In this example, a router that is running an IS-IS service goes down. The example assumes that the device has multiple physical interfaces that have multiple IS-IS interfaces, which means that the device supports multiple IS-IS adjacencies.
In this example, IP Availability Manager:
-
Diagnoses a Router Down problem.
-
Generates multiple Router Unresponsive events as impacts of the Router Down problem.
-
Generates a NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping event as an impact of the Router Down problem.
-
Exports the Router Down problem, the multiple Router Unresponsive events, and the NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping event to the Global Manager.
-
Exports multiple NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping event-type statuses and a NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping event-type status to Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS.
Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS:
-
Receives the multiple Router Unresponsive event-type statuses from IP Availability Manager.
-
Receives the NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping event-type status from IP Availability Manager.
-
Detects alarming IS-IS adjacencies for which the Router Unresponsive event-type statuses are associated with the physical interfaces that are underlying the alarming IS-IS adjacencies.
As indicated in GUID-03D4DEAE-068A-4BD8-B4F0-EB4112535CD5.html#GUID-03D4DEAE-068A-4BD8-B4F0-EB4112535CD5___NPM_ISIS_USER_CROSS_COR_EVENT_79289, Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS perceives the Router Unresponsive event-type status as a problem-type status.
Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS then:
-
Generates multiple ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm events.
-
Generates multiple Router Unresponsive problems.
-
Correlates each ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm event with the associated Router Unresponsive problem and marks the event as an impact of the problem.
-
Exports the Router Unresponsive problems and the ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm events to the Global Manager.
The Global Manager:
-
Receives the Router Down problem and the Router Unresponsive and NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping events from IP Availability Manager.
-
Receives the Router Unresponsive problems and the ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm events from Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS.
-
Combines each Router Unresponsive event from IP Availability Manager with the identical Router Unresponsive problem from Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS to form one notification that has two sources.
-
Associates the multiple Router Unresponsive notifications as impacts of the Router Down notification.
-
Associates the multiple ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm notifications from Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS as impacts of the Router Down notification.
-
Associates the NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping notification from IP Availability Manager as an impact of the Router Down notification.
What follows is a summary of the notifications that are created for the Router Down problem, followed by a display in Notification Properties dialog box that shows a Router Down problem that shows how the Global Manager associates the network and IS-IS events as impacts of the Router Down problem:
-
IP Availability Manager events:
-
Problem: Router Down
-
Event (impact): Router Unresponsive, Router Unresponsive, ...
-
NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping
-
Network Protocol Manager for IS-IS events:
-
Problem: Router Unresponsive, Router Unresponsive, ...
-
Event (impact): ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm,
-
ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm, ...
-
Global Manager notifications:
-
Root cause: Router Down
-
Impacts: Router Unresponsive, Router Unresponsive, ...,
-
NetworkConnection DownOrFlapping, ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm,
-
ISISAdjacency NeighborStateAlarm, ...
Figure 1. Notification Properties dialog box that shows a Router Down problem 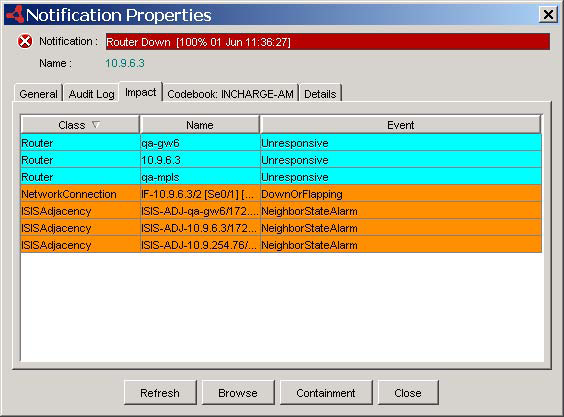
Chapter 2, Viewing IS-IS Analysis Results and Topology, provides instructions on viewing detailed notification information.