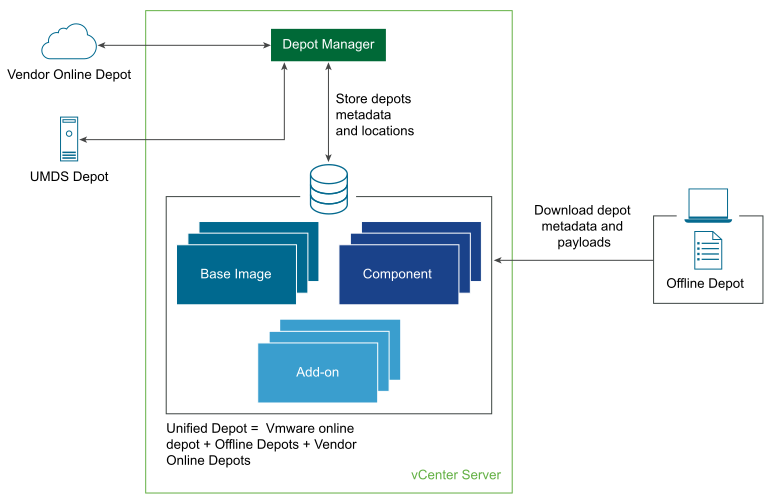
A software depot represents a well-defined file structure used for storing and hosting the ESXi software updates, patches, and upgrades that VMware, partners, and third-party vendors provide. You can use the vSphere Automation APIs to manage the life cycle of the hosts in your environment by applying software updates hosted on different depots.
Software depots are managed by the Depot Manager which is part of the vSphere Lifecycle Manager. Software depots contain the actual payloads and the metadata of the software updates. Depending on the way you access the software updates, the Depot Manager recognizes three types of software depots: online, offline, and UMDS.
The following section of the documentation explains the concept of a software depot in terms of the vSphere Lifecycle Manager feature. You can also find common use cases available through the APIs for working with the different types of depots and their content.
Types of Software Depots
Depot Manager works with the software updates provided by three different types of software depots: online, offline, and UMDS.
Regardless of the different way in which you access each type of software depot, all depots have the same structure. The same depot structure allows content from different vendors to be uploaded to one depot. By default, you can access the content of the VMware online depot at https://hostupdate.vmware.com/software/VUM/PRODUCTION/.... Furthermore, partners and third-party customers can use the ESXi Packaging Kit to build and distribute software updates in the form of offline or online depots. You can access their content by adding the online vendor depot to the vSphere Lifecycle Manager or by downloading the content of the offline depot to the vCenter Server instance.
Online Depot
- https://hostupdate.vmware.com/software/VUM/PRODUCTION/main/vmw-depot-index.xml
- https://hostupdate.vmware.com/software/VUM/PRODUCTION/addon-main/vmw-depot-index.xml
- https://hostupdate.vmware.com/software/VUM/PRODUCTION/iovp-main/vmw-depot-index.xml
- https://hostupdate.vmware.com/software/VUM/PRODUCTION/vmtools-main/vmw-depot-index.xml
When you deploy the vCenter Server, the vSphere Lifecycle Manager is configured to access the VMware online depot, by default. You can use the vSphere Automation APIs to add a custom online depot to be managed by Depot Manager. The metadata of the newly added online depot is not synchronized immediately. To synchronize the metadata, you can run a synchronization operation or wait for the scheduled synchronization to take place.
The Depot Manager stores in the vCenter Server database only the metadata of the software updates and the location of the added online depots. You can create a schedule to synchronize the software updates metadata stored in the vCenter Server with the metadata available in the accessible depots. The payloads of the software updates are downloaded only during the cluster remediation process.
To add, remove, list, and retrieve information about the online depots, you can use the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Online interface. See Working with Online Depots.
Offline Depot
The offline depot is also called an offline bundle and is distributed as a downloadable ZIP file. Offline depots contain both the metadata and the payloads of the software update. Partners and third-party customers can use the ESXi Packaging Kit to build and distribute offline bundles. You can download offline bundles from the VMware website or from the websites of third-party vendors. When you add an offline depot to the vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot, the software updates are downloaded to the vCenter Server database.
To manage offline depots, you can use the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Offline interface. See Working with Offline Depots.
UMDS Depot
In case, the vCenter Server instance is in an air-gapped environment and has no access to any wire or wireless network, you can use a UMDS depot. The Update Manager Download Service (UMDS) is available as a VMware-UMDS-8.0.1.-build_number.tar.gz file within the ISO image of the vCenter Server appliance 8.0 UMDS is a 64-bit application and requires a 64-bit Linux-based system. Install UMDS on a machine that has Internet access and is different from the machine on which the vSphere Lifecycle Manager is running. For further information about how to install and configure the UMDS module, see the Managing Host and Cluster Lifecycle.
You can set up a synchronization schedule for downloading specific software updates from online vendor depots to the UMDS depot. Then use these updates to create desired software state for the clusters in your environment.
To manage UMDS depots through the vSphere Automation API, you can use the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Umds interface.
Working with Online Depots
You can use the vSphere Automation APIs to add online depots to the list of currently configured online software depots.
Use online depots to add new content over time to the management scope of Depot Manager. Depot Manager periodically updates the software depots metadata stored on the vCenter Server instance. In case, new software updates are uploaded to the online depots, the Depot Manager makes sure that the metadata stored on the vCenter Server database is updated accordingly.
To add an online depot to the Depot Manager, you must first create the online depot specification by using the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.OnlineTypes.CreateSpec class. To specify the URI to the vendor-index.xml file of the online depot, use the setLocation(location) method of the OnlineTypes.CreateSpec class. Optionally, you can add a description and enable the depot. By default, when you add an online depot to the Depot Manager, the depot is enabled and its metadata is synchronized following the defined schedule. If you want to synchronize the added online depot immediately, call the sync_Task() method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.Depots interface. When you complete the depot specification, call the create(spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Online interface to add the depot.
You can edit the depot description and deactivate the depot by creating an com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.OnlineTypes.UpdateSpec object and pass it to the update( depot, update_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Online interface.
You can remove an online depot from the list of currently configured depots by using the delete(depotID) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Online interface. This operation does not remove the already downloaded metadata and payloads from the deleted depot. You cannot delete the default VMware online depot, you can only deactivate it.
To retrieve a list of currently configured online depots, call the list() method of the Online interface. You can also retrieve information about a currently configured online depot by using the get(depotID) method of the Online interface.
Working with UMDS Depots
In an air-gapped vCenter Server environment, you can use the vSphere Automation API to add a UMDS depot to the depots managed by Depot Manager.
After you install and configure the Update Manager Download Service (UMDS) on a physical machine with Internet access, you can add the UMDS depot to Depot Manager. Only one UMDS depot can be added at a time to Depot Manager. When you add a UMDS depot, its content is not immediately synchronized. To synchronize the content of the UMDS depots, you must call the sync_Task() method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.Depots interface or wait for the scheduled synchronization to take place.
To add a UMDS depot, call the set(set_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Umds interface and pass a com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.UmdsTypes.SetSpec object as an argument. The UMDS specification must contain the URI location to the index.xml file of the depot. Optionally, you can set a description and indicate whether the depot must be enabled. By enabling the UMDS depot, you instruct Depot Manager to synchronize only the content that is available on that depot.
You can always edit the initial UMDS depot settings, by calling the update(update_spec) method of the Umds interface and passing an com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.UmdsTypes.UpdateSpec object.
To retrieve information about the currently configured UMDS depot, use the get() method of the Umds interface. You can remove a currently configured UMDS depot and all its downloaded content from Depot Manager by calling the delete_Task() method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Umds interface.
Synchronizing Software Depots
The VMware online depot, the vendor online depots, and the UMDS depot must be synchronized regularly if you want to have the most recent software updates delivered by VMware, partners, and other third-party vendors. Use the vSphere Automation APIs to create a synchronization schedule or to synchronize the added depot immediately.
The Depot Manager does not synchronize immediately the metadata of the newly added online and UMDS depots. If you want to force the synchronization and not wait for the scheduled synchronization to take place, call the sync_Task() method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.Depots interface. You can also define a custom schedule to sync the metadata from the currently configured online or UMDS depots.
To create a custom schedule for checking for new software updates, you must first define the schedule parameters by using the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.SyncScheduleTypes.Schedule class. Then you can add the schedule to the schedule specification by using the setSchedule(schedule) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.SyncScheduleTypes.Spec class. Optionally, you can use the schedule specification to add an email to which notifications will be sent and define whether updates will be downloaded automatically. To apply the custom schedule, call the set(spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.SyncSchedule interface.
The default schedule is set to update the metadata daily at a random time. To reset the schedule to the default settings, call the set(spec) of the SyncSchedule interface and pass null as an argument.
Working with Offline Depots
An offline depot is a ZIP file that contains the metadata and payloads of software updates and follows the same structure as the online depot. Use the vSphere Automation APIs to import the content of an offline depot to the vCenter Server database.
To add an offline depot to the depots managed by the Depot Manager, you must create an offline depot specification by using the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.OfflineTypes.CreateSpec class. When you define the offline depot parameters, call the create_Task(create_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depots.Offline interface. Depending on the location of the offline depot, when you create the offline depot specification, you must provide either the URI location or the file ID returned by the Jetty Web server embedded in the vSphere Lifecycle Manager. You set the type of the source from which the offline depot is downloaded by using the setSourceType(sourceType) method of the OfflineTypes.CreateSpec class.
Pull Depot Content from a URI
To indicate that the offline depot resides on a URI location, call the setLocation(java.net.URI location) method of the OfflineTypes.CreateSpec class. You can pass as an argument the depot location in one of the following URI schemes: http, https, or file. If you provide an HTTPS location to the offline depot, make sure you also provide a certificate trusted by the VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA) or a custom certificate from the VMware Endpoint Certificate Store (VECS). For detailed information about how to manage certificates, see the vSphere Authentication documentation.
Push Depot Content to the Depot Manager
To push the content of an offline depot to the Depot Manager, you must first upload the ZIP file to the Jetty Web server at the https://<vcenter_FQDN>:9087/vum-fileupload URL. The server returns a file identifier that you can pass as an argument to the setFileId(fileId) method of the OfflineTypes.CreateSpec class.
Managing Depot Overrides
In case, you have a smaller Remote Office/ Branch Office (ROBO) cluster environment, or Edge computing environment, your clusters have no, or limited access to the Internet and limited connection to a vCenter Server instance. In such an environment, you can use Depot Manager to fetch the metadata and payloads of a desired software state from a local to the cluster depot.
To remediate a ROBO cluster, you must have access to a local software depot that hosts the components of the desired state. You can use Depot Manager to either export the whole vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot to an offline bundle, or export only the content of the desired state required for remediating the ROBO cluster.
To export the desired state image from the vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot, call the export(cluster,export_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.clusters.Software interface. The method returns the URI of the offline bundle that is hosted on the vSphere Lifecycle Manager Jetty Web server. To move the content of the offline bundle to the ROBO location, you must physically copy the ZIP file, unarchive, and mount its content to an HTTP server inside the ROBO environment.
To redirect a ROBO cluster to download software updates from a local repository and not from the vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot on the vCenter Server instance, the vSphere Automation API offer the cluster DepotOverrides service. To add a depot override location to a ROBO cluster, call the add(cluster,override_depot) method of the DepotOverrides interface. Specify the URI location of the local depot with the setLocation(location) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.clusters.DepotOverridesTypes.Depot class. During the ROBO cluster remediation, Depot Manager instructs the hosts in the ROBO cluster to download the software updates from the configured local depots within the ROBO cluster.
Inspecting Depot Contents
You can use the vSphere Automation API to inspect the contents of the already synchronized and imported depots. You can list the available base images, add-ons, and components, or retrieve some detailed information about a specific software update.
To retrieve a list of the base images available on a vCenter Server instance, call the list(filter_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.BaseImages interface. To narrow the list of returned base images and retrieve only items matching to specific criteria, you must pass a com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.BaseImagesTypes.FilterSpec instance as an argument to the list method. Use the retrieved list to get some information about each base image, including their display name and version, release date, and their category. You can also get some detailed information about a single base image by using the get(version) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.base_images.Versions interface. The information includes a list of the components present in this base image.
To retrieve a list of all currently available add-ons in the vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot, call the list(filter_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.AddOns interface and pass null as an argument. You can filter the available add-ons by using some specific criteria such as the add-on vendor, name, versions, or minimum version. You can retrieve some detailed information about a single add-on version, by calling the get(name,version) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.add_ons.Versions interface. The information includes the list of components part of the add-on, and the list of components that were removed by this add-on version.
To retrieve a list of all components currently available in the vSphere Lifecycle Manager depot, you can call the list(filter_spec) method of the com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.Components interface and pass null as an argument. To retrieve a list of components that matches some specific criteria, define your preferences with a com.vmware.esx.settings.depot_content.ComponentsTypes.FilterSpec instance and pass it as an argument to the list method. Use the retrieved list to get some information regarding each component.