You can configure GNS-scoped actionable SLO through the UI or API to track SLIs for a microservice.
A GNS-scoped actionable SLO can monitor and influence a scaling action on a single service in a global namespace. In addition, you can associate an autoscaling policy with an actionable SLO. The actionable SLO prevents the autoscaling policy in efficiency mode from scaling down resources when one or more SLIs for the SLO are in violation. For more information about autoscaling policies, see the Service Autoscaling with Tanzu Service Mesh User’s Guide.
On configuring the GNS-scoped actionable SLO, a monthly error budget based on the set SLO target is allocated across all service instances pertaining to the service inside the global namespace. When any of the service instances violates one or more SLIs, the error budget is depleted.
Example of Use Case 1B
To apply a GNS-scoped actionable SLO to a service first set up an SLO. SLIs that indicate the service quality level and what thresholds are expected to be met.
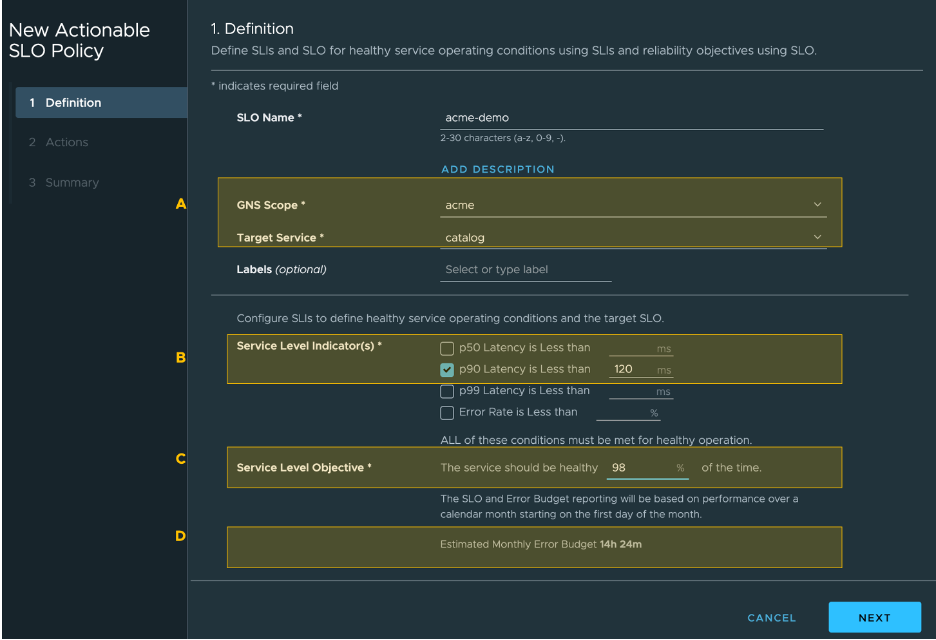
This screenshot shows that (A) is gns-scoped (applied at the GNS level) and Target Service is catalog. The SLO applies to all the versions of the selected service, that is 'catalog'.Additionally, all existing and future versions of the service will also be monitored by the SLO. This allows SLO as a service-level contract to remain intact regardless of the various versions underneath the service. (B) 90th percentile latency (the latencies for more than 90 percent of the requests) must be below 120 ms, (C)at least 98 percent of the time (D). That means that users can experience the service to have latencies exceed the threshold 14 hours and 24 minutes in a month without violating the SLO. The error budget depletion is done over a calendar month and replenished on the first day of every month.
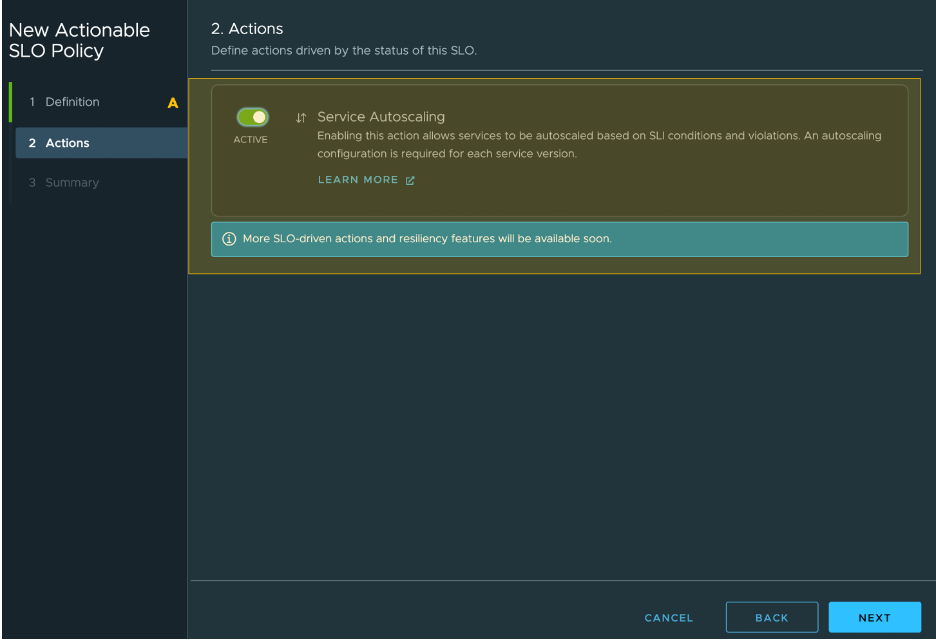
Optionally the Actionable SLO can influence resiliency functions for service versions like Service Autoscaling.
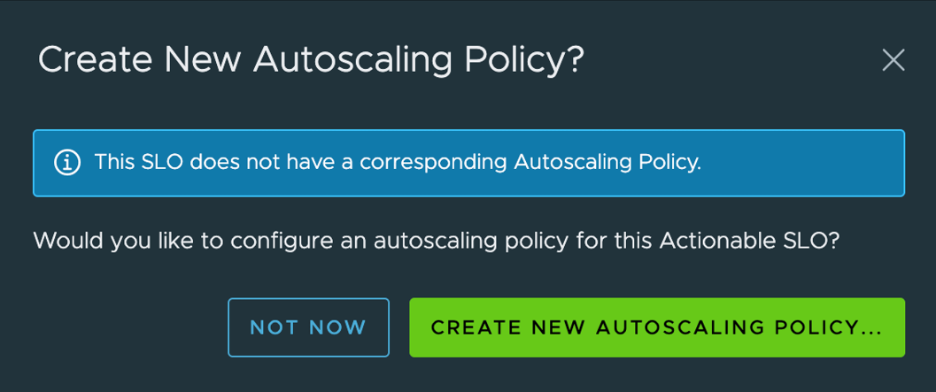
If the service doesn't have an autoscaling policy, the following dialog box prompt you to configure one for the actionable SLO.
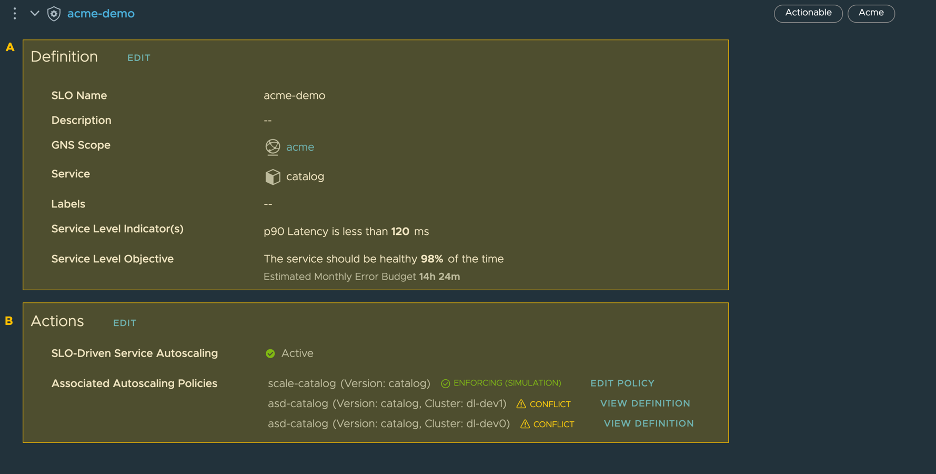
Once an autoscaling policy is associated with an actionable SLO, we can edit the autoscaling policy through the SLO page, as shown in the screenshot below.
A. Definition. This section provides the summary of the created SLO.
B. Actions. This section provides details of the autoscaling policies associated with the service on which the actionable SLO is enabled. It also provides the status of those associated autoscaling policies, along with an option to edit the associated autoscaling policy. Note that autoscaling policies are configured at service version level.
You can also track the SLO error budget depletion, the SLO status, and the SLIs for the service on the SLO Dashboard. You can also track this information on the Service Performance Tab. To find autoscaling in action, see Use Case 3: Use Actionable SLOs to Influence Autoscaling.