Each NSX Manager has a 1:1 relationship with vCenter Server. Therefore, two NSX Managers are created in the management cluster.

The first NSX Manager in the Management pod is solely responsible for deploying and operating the highly available ESG instances that provide load balancing functionality. Every component in the management cluster, which relies on multiple external services such as Platform Services Controllers, use the ESG as a load balancer to ensure reachability should a component fail. VMware Integrated OpenStack comes with its own built-in High Availability control plane implemented using HA proxy on the load balancer VMs.
The second NSX Manager in the Management pod is responsible for all Edge/Resource pod networking. It is registered with VMware Integrated OpenStack to provide networking services to tenants, including stateful firewalls and load balancers. The same NSX Manager is used to configure East-West VNF connectivity, North-South routing, and out-of-band management access for VNFs.
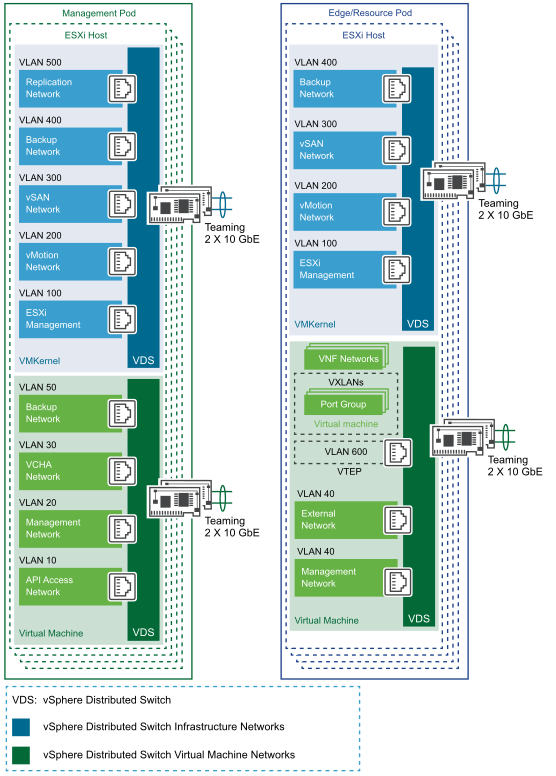
Infrastructure networks are used by the ESXi hypervisor for vMotion, VMware vSphere® Fault Tolerance, and vSAN traffic. The Virtual Machine networks are used by Virtual Machines to communicate with each other. For each pod, the separation between infrastructure and Virtual Machine networks ensures security and provides network resources where needed. This separation is implemented by two distributed switches, one for infrastructure networks and the other for Virtual Machine networks. Each distributed switch has separate uplink connectivity to the physical data center network, completely separating its traffic from other network traffic. The uplinks are mapped to a pair of physical NICs on each ESXi host, for optimal performance and resiliency.
NSX for vSphere provides the network infrastructure for the East-West connectivity VNFCs require and edge services for their North-South connectivity. When tenants deploy a logical router, they can choose from three types of routers.
- Centralized and exclusive router
- Centralized and shared router
- Distributed router
In case of centralized and exclusive, Neutron service in VMware Integrated OpenStack installs a dedicated instance of an ESG for that tenant. This design ensures separation of VNF traffic across tenants. This is the preferred way to secure tenant level isolation. Centralized and shared router type shares ESG with other tenants as long as there no overlapping subnets. Distributed router provides East-West routing capabilities. Edge function is also deployed by default with distributed router which is used for firewall and dynamic routing
The two-pod design places NSX Controllers in the Edge/Resource pod to be positioned close to the data plane components of the NFVI platform. Three controllers are deployed as a cluster, ensuring control plane resiliency. NSX Controller Disconnect Operations (CDO) is a new feature introduced in NSX for vSphere. It ensures that data plane connectivity is unaffected when hosts lose connectivity with the controller.
In two-pod design, both the East-West and North-South networks are provisioned by the tenant from within VMware Integrated OpenStack.