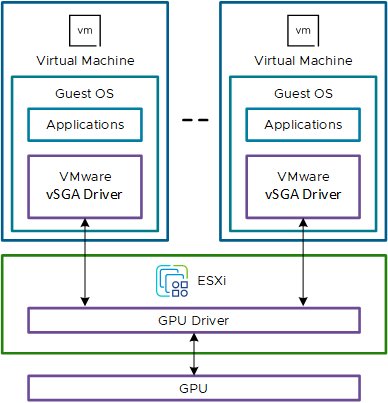
Virtual Shared Graphics Acceleration (vSGA) enables sharing a physical GPU across multiple virtual desktops.
- Virtual Shared Graphics Acceleration (vSGA).
- Virtual Shared Graphics Passthrough Graphics Acceleration (vGPU/DVX).
- Virtual Dedicated Graphics Acceleration (vDGA).
With vSGA, the physical GPUs in the ESXi host are virtualized and shared across multiple VMs.
Graphics Acceleration Types Comparison
The following table compares the features of the three types of graphics acceleration.
| vSGA | vGPU/DVX | vDGA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consolidation | High (limited by video memory) | Up to 1:32 | None (1:1) |
| Performance Level | Lightweight to mid-level | Mid-level or Workstation | Workstation |
| Application Compatibility | Limited | All supported versions | All supported versions |
| Maximum DirectX Level |
|
All supported versions | All supported versions |
| Maximum OpenGL version |
|
All supported versions | All supported versions |
| Video encoding and decoding | Software | Hardware | Hardware |
| OpenCL or CUDA compute | No | Yes | Yes |
| vSphere vMotion Support | Yes | Limited | No |
| Microsoft Virtualization-based Security (VBS) | Yes | No | No |
Use Case for vSGA Graphics
vSGA is designed to address the knowledge worker use case where the graphics load is usually low. The knowledge workers use various non-specialized end-user applications that do not demand complex models to render.
Advantages of vSGA
The use of vSGA results in enhanced manageability, streamlined consolidation, and efficiency.
- Manageability
-
vSGA supports the following features which allow an Administrator to easily manage their infrastructure at scale.
- Suspend and resume a VM.
- VM migration with vMotion.
- Guest operating system and ESXi host driver compatibility across vSphere versions.
- vSphere DRS for initial placement of VMs and load-balancing.
- Consolidation
-
vSGA allows efficient use of hardware acceleration by leveraging VMs with different performance requirements on a single GPU.
The elasticity of vSGA allows a higher density of VMs per graphics card compared to vGPU and DVX solutions.
Hardware Requirements for Hardware Accelerated Graphics
For more information about the hardware requirements for graphics acceleration solutions, see the following table.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Space for Graphics Cards | Many high-end graphics cards are full-height, full-length, and double-width. Most of them take two slots on the motherboard but use a single PCIe x16 slot. To accommodate the selected GPU card in the appropriate PCIe slot, verify that the ESXi host has enough disk space. |
| Host Power Supply Units (PSU) | Check the power requirements of the GPU and cooling requirements of the server to make sure that the PSU is powerful enough and contains the proper power cables to power the GPU. |
| Two Display Adapters | If the ESXi host does not have an extra graphics adapter, you can install an additional low-end display adapter to act as a primary display adapter. If the GPU is set as a primary display for the ESXi host, vSGA cannot use the GPU for rendering. If two GPUs are installed, the server BIOS might have the option to select which GPU is primary and which is secondary. |