Domain manager provides the sm_edit utility to ensure that modified files are always saved to the appropriate local area and that original copies of the files remain unchanged. Preview of how the sm_edit utility works previews the operation of the sm_edit utility.
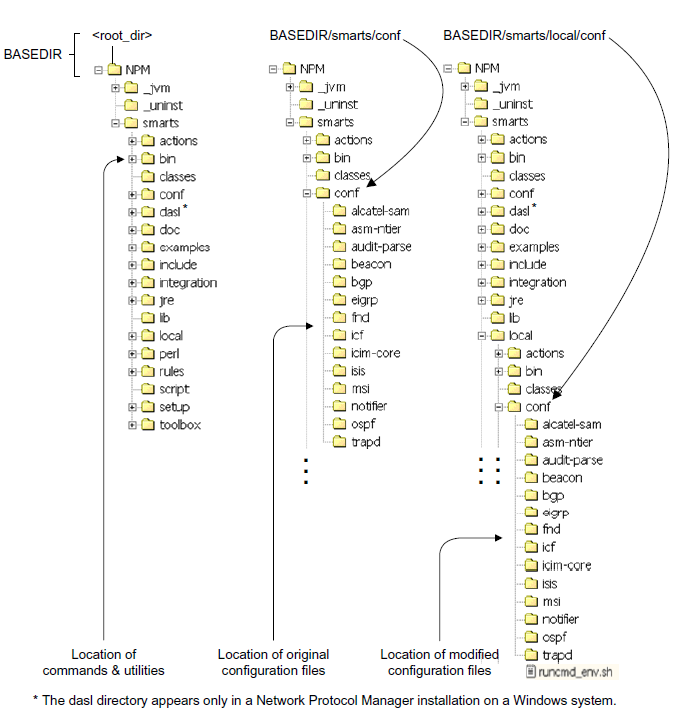
All products use the same basic installation directory structure that is shown in Preview of how the sm_edit utility works.
To invoke the sm_edit utility, go to the BASEDIR/smarts/bin directory and specify the path and the name of the file, relative to the BASEDIR/smarts directory, that you want to edit. For example,
sm_edit conf/bgp/bgp.conf
opens in a text editor either a local copy of the bgp.conf file in BASEDIR/smarts/local/conf/bgp or an original copy of the bgp.conf file in BASEDIR/smarts/conf/bgp if no local copy exists.
After you modify and save the bgp.conf file, the sm_edit utility saves the modified version of the file to the BASEDIR/smarts/local/conf/bgp directory.
You can use the sm_edit utility to edit any text file, not just a configuration file, in the BASEDIR/smarts or BASEDIR/smarts/local directory. Because sm_edit assumes a starting point of BASEDIR/smarts, the text-file path that you specify begins with the directory name (conf, rules, script, and so on) under the BASEDIR/smarts directory.
Original versions of files may be changed or updated as part of a software upgrade. However, files in the BASEDIR/smarts/local directory are retained during an upgrade.
The System Administration Guide provides additional information about the sm_edit utility.