MPLS VPN-Tagging Server discovery in the Cisco environment shows the design architecture of MPLS VPN overlapping IP discovery in the Cisco environment.
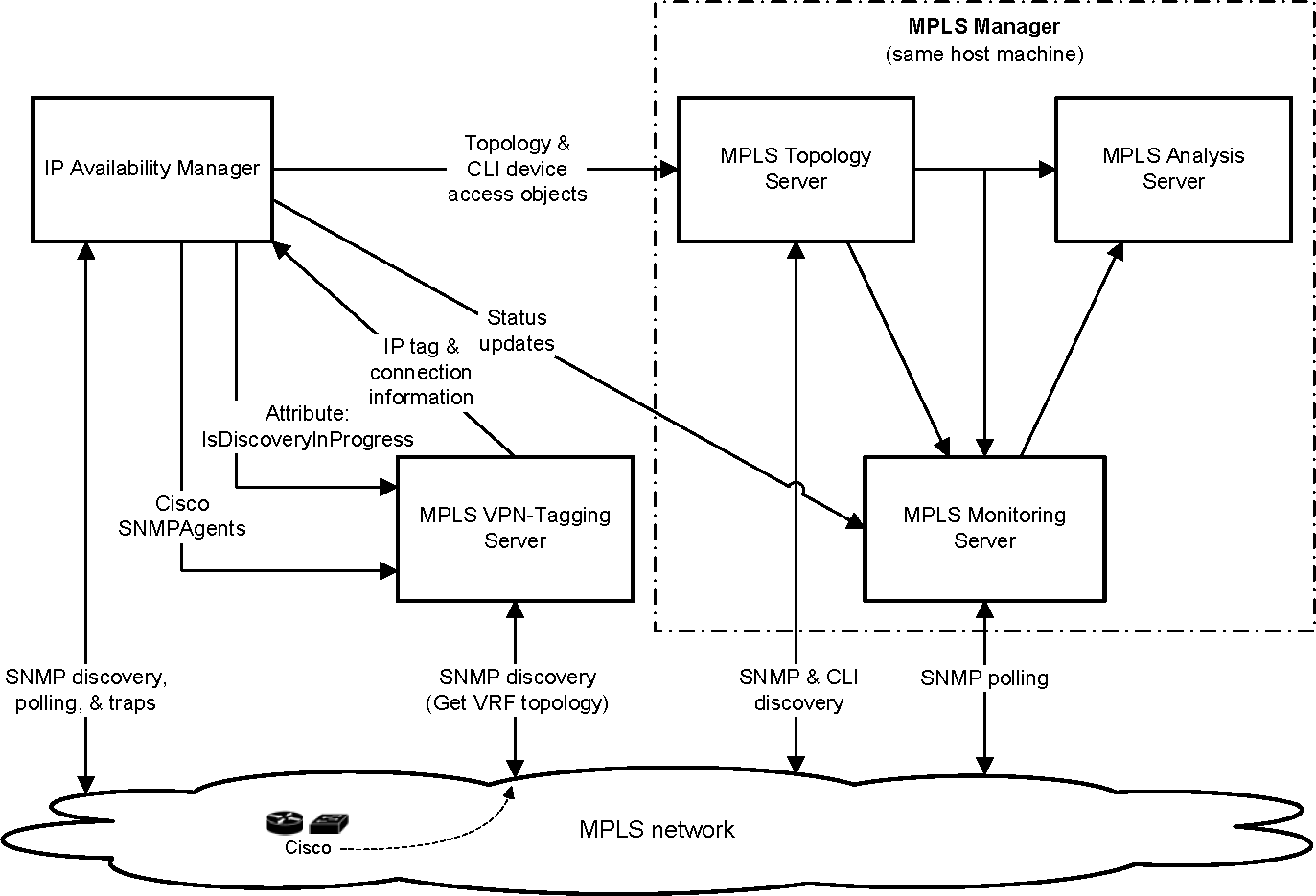
The MPLS VPN-Tagging Server performs SNMP discovery on Cisco routers or switches to discover VRF-based network connections for the devices. When the MPLS VPN-Tagging Server discovers these connections, it sends the connection information to IP Availability Manager so that IP Availability Manager is able to distinguish overlapping IPs on the same device.
The flowchart in MPLS VPN overlapping IP discovery flow in the Cisco environment shows how MPLS VPN overlapping IP discovery works in the Cisco environment.
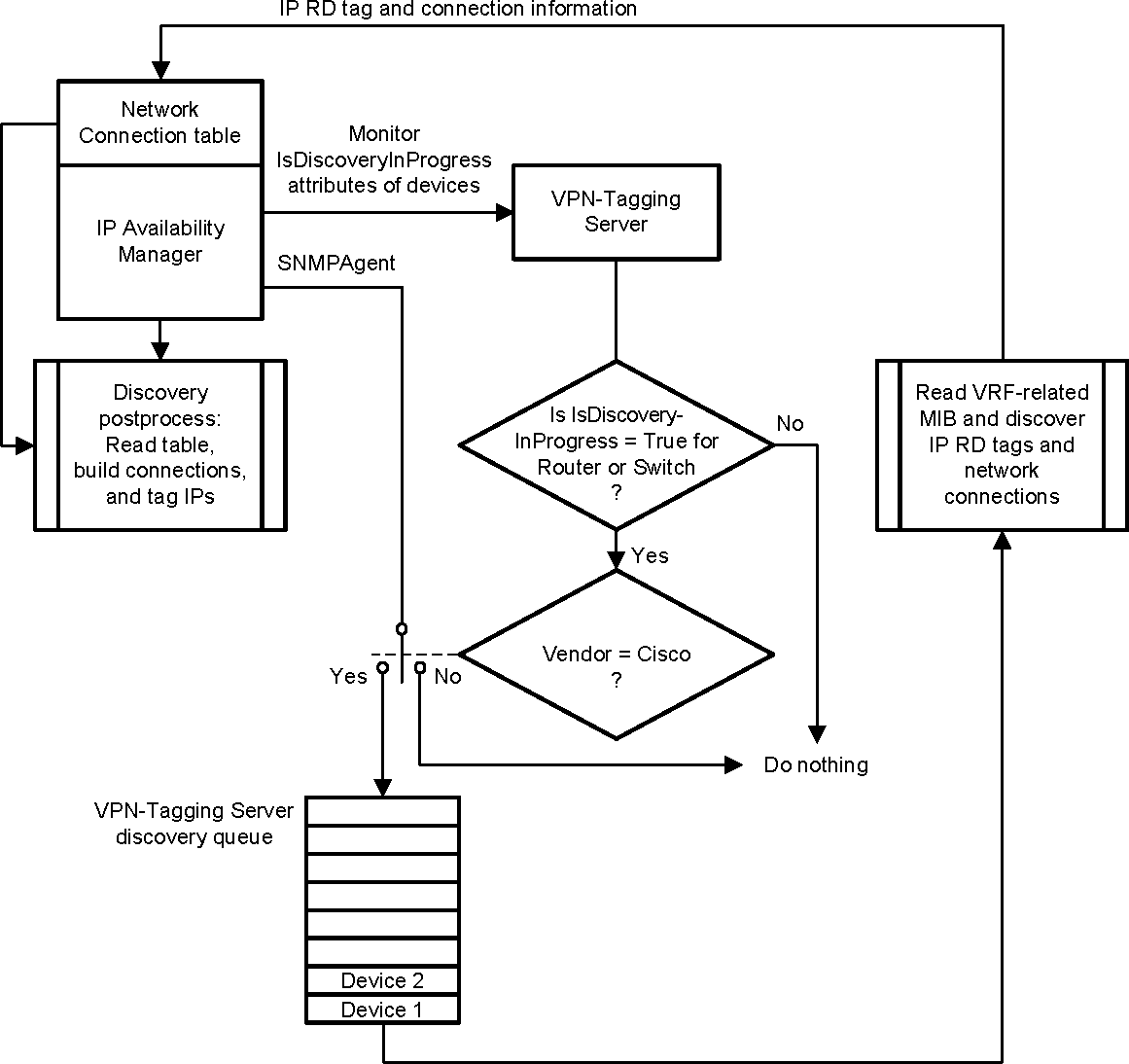
Overlapping IP discovery of a Cisco device is triggered by IP Availability Manager when it sets a device’s IsDiscoveryInProgress attribute to True during the course of discovering the device. The MPLS VPN-Tagging Server subscribes to IsDiscoveryInProgress attributes.
When the MPLS VPN-Tagging Server receives an IsDiscoveryInProgress attribute = True for either a Cisco router or switch, it retrieves the address of the device’s SNMP agent from IP Availability Manager and places the address in its discovery queue. It then initiates SNMP discovery on the SNMP agent, obtains the IP route-distinguisher tag and other related network connection information by querying the agent’s VRF-related MIB, and writes that information to IP Availability Manager’s Network Connection table.