The MPLS Topology Server is able to discover LDP-signaled VPWS and VPLS instances, and BGP-signaled VPWS and VPLS instances.
Because VPLS has many prototypes and is configured in many different ways from vendor to vendor, the MPLS Topology Server focuses on support of the more dominant types of VPLS. Specifically, the MPLS Topology Server focuses on the following:
-
VPLS architectural type: flat architecture
The MPLS Topology Server discovers VPLS instances that employ the flat architecture type of VPLS, but does not discover VPLS instances that employ the hierarchical architecture (H-VPLS) type of VPLS. The latter type of VPLS is used to overcome control-plane scalability issues in an LDP-signaled VPLS.
-
VPLS topology type: full mesh
MPLS Manager discovers VPLS instances that employ the full mesh topology, but does not discover VPLS instances that employ the hub-and-spoke topology.
-
VPLS signaling protocol types: LDP, BGP
The MPLS Topology Server discovers VPLS instances that are exclusively signaled by either LDP or BGP, but does not discover VPLS instances that are signaled by both LDP and BGP.
The MPLS Topology Server is able to discover all independent pseudowires (VPWS instances), even if some of those pseudowires use the same VC ID. For LDP-signaled VPLS, the MPLS Topology Server assumes that:
-
All pseudowires within a VPLS instance use the same VC ID.
-
No two VPLS instances in the managed MPLS network use the same VC ID.
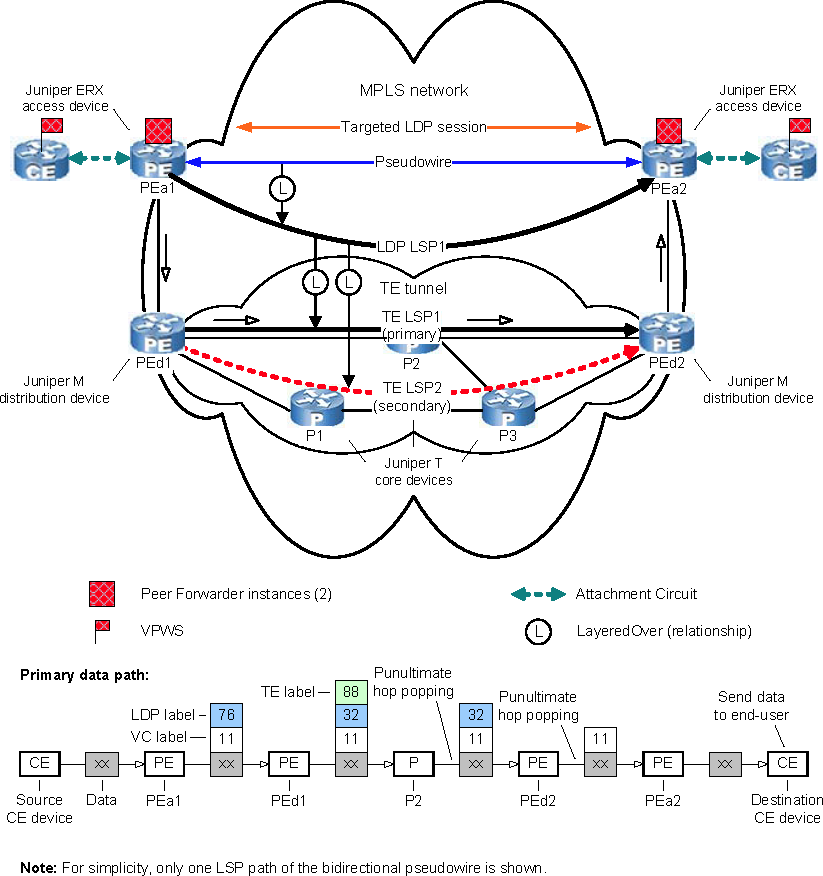
Discovering a VPWS instance that is configured with LSP protection is an example of one of the more complex L2VPN deployments that the MPLS Topology Server is able to discover. Because the default value of the ASSOCIATE_LSP_TO_LDP parameter in the mpls.conf file is TRUE, the MPLS Topology Server will create by default the LDP-LSP-to-TE-LSP LayeredOver relationships that are shown in the figure.
Figure 1. Discovering a VPWS instance that is configured with LSP protection