Starting with VMware Cloud Director 10.6, service providers can assign to organizations the rights to create and manage other organizations, making them sub-providers.
VMware Cloud Director 10.6 introduces the concept of the sub-providers in addition to the service providers and tenants. A sub-provider is a tenant persona that can create tenant organizations and manage them. A provider can empower a tenant organization to become a sub-provider by granting it the necessary administrative rights and a right to traverse into other organizations. You, as a sub-provider administrator cannot further grant these rights to your tenants.
- Create organizations
- Create, view, manage, and delete organization VDCs
- Create, view, manage, and delete organization VDC networks
- Switch in to organizations
- Set up organization IdPs
- Perform all standard tenant operations
- Create and publish roles
- Create and publish rights bundles
- View external networks
- Share and publish catalogs
- Manage catalog subscriptions
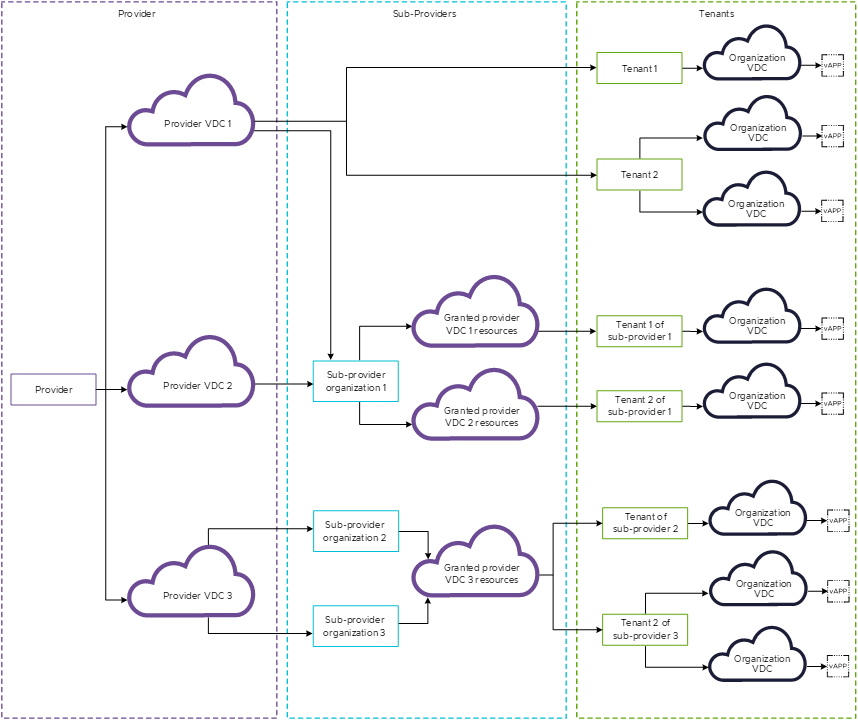
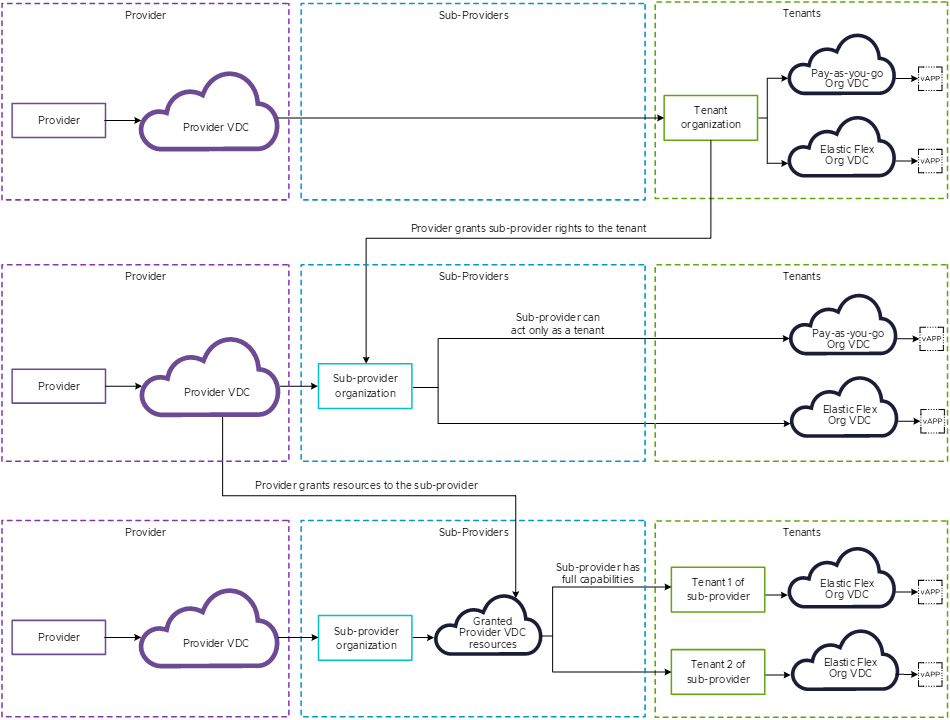
A sub-provider organization can receive grants from more than one provider VDCs. See View All Provider VDCs Available to Your Sub-Provider Organization. You can use those grants, or in other words, the finite granted provider VDC resources, to create elastic Flex organization VDCs. See Create a VMware Cloud Director Organization VDC as a Sub-Provider.
You cannot exceed your granted resources. For example, if a provider has a provider VDC with 100 GB of memory reservation available, but they grant to your sub-provider organization 10 GB memory reservation, in your sub-provider organization, you can see only 10 GB memory reservation available.
Compute Overprovisioning
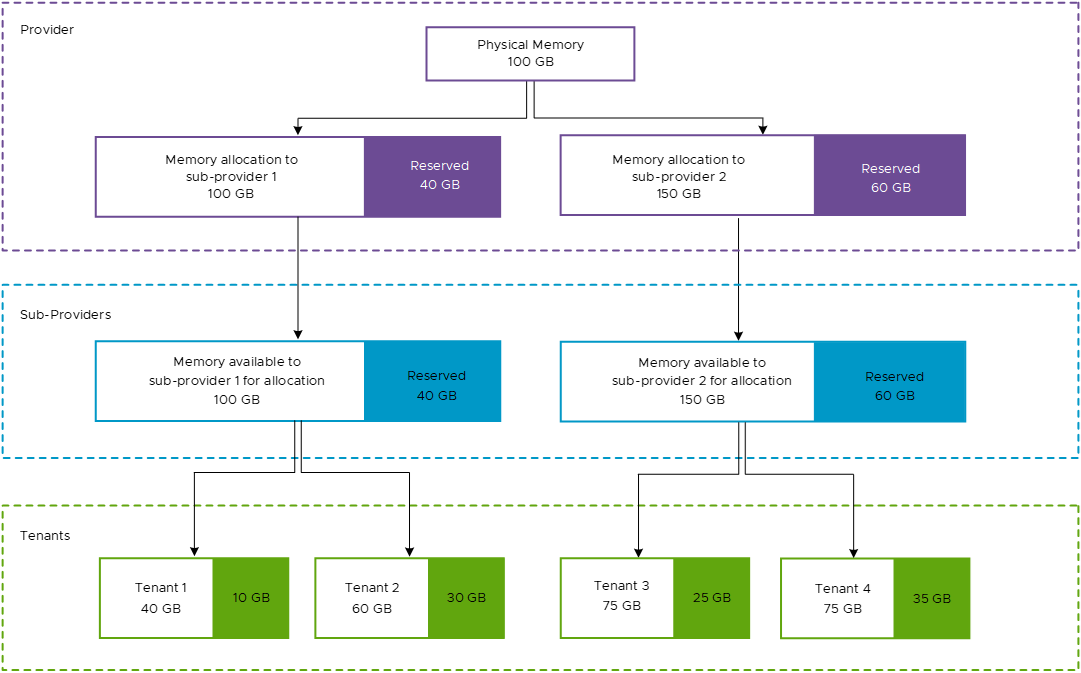
CPU and memory allocation and overprovisioning are identical.
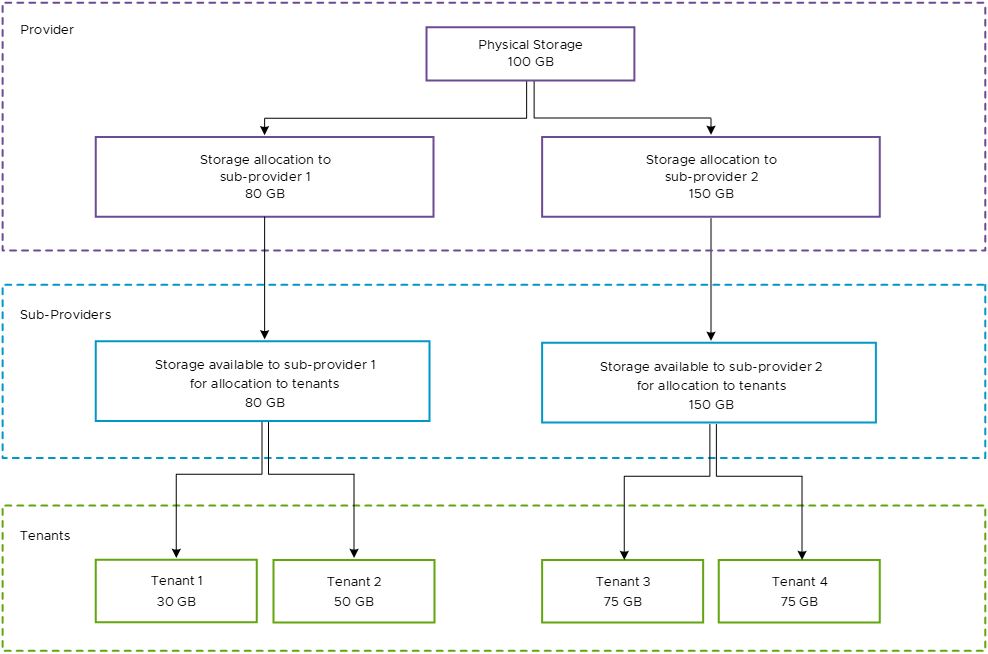
Storage Provisioning
Providers can grant provider VDC storage policies to their tenants. Sub-providers can consume granted storage policies by publishing them to their tenant organization VDCs. Unlike CPU and memory, you cannot overprovision storage. As a sub-provider, you cannot allocate to your tenants more than your storage allocation. For example, if a provider has 100 GB of storage and grants to a sub-provider a storage policy with only 50 GB, the sub-provider can allocate to their tenant organization VDCs a total of 50 GB.
A provider can grant more storage than physically available. However, the sub-providers do not have any visibility into how much they are overprovisioning to their tenants because they do not know how much physical storage there is.
Provisioning Networking Resources
On the Cloud Resources tab, you can view all NSX edge clusters and network pools that your service provider granted to your sub-provider organization.
The behavior between VMware Cloud Director service providers and tenants is identical to the behavior between sub-providers and their tenants.
As a sub-provider administrator, you can create an edge gateway in the context of your tenant and connect the edge gateway to a provider gateway that you own. See Create an Edge Gateway Backed by an NSX Provider Gateway in the VMware Cloud Director Tenant Portal.
You can configure private IP spaces that you can use to give IPs and prefixes to your tenants. You can manage quotas for IP spaces that you own. See Managing IP Spaces in your VMware Cloud Director Tenant Portal.
You can configure a network that stretches from your sub-provider organization to the organizations of your managed tenants. In this scenario, your tenants can only connect to those networks without the ability to manage them. See Manage the Participating VDCs in a Data Center Group in the VMware Cloud Director Tenant Portal.
Limitations of tenant organizations that sub-providers manage
- You cannot reassign a tenant organization managed by the
Systemorganization to a sub-provider. - You cannot reassign to the
Systemorganization a tenant organization that a sub-provider manages. - You cannot reassign to a different sub-provider a tenant organization already managed by a sub-provider.