Running a hardware compatibility check on your clusters before remediating them helps you ensure good vSAN cluster health and avoid entering into unsupported and unwanted configurations after remediation.
Cluster-level hardware compatibility checks are available only for vSAN clusters that you manage with a single image. If a vSAN cluster uses baselines, hardware compatibility checks are not available. Also, if a cluster uses a single vSphere Lifecycle Manager image but vSAN is not enabled for that cluster, hardware compatibility checks for that cluster are not available. Hardware compatibility checks for vSAN clusters are performed against the vSAN HCL.
To perform a hardware compatibility check for a vSAN cluster, the vSAN HCL data that is available to vSphere Lifecycle Manager must be up to date. vSAN HCL data is synchronized automatically or, in environments without connection to the Internet, manually. For more information about maintaining the vSAN HCL data up-to-date, see the vSAN documentation.
Hardware compatibility issues are reported as warnings, and as such, they do not prevent you from remediating the hosts in the cluster against the image unless you change that behavior by editing the remediation settings for the cluster. For information about configuring remediation settings for a cluster, see Configure vSphere Lifecycle Manager Remediation Settings for Clusters or Standalone Hosts that You Manage with a Single Image and Override the Global vSphere Lifecycle Manager Remediation Settings for a Cluster or Host That You Manage with a Single Image.
| Device Type | vSphere Lifecycle Manager Validation |
|---|---|
| Storage I/O controllers | For storage I/O controllers, vSphere Lifecycle Manager performs the following verifications:
|
| Network controllers | For NIC devices, vSphere Lifecycle Manager performs the following verifications:
|
| Disk drives | For disk drives, vSphere Lifecycle Manager performs the following verifications:
|
What Are the Currently Active Features
The list of active features for a device is a list of the software features that are enabled on the device and that the device can support. The active features that a device has enabled are the result of enabling or using a solution or a service. In the vSphere Client, information about the currently active features on a device is only available for PCI devices - storage controllers and network controllers. A list of the currently active features is not displayed for disk drives.
When a solution or service, for example vSAN or NSX, enables a set of features on a device, those features impose certain hardware compatibility constraints upon the device. The device must be certified for those active features that vSAN uses. During a hardware compatibility check, in addition to validating the driver and firmware combination for a PCI device, vSphere Lifecycle Manager also validates the constraints that the active features impose on that device. So, by running a hardware compatibility check, you ensure that only certified features are enabled on the devices in the vSAN cluster. You don't get compatibility issues for features that are not enabled on the device.
When the set of active features for a device changes, you must re-run the hardware compatibility check to get correct compliance results.
Hardware Compatibility Check Results
After a hardware compatibility check, vSphere Lifecycle Manager lists a device as compliant or non-compliant. In some cases, the compatibility status is unavailable.
- Compliant
- A device is compliant when it is compatible with the ESXi version and the driver and firmware version defined in the cluster for the image. For PCI devices, the driver-firmware version combination must also be certified for all active features enabled on the respective device.
- Non-compliant
-
A device is non-compliant when it is incompatible with the
ESXi, driver, or firmware version defined in the cluster for the image. Additionally, PCI devices are non-compliant when the driver-firmware version combination is not certified for all active features enabled on the respective device.
If a device is not present in the vSAN HCL at all, vSphere Lifecycle Manager marks the device as non-compliant.
- Unavailable
-
The hardware compatibility status for a NIC device is unavailable in the following cases:
- Compatibility information for PCI devices is unavailable if the vSAN HCL data is not updated and does not contain information about the constraints imposed upon a device by the active features that are enabled on that device.
- The cluster has no hosts or some hosts in the cluster are inaccessible.
- No hardware support manager is registered in vCenter Server or the image for the cluster does not contain a firmware and drivers add-on.
When Does the Hardware Compatibility Check Task Run
vSphere Lifecycle Manager performs regular hardware compatibility checks for the vSAN clusters that you manage with a single image. In addition, certain vSphere Lifecycle Manager operations also trigger an automatic hardware compatibility check. Automated hardware compatibility checks are available for vSAN clusters that use a single image.
For information about hardware compatibility checks and instructions how to manually perform a hardware compatibility check for a cluster or for a single host, see vSphere Lifecycle Manager Hardware Compatibility Checks for Clusters and Hosts.
The Hardware Compatibility Check Task
The vSAN Hardware Compatibility List (vSAN HCL) database changes regularly. For example, when VMware certifies new OEM devices, drivers, or firmware, those become part of the vSAN HCL database. Similarly, devices, drivers, or firmware that are not supported anymore are removed from the vSAN HCL database.
Changes in the vSAN HCL database might make your hardware compatibility results invalid and outdated. To provide you with valid hardware compatibility information, vSphere Lifecycle Manager runs a periodic hardware compatibility check against the latest vSAN HCL data.
The periodic hardware compatibility check is a preconfigured scheduled task that you can edit and force to run at any time. By default, the task runs every 24 hours. The scheduled task is configured at a vCenter Server level. If a vCenter Server system contains no vSAN clusters that you manage with a single image, vSphere Lifecycle Manager skips the scheduled hardware compatibility check. This periodic task runs only for vSAN clusters that you manage with a single image.
vSphere Lifecycle Manager Operations That Trigger a Hardware Compatibility Check
- You edit the image for the cluster and save the image.
When you edit and save an image, vSphere Lifecycle Manager starts the Check hardware compatibility of cluster's host with image task even for clusters without vSAN. In such case, vSphere Lifecycle Manager only returns a warning that image hardware compatibility is not verified in non- vSAN clusters.
If the automatically triggered hardware compatibility task fails, you can still save the new image for the cluster.
- You initiate a remediation pre-check or remediation.
The hardware compatibility check is a part of the remediation pre-check and remediation task for vSAN clusters. If a cluster is not vSAN-enabled, vSphere Lifecycle Manager does not perform a hardware compatibility check when you initiate a remediation pre-check or remediation.
You can configure how vSphere Lifecycle Manager behaves in case of hardware compatibility issues by editing the remediation settings for the cluster. For information about configuring remediation settings for a cluster, see Configure vSphere Lifecycle Manager Remediation Settings for Clusters or Standalone Hosts that You Manage with a Single Image and Override the Global vSphere Lifecycle Manager Remediation Settings for a Cluster or Host That You Manage with a Single Image.
- You add or remove a host to and from the cluster.
When you add or remove a host to and from the cluster, vSphere Lifecycle Manager invalidates the hardware compatibility check results for the cluster and issues a warning. You must rerun a hardware compatibility check to obtain valid information about potential hardware compatibility issues. Alternatively, you can remediate the cluster or run a remediation pre-check, which both automatically trigger a hardware compatibility check.
NIC validation
Starting with vSphere 8.0, hardware compatibility checks for vSAN clusters are enhanced to incorporate NIC validation against the vSAN HCL. Determining the compatibility between the NICs in a vSAN cluster and the software defined in the image that the cluster uses is crucial to a successful cluster upgrade.
During a hardware compatibility check, for each NIC device, vSphere Lifecycle Manager verifies that the driver and firmware version combination defined in the image for the cluster is certified for use with all active features enabled on the device.
For NIC devices, vSphere Lifecycle Manager checks the exact firmware version during the hardware compatibility check.
In a vSAN cluster, during a hardware compatibility check, vSphere Lifecycle Manager validates only the RDMA-capable NICs that vSAN uses. That is, if a host has a RDMA-capable NIC but the NIC is not in use, vSphere Lifecycle Manager does not calculate the hardware compatibility of that device. vSphere Lifecycle Manager does not validate non-RDMA NICs. Non-RDMA NICs in use by vSAN need no certification and therefore vSphere Lifecycle Manager does not validate them during a hardware compatibility check.
System Requirements for NIC Validation
- vCenter Server 8.0 and later
- ESXi 8.0 and later
Disk Drive Validation
During a cluster-level hardware compatibility check, vSphere Lifecycle Manager verifies that the disk drives that vSAN uses are supported and certified as per the vSAN Hardware Compatibility List (vSAN HCL). vSphere Lifecycle Manager also ensures that the disk drive firmware version specified in the cluster image is compatible with the cluster hardware.
Supported Disk Drives Types
- HDD (SAS/SATA)
- SSD (SAS/SATA)
- SAS/SATA disk drives behind single-disk RAID-0 logical volumes
- NVMe devices behind a VMD controller
Note: vSphere Lifecycle Manager treats NVMe devices that are not VMD-enabled as PCI storage controllers. In the vSphere Client, hardware compatibility information about NVMe devices that are not VMD-enabled is available on the PCI Devices tab and not on the Disks tab.
System Requirements for Disk Drive Validation
- vCenter Server 7.0 Update 3 and later
- ESXi 7.0 and later
- For validation of NVMe devices behind a VMD controller, vCenter Server 8.0 and later and ESXi 8.0 and later
Important: Hardware compatibility checks do not validate NVMe devices behind a VMD controller, if the ESXi version of the hosts is earlier than 8.0. If you want to check the hardware compatibility of NVMe devices behind a VMD controller for hosts running an earlier version of ESXi, for example 7.0 Update 3, you have the following workarounds:
- Override manually the compliance status of the NVMe device behind a VMD controller.
- Upgrade your hosts to ESXi 8.0 or later.
RAID-0 Logical Volumes
- The RAID controller is in a RAID or mixed mode.
For more information about the RAID and mixed mode, see the VMware knowledge base article at https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/53573.
- vCenter Server 7.0 Update 3 and later
- ESXi 7.0 and later
- The hardware support manager must be upgraded and certified to work with vSphere 7.0 Update 3.
If the you do not use an upgraded version of the hardware support manager, the compliance status of the physical drives behind RAID-0 logical volumes is unknown. In this case, you must manually validate the disk drives and the target firmware version and override the compliance status for those disks.
Disk Drive Validation Results
vSphere Lifecycle Manager does not display a disk drive compatibility status and compatibility information for every single disk in the vSAN disk group. vSphere Lifecycle Manager groups the disk drives that vSAN uses by vendor, model, target firmware version, capacity, and part number. That is, all disk drives by the same vendor, the same model, and with the same target firmware version form one entry in the list of disk devices.
Disk drives can be compliant or non-compliant. In the cases when vSphere Lifecycle Manager cannot find a unique match for a disk device in the vSAN HCL, vSphere Lifecycle Manager prompts you to manually specify the exact device that you want to validate. vSphere Lifecycle Manager then calculates the compliance status based on your selection.
When vSphere Lifecycle Manager is unable to determine the disk drive compliance, the respective devices are listed as non-compliant. You can manually validate those devices and set the compliance status to compliant or non-compliant. For more information, see Change the Compliance Status of a Disk Device Manually.
For each entry in the disk device list, you can view summarized information about the disk, the compliance status, the number of affected hosts, and a label that shows whether the compliance status is manually set or whether the device is certified. The Used by vSAN label is attached to all disk devices that vSAN uses.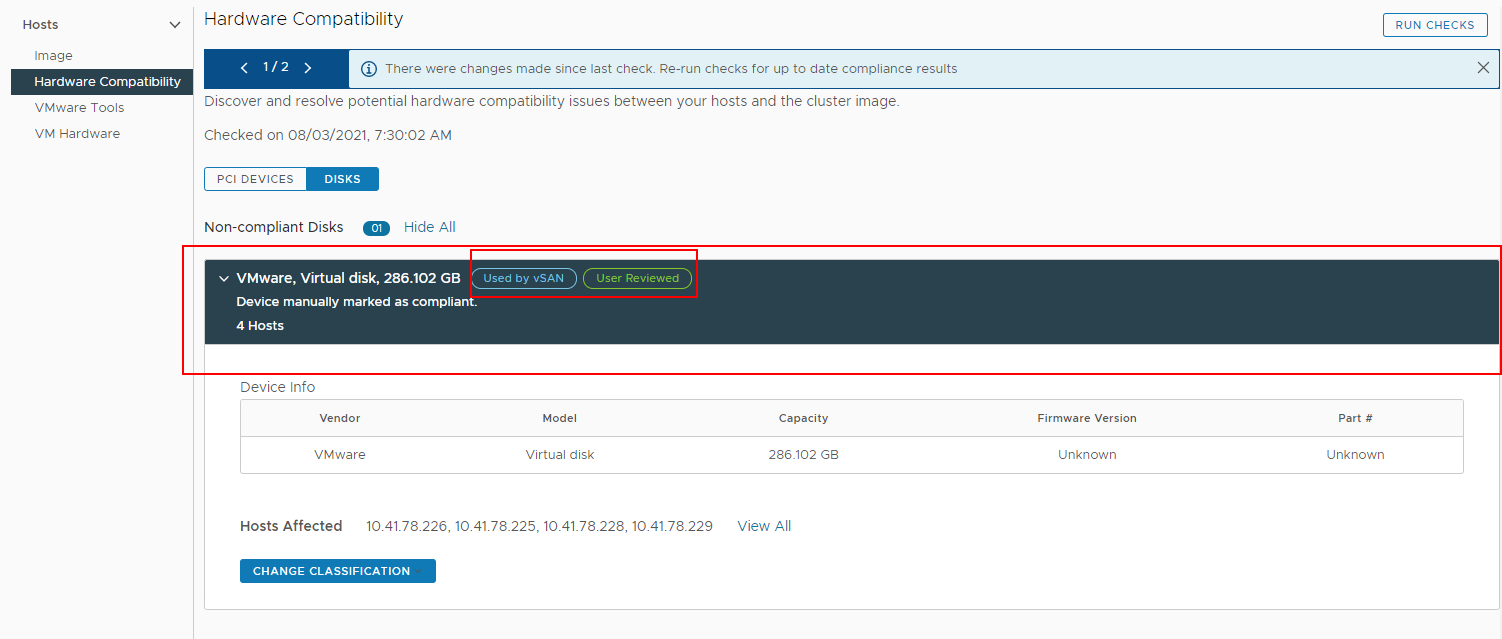
If you expand the entry, you can view detailed compliance information about the respective disk device and the affected hosts.
When a new disk is added to a vSAN cluster, you must manually re-run the check to obtain the new compliance information about the cluster. Similarly, if you remove a disk from the vSAN disk group, you must re-run the hardware compatibility check to obtain an updated compliance information about the cluster.