When you start your ESXi host or rescan your storage adapter, the host discovers all physical paths to storage devices available to the host. Based on a set of claim rules, the host determines which multipathing module, the NMP, HPP, or an MPP, owns the paths to a particular device.
The module that owns the device becomes responsible for managing the multipathing support for the device. By default, the host performs a periodic path evaluation every five minutes and assigns unclaimed paths to the appropriate module.
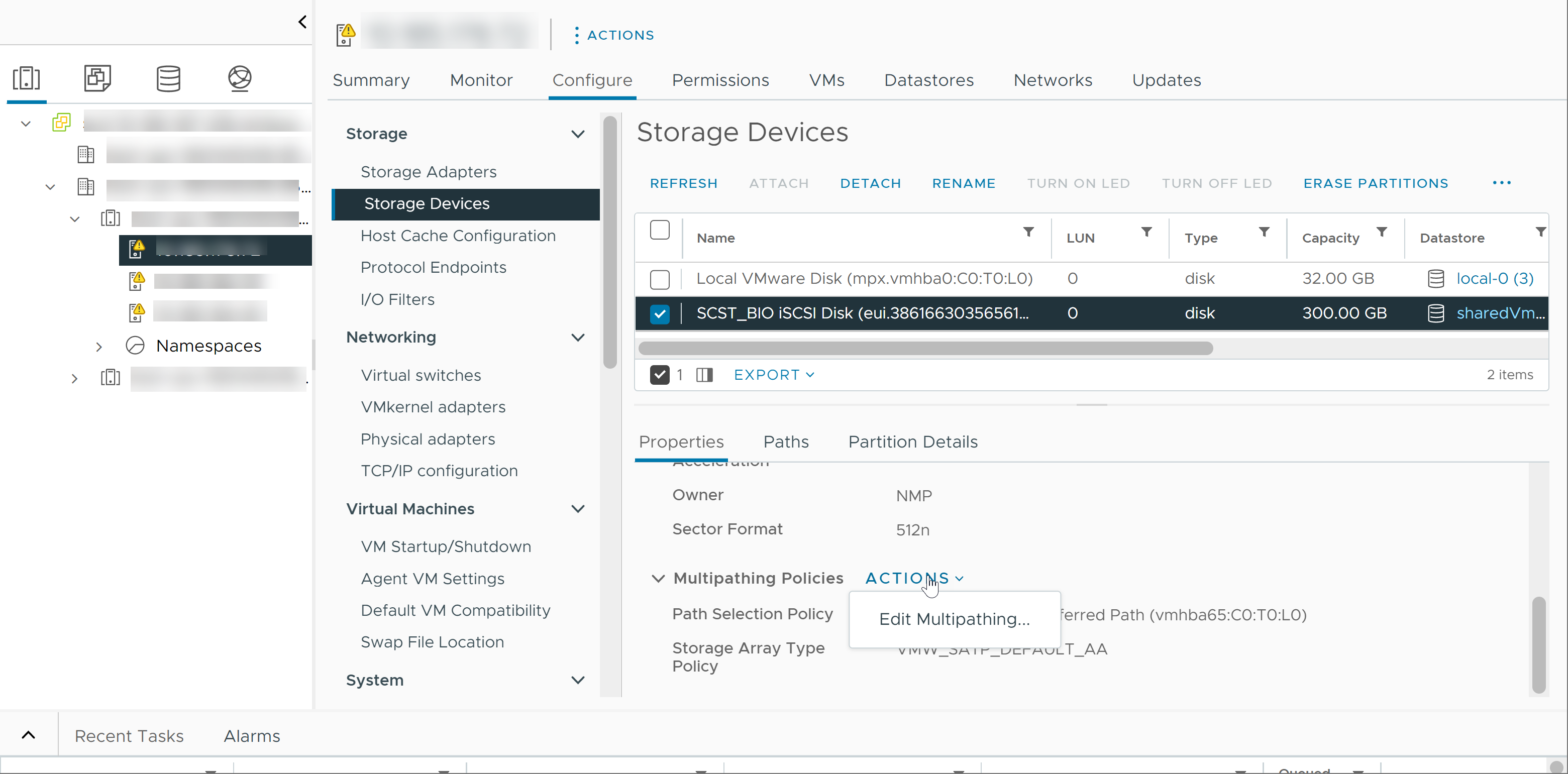
For the paths managed by the NMP module, a second set of claim rules is used. These rules assign an SATP and PSP modules to each storage device and determine which Storage Array Type Policy and Path Selection Policy to apply.
Use the vSphere Client to view the Storage Array Type Policy and Path Selection Policy assigned to a specific storage device. You can also check the status of all available paths for this storage device. If needed, you can change the default Path Selection Policy using the client.
To change the default multipathing module or SATP, modify claim rules using the vSphere CLI.
You can find some information about modifying claim rules in Using Claim Rules to Control ESXi Multipathing Modules.
To learn more about multipathing modules, see Multipathing Concepts and Acronyms.
View Storage Device Paths
View which multipathing policies the host uses for a specific storage device and the status of all available paths for this storage device.
Procedure
View Datastore Paths
Review the paths that connect to storage devices backing your VMFS datastores.
Procedure
Change the Path Selection Policy
Generally, you do not need to change the default multipathing settings that your ESXi host uses for a specific storage device. If you want to make any changes, you can use the Edit Multipathing Policies dialog box to modify the path selection policy. You can also use this dialog box to change multipathing for SCSI-based protocol endpoints.
Procedure
Change Default Parameters for Latency Round Robin
On the ESXi host, you can activate the latency mechanism for the Round Robin path selection policy. The mechanism considers I/O bandwidth and path latency to select an optimal path for I/O. When using the latency mechanism, the Round Robin policy can dynamically select the optimal path and achieve better load balancing results.
When latency is activated, usage of paths for the I/Os depends on the workload. When a large number of paths is available, but the workload is not high enough, the system might not use some paths for I/Os.
You use the esxcli command to change the default parameters of the latency mechanism or deactivate the mechanism.
Prerequisites
Set the path selection policy to Round Robin. See Change the Path Selection Policy.
Procedure
What to do next
To deactivate the latency mechanism, in the Advanced System Settings for your host, change the Misc.EnablePSPLatencyPolicy parameter to 0.
Deactivate Storage Paths
You can temporarily deactivate paths for maintenance or other reasons.