A storage provider is a software component that is offered by VMware or developed by a third party through vSphere APIs for Storage Awareness (VASA). The storage provider can also be called VASA provider. The storage providers integrate with various storage entities that include external physical storage and storage abstractions, such as vSAN and Virtual Volumes. Storage providers can also support software solutions, for example, I/O filters.
Storage Provider Concepts
- Persistence Storage Providers
- Storage providers that manage arrays and storage abstractions, are called persistence storage providers. Providers that support Virtual Volumes or vSAN belong to this category. In addition to storage, persistence providers can provide other data services, such as replication.
- Data Service Providers
- Another category of providers is I/O filter storage providers, or data service providers. These providers offer data services that include host-based caching, compression, and encryption.
- Built-in Storage Providers
- Built-in storage providers are offered by VMware. Typically, they do not require registration. For example, the storage providers that support vSAN or I/O filters are build-in and become registered automatically.
- Third-Party Storage Providers
- When a third party offers a storage provider, you typically must register the provider. An example of such a provider is the Virtual Volumes provider. You use the vSphere Client to register and manage each storage provider component.
The following graphic illustrates how different types of storage providers facilitate communications between vCenter Server and ESXi and other components of your storage environment. For example, the components might include storage arrays, Virtual Volumes storage, and I/O filters.
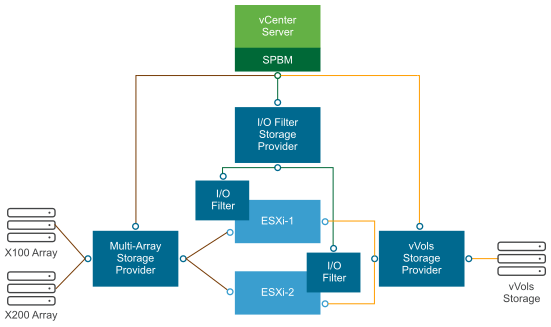
Storage Providers and Data Representation
Information that the storage provider supplies can be divided into the following categories:
- Storage data services and capabilities. This type of information is essential for such functionalities as vSAN, Virtual Volumes, and I/O filters. The storage provider that represents these functionalities integrates with the Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM) mechanism. The storage provider collects information about data services that are offered by underlying storage entities or available I/O filters.
You reference these data services when you define storage requirements for virtual machines and virtual disks in a storage policy. Depending on your environment, the SPBM mechanism ensures appropriate storage placement for a virtual machine or enables specific data services for virtual disks. For details, see Creating and Managing vSphere VM Storage Policies.
- Storage status. This category includes reporting about status of various storage entities. It also includes alarms and events for notifying about configuration changes.
This type of information can help you troubleshoot storage connectivity and performance problems. It can also help you to correlate array-generated events and alarms to corresponding performance and load changes on the array.
- Storage DRS information for the distributed resource scheduling on block devices or file systems. This information helps to ensure that decisions made by Storage DRS are compatible with resource management decisions internal to the storage systems.
Storage Provider Requirements and Considerations
When you use third-party storage provider, vendors are responsible for supplying storage providers. The VMware VASA program defines an architecture that integrates third-party storage providers into the vSphere environment, so that vCenter Server and ESXi hosts can communicate with the storage providers.
To use storage providers, follow these requirements:
- Make sure that every storage provider you use is certified by VMware and properly deployed. For information about deploying the storage providers, contact your storage vendor.
- Make sure that the storage provider is compatible with the vCenter Server and ESXi versions. See VMware Compatibility Guide.
- Do not install the VASA provider on the same system as vCenter Server.
- If your environment contains older versions of storage providers, existing functionality continues to work. However, to use new features, upgrade your storage provider to a new version.
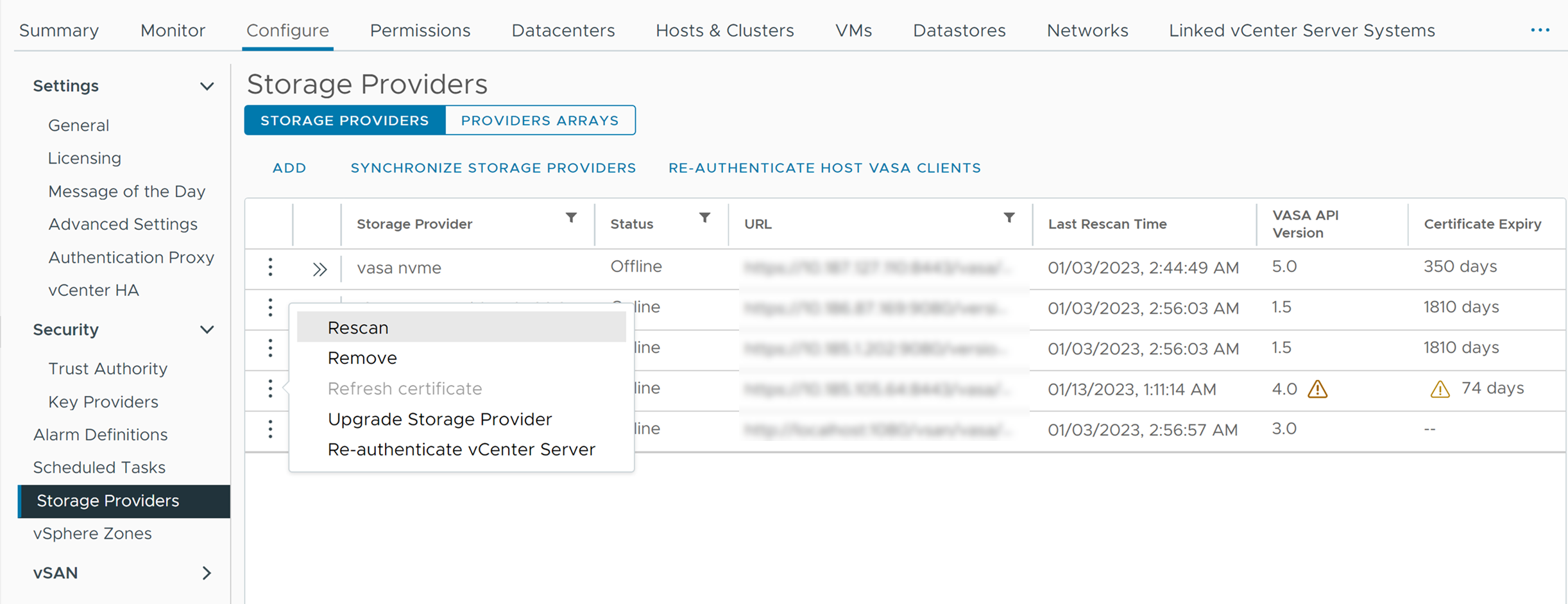
Managing Storage Providers
You might need to register certain types of storage providers to establish their connection to vCenter Server. You can then review and manage the storage providers.
Register Storage Providers
Use the vSphere Client to register a separate storage provider for each host in a cluster.
Prerequisites
Procedure
- Navigate to vCenter Server.
- Click the Configure tab, and click Storage Providers.
- Click the Add icon.
- Enter connection information for the storage provider, including the name, URL, and credentials.
- Click OK.
Results
What to do next
To troubleshoot registration of your storage provider, see the VMware Knowledge Base article https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/49798.
View Storage Provider Information
After you register a storage provider component with vCenter Server, the storage provider appears on the storage providers list. Certain storage providers are self-registered and automatically appear on the list after you set up the entity they represent, for example, vSAN or I/O filters.
Procedure
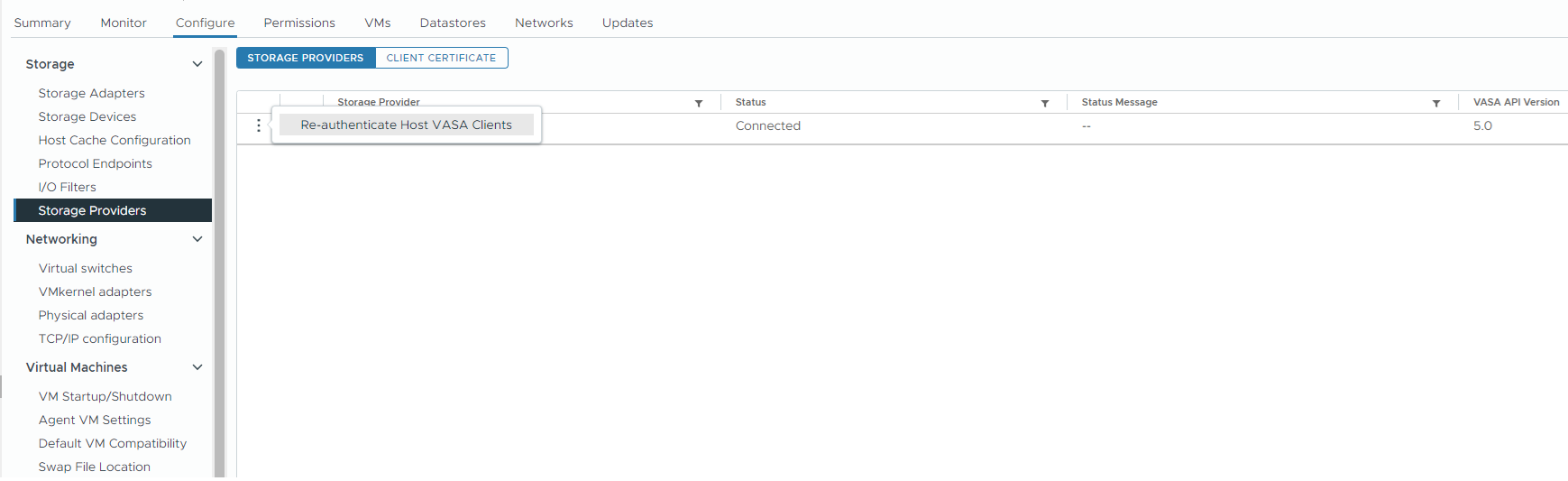
Re-authenticate Host VASA Client
Starting from vSphere 8.0 Update 3, you can monitor the storage provider connection and authentication status on each ESXi host. If there is an authentication issue in a specific host, you can re-authenticate the specific host against the storage provider.
Use the vSphere Client to monitor the storage providers.
Prerequisites
Register storage providers. See Register Storage Providers for Virtual Volumes.
Procedure
Manage Storage Providers
Use the vSphere Client to perform several management operations on the registered storage providers.