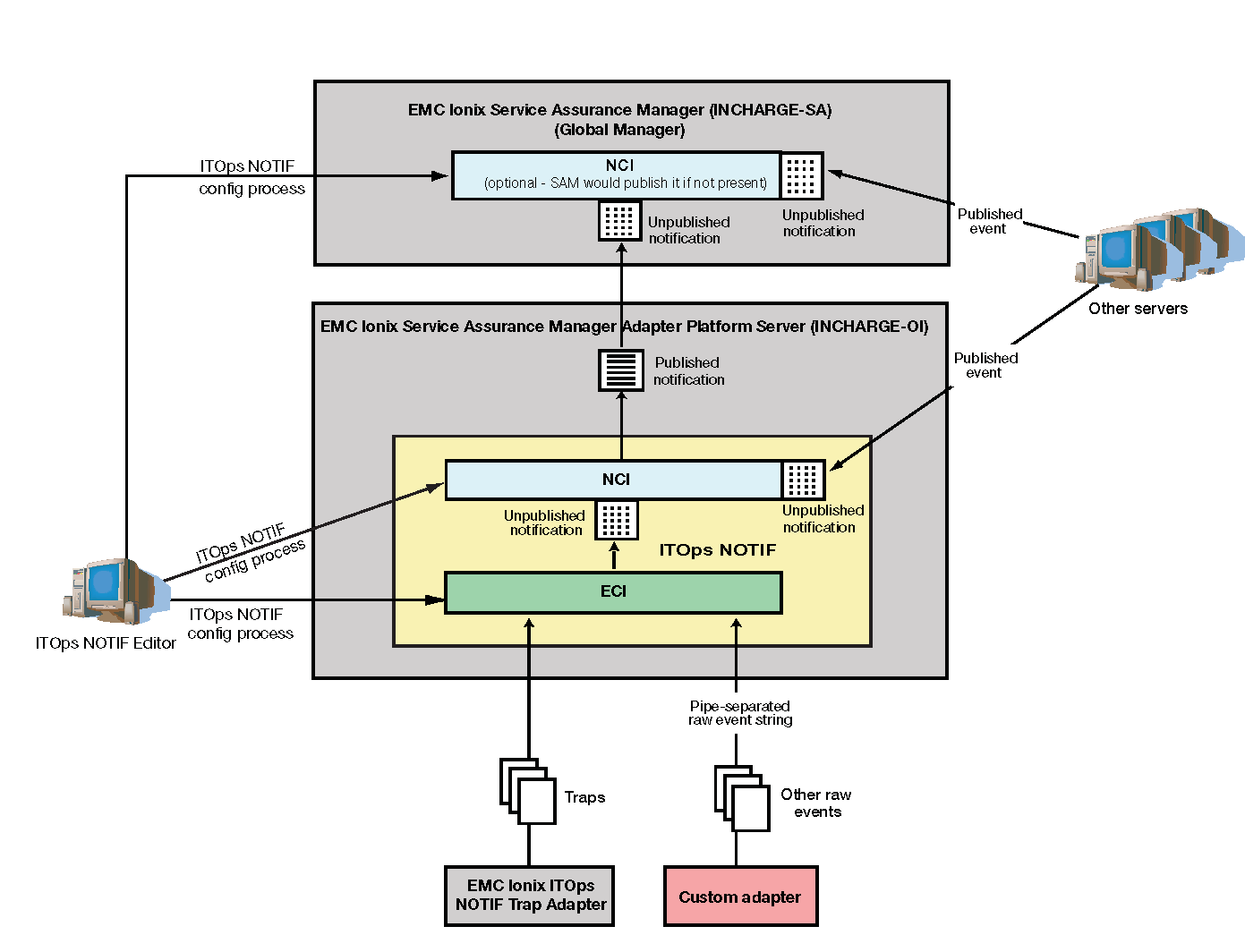
There are two main components of Smarts NOTIF. The first is the real-time component which processes SNMP traps or other raw event types according to configuration settings. This configuration processing is performed on raw events by the Event Configuration Information (EventConfigInfo or ECI) objects. ECI objects determine whether a particular event will be processed, that is, whether a notification for an event will be created. ECI processing is discussed in Chapter 2, “Event Configuration Information Processing.”
The second Smarts NOTIF component is notification processing, which is configured by the Notification Configuration Information (NCI) objects. NCI objects determine how notifications are processed. NCI processing is discussed in Chapter 3, “Notification Configuration Information Processing.”
It is important to note the separation of raw event processing (through ECI objects) versus notification processing (through NCI objects) since this allows Smarts NOTIF to operate in various architectures. The Smarts NOTIF Editor allows the user to manipulate the configuration settings for both ECI and NCI objects.
In an Smarts implementation, Smarts NOTIF can reside on a SAM server or an Adapter Platform Open Interface (OI) server. Smarts NOTIF ECI/NCI structure in an Smarts environment shows how ECI and NCI objects are used in an Smarts NOTIF solution where low-level raw events are filtered and processed, and notifications are grouped within the Adapter Platform. An additional Smarts NOTIF process is run within the SAM server to combine and group notifications from the adapter servers and other (analysis) servers.