DuplicateIP notification and a DuplicateIP object.
-
Discard the most recently received overlapping address.
-
Remove the initially received overlapping address from its repository.
With the IP tagging feature, the IP Manager is able to distinguish between overlapping addresses belonging to different customers by adding a distinguishing tag to their names.
That is, instead of using the standard naming scheme of “IP-<IP address>” to name an overlapping IP address instance, the IP Manager uses the “IP-<IP address>/<tag>” naming scheme to name the instance.