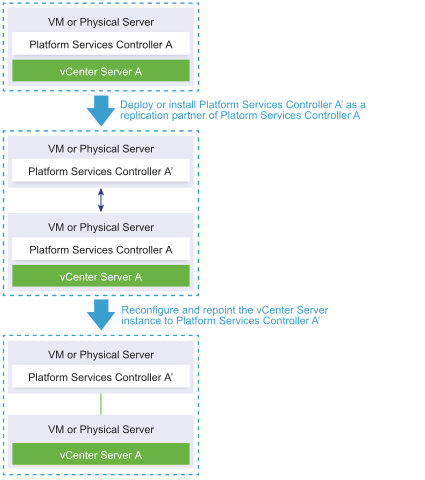
If you have deployed or installed a standalone vCenter Server instance with an embedded Platform Services Controller and you want to extend your vCenter Single Sign-On domain with more vCenter Server instances, you can reconfigure and repoint the existing vCenter Server instance to an external Platform Services Controller.
Note: The reconfiguration of a
vCenter Server instance with an embedded
Platform Services Controller and repointing it to an external
Platform Services Controller instance is a one-way process after which you cannot switch back to
vCenter Server with an embedded
Platform Services Controller.
Prerequisites
- Deploy or install the external Platform Services Controller instance as a replication partner of the existing embedded Platform Services Controller instance in the same vCenter Single Sign-On site.
Note: You can determine the current vCenter Single Sign-On site by using the vmfad-cli command.
- For a vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, log in to the appliance shell as root and run the command. /usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vmafd-cli get-site-name --server-name localhost
- For a Windows installation of vCenter Server instance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, log in to the Windows machine as an administrator, open the Windows command prompt, and run the command. C:\Program Files\VMware\vCenter Server\vmafdd\vmafd-cli get-site-name --server-name localhost
- For a vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, log in to the appliance shell as root and run the command.
- Create snapshots of the vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller and the external Platform Services Controller instance, so that you can revert to the snapshots if the reconfiguration fails.
- If you want to reconfigure a vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller that is configured in a vCenter HA cluster, remove the vCenter HA configuration. For information about removing a vCenter HA configuration, see vSphere Availability.
Procedure
Results
What to do next
- You can deploy or install additional vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller instances in the vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
- If you reconfigured a vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller that was configured in a vCenter HA cluster, you can reconfigure the vCenter HA cluster. For information about configuring vCenter HA, see vSphere Availability.


