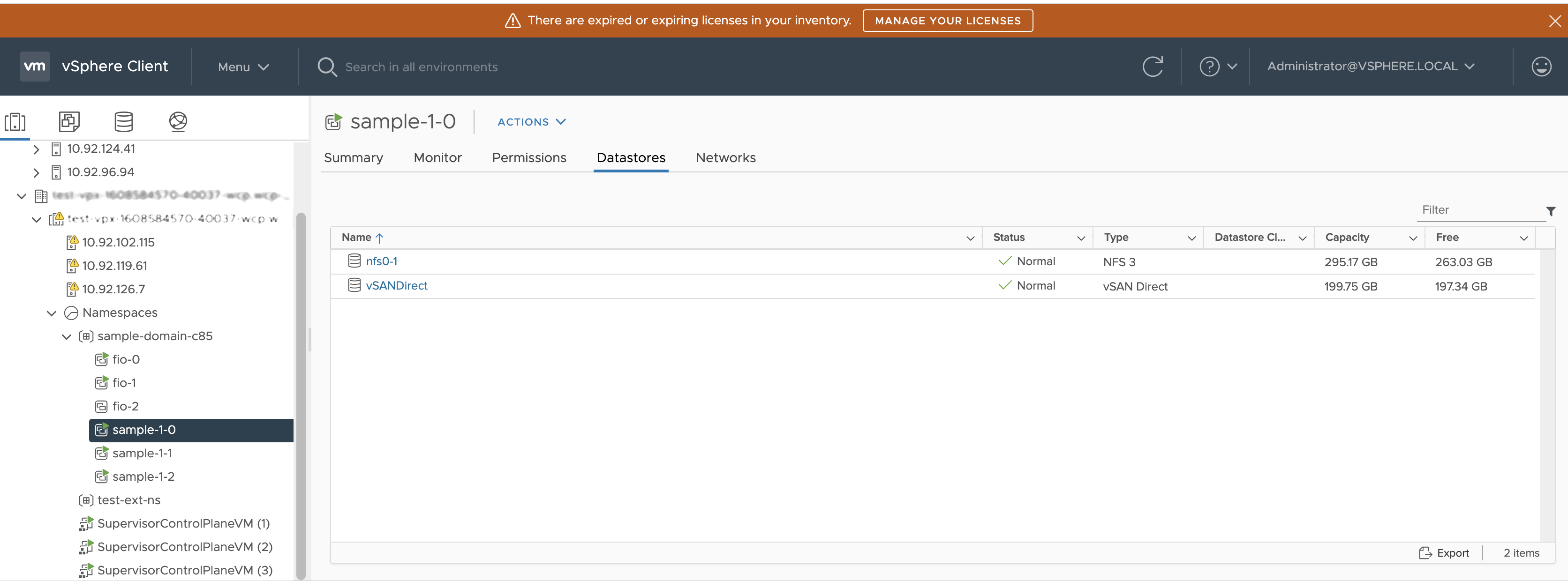
When you use vSAN Direct in the vSphere with Tanzu environment, you can use external shared storage to store management internal VMs and other metadata.
Problem
When you deploy a homogeneous vSAN Direct cluster, you must create a replicated vSAN datastore on each ESXi host in the cluster to store vSphere with Tanzu management VMs and other metadata. The vSAN datastore consumes space, requires an additional I/O controller on each host, and limits hardware configuration on which vSAN Direct can be supported.
Instead of configuring the vSAN datastore, you can use external shared storage for storing management internal VMs and other metadata.
Solution
- If vSAN or vSAN Direct was deployed on the ESXi hosts in the cluster, clear the hosts from any configuration.
- Remove any disks assigned to vSAN or vSAN Direct. See Remove Disk Groups or Devices from vSAN.
- (Optional) Use the script to tag disks on the hosts for vSAN Direct. See Using Script to Tag Storage Devices for vSAN Direct.
- Use VMware Cloud Foundation to create a workload domain with external storage.
Make sure to select one of the storage options, such as NFS, vVols, or FC. Only one of these options can be selected.
This step deploys a workload domain with
vCenter Server and specified
ESXi hosts. The external storage is mounted on all hosts and added to the default cluster.
- Enable vSAN.
Make sure that no disks are claimed for vSAN.
This step creates a zero byte vSAN datastore with vSAN network. No local disks are used for vSAN.
- Claim local disks on the hosts for vSAN Direct.
For each device you claim,
vSAN Direct creates a separate datastore.
- Create storage policies for vSAN Direct.
- Configure and enable Workload Management.
Example
In this example, a setup includes external NFS storage and a vSAN Direct datastore. Control plane VMs and vSphere Pods are running on external NFS storage. Persistent volume claims run on vSAN Direct.