In the physical-transport domain, IP Availability Manager discovers Layer 2 (data-link) and Layer 3 (network) connectivity in multivendor, switched, and routed networks. It discovers the network systems by sending them Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and SNMP polls.
In an MPLS network, as shown in Physical-transport domain discovered by IP Availability Manager, IP Availability Manager discovers the Layer 2 and Layer 3 network object connectivity between PE, P, and CE devices.
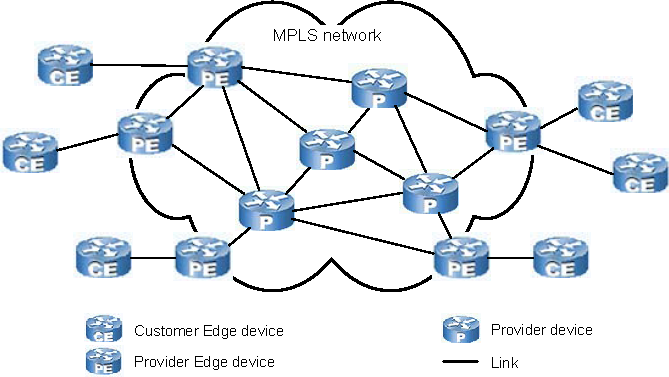
IP Availability Manager uses the discovered topology to model the network, and uses SNMP polling and traps to diagnose and pinpoint the root cause of network failures. It exports the analysis results along with topology information to the Global Manager. IP Availability Manager also exports MPLS-relevant topology and CLI device-access objects to the MPLS Topology Server, and exports MPLS-relevant status updates to the MPLS Monitoring Server.
The topology exported to the MPLS Topology Server includes SNMPAgent objects, which carry SNMPv1, v2c, or v3 credential information. The SNMP credentials are required by the MPLS Topology Server for two purposes:
-
To perform SNMP discovery
-
To execute on-demand remote ping requests
The CLI device-access objects exported to the MPLS Topology Server carry CLI login credential information. The CLI login credentials are required by the MPLS Topology Server for two purposes:
-
To perform CLI discovery
-
To execute on-demand label switched path (LSP) ping requests
The MPLS Manager Configuration Guide provides information about creating CLI device-access objects.