BGP failures, or apparent failures, that are detected by Network Protocol Manager for BGPcannot be analyzed in isolation. Rather, those failures must be correlated with the physical-transport failures that are detected by IP Availability Managerin order to determine the root-cause problem that is underlying all observed symptoms. Network Protocol Manager for BGPanalyzes BGP and physical-transport failures to determine whether a BGP failure is indeed a root-cause problem, or simply a symptom (impact) of an underlying physical-transport root-cause problem.
When Network Protocol Manager for BGPdetects a BGP failure, it checks for any physical-transport problem that might be causing the failure. If it does not find such a problem, Network Protocol Manager for BGPfocuses its analysis on just the BGP domain and performs the root-cause analysis described in Chapter 3, “BGP Objects and their Failures.”
If it does find such a problem, Network Protocol Manager for BGPdiagnoses the BGP failure as an impact and exports the underlying physical-transport problem and the BGP failure to the Global Manager. The Global Managerresponds by adding the BGP failure as an impact of the underlying physical-transport root-cause problem.
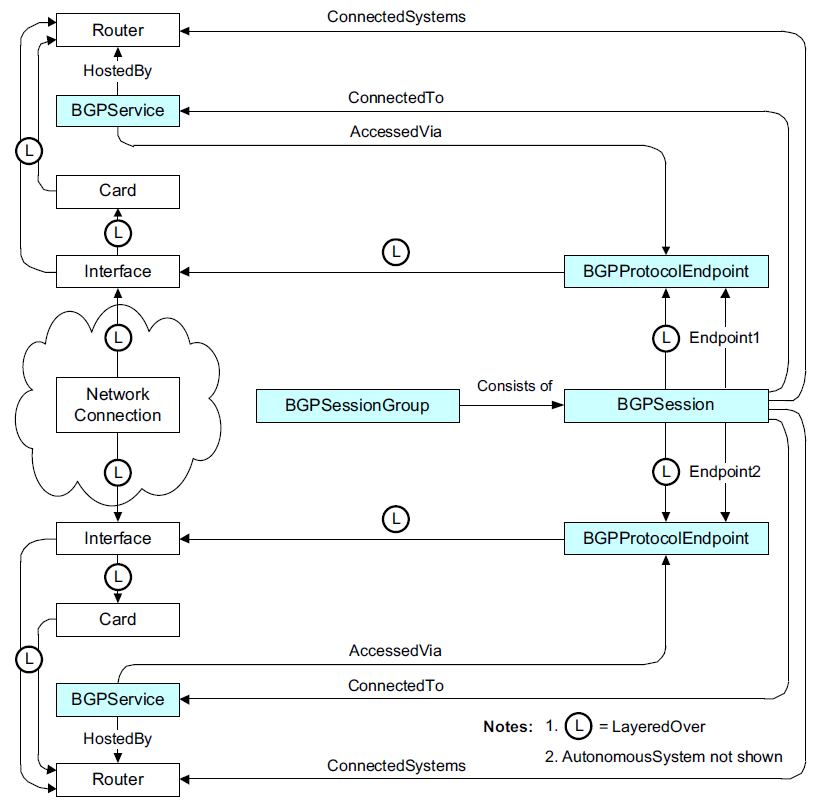
BGP and global impact analysisshows the flow of information between the components in a Network Protocol Manager for BGPdeployment to achieve BGP and global impact analysis.
Status updates received from IP Availability Manageridentifies the IP Availability Managerstatus updates to which Network Protocol Manager for BGPsubscribes.
| Object |
Problem-type status |
Event-type status |
|---|---|---|
| 1**Indentation indicates class hierarchy. 2**Perceived as a problem-type status by Network Protocol Manager for BGP. |
||
| Card |
Down |
|
| NetworkAdapter Interface 1 Port |
Disabled, Down |
|
| NetworkConnection Cable 1 TrunkCable |
DownOrFlapping 2 |
|
| UnitaryComputerSystem Router 1 Switch and so on |
Unresponsive 2 |
|
Network Protocol Manager for BGPimports status information from IP Availability Managerthrough a remote repository access or, as shown in Synchronizing topology object event status.
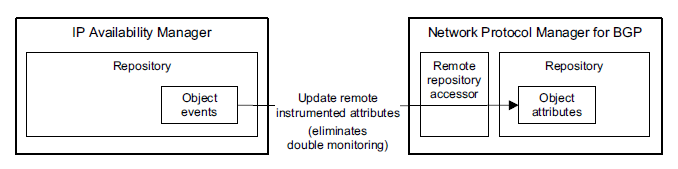
“Update remote instrumented attributes” in Synchronizing topology object event statuscorresponds to “Status updates” in BGP and global impact analysisand in Status updates received from IP Availability Manager. Status updates represent the activation or clearing of events for the topology objects that are identified in Status updates received from IP Availability Manager.
Adding IP Availability Manageras a source to Network Protocol Manager for BGPcauses Network Protocol Manager for BGPto import topology and status from the IP Availability Manager. The Network Protocol Manager Discovery Guide Supplementprovides the instructions for completing this task.