This section describes how to configure a Security Policy for VMware Cloud Web Security.
Before you begin:
To configure a Security Policy, users must have first created a Security Policy. For specific instructions on how to create a Security Policy, see Creating a Security Policy.
About this Task:
In this section, users will learn how configure the Security Policy that was created in the section titled, Creating a Security Policy. When creating a Security Policy, the following are the rule categories that users can configure: Secure sockets layer (SSL) Inspection, Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Web Security, and Web Application.
When creating a Web Security policy rule, users can configure: URL Filtering, Geo-Based Filtering, Content Filtering, and Content Inspection.
Google developed the QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) protocol to increase the performance of HTTPS and HTTP (TCP 443 and TCP 80) connections. Chrome browsers have had experimental support for it since 2014, and it is also used in Chromium (for example, Microsoft Edge, Opera, and Brave) and Android devices.
QUIC connections do not require TCP handshakes. However, SSL inspection requires TCP session information and Cloud Web Security performs SSL Inspection by default (unless a bypass rule is explicitly configured to prevent it) and thus Cloud Web Security cannot examine QUIC sessions where SSL Inspection is being done. In such instances where QUIC is activated and SSL Inspection is being performed, this can result in a policy not being applied during a user session.
To ensure that Cloud Web Security policies are consistently applied, it is recommended that the QUIC protocol is either blocked or deactivated on the browser.
To block QUIC, configure your browser or firewall to block UDP 443 and UDP 80 as these are the ports the QUIC protocol uses. When the QUIC protocol is blocked, QUIC has a failsafe to fall back to TCP. This activates SSL inspection without negatively impacting the user experience.
To deactivate QUIC on a Chromium browser, please check the documentation for the respective browser.
To deactivate QUIC on a Chrome browser:
- Open Chrome
- In the address bar type: chrome://flags
- In the search bar, type "quic".
- Click the drop-down and select Disabled.
- When Default is selected, Chrome will attempt to use QUIC.
- When prompted, click Relaunch Now to restart Chrome and apply your changes.
Procedure:
- In the Security Policies page of the new UI of the VMware SD-WAN Orchestrator, click the Security Policy name for the policy to be configured.

The Security Policies screen for the selected policy appears.
- From the selected Security Policy page, users can configure rules from the following rule categories: SSL Inspection, Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Web Security, Web Application, and Data Loss Prevention (DLP).
Important: By default, a Security Policy has “allow all” and “decrypt all” rules. By configuring any of the five rule categories listed above, users are overriding default rules and creating a policy comprised of their own rules.
For a complete description of how to configure rules for each category, see:
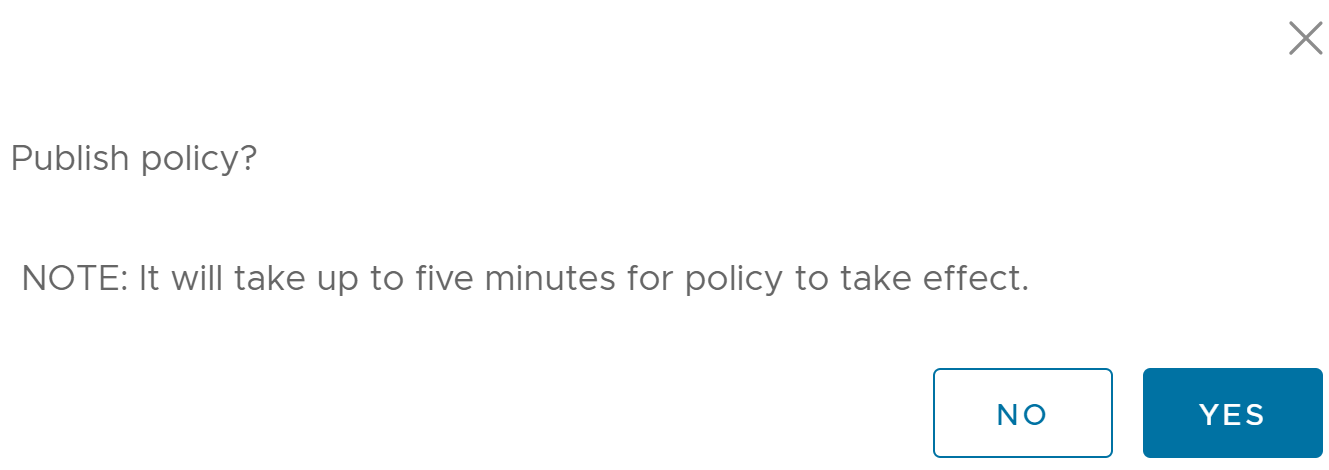
- After configuring the Security Policy, click the Publish button to publish the Security Policy.
- Click the Yes button in the Publish Policy pop up dialog to publish the policy.
A green banner appears on the top of the screen indicating that the Security Policy is being published.
Note: A Security Policy can be published at any time in the configuration process and be republished whenever users reconfigure it.