VMware SD-WAN Gateways are a distributed network of gateways, deployed around the world or on-premises at service providers, provide scalability, redundancy and on-demand flexibility. The SD-WAN Gateways optimize data paths to all applications, branches, and data centers along with the ability to deliver network services to and from the cloud.
By default, the Gateways named as gateway-1 and gateway-2 are available when you install SASE Orchestrator. If required, you can create additional Gateways.
Partner Super user and Admin with Gateway management access activated can create, manage, and delete Gateways created by a Partner or Partner managed Gateways created by an Operator. The Partner IT support users can only view the configured Gateways.
-
Log into the Orchestrator as a Partner Super user or Admin user.
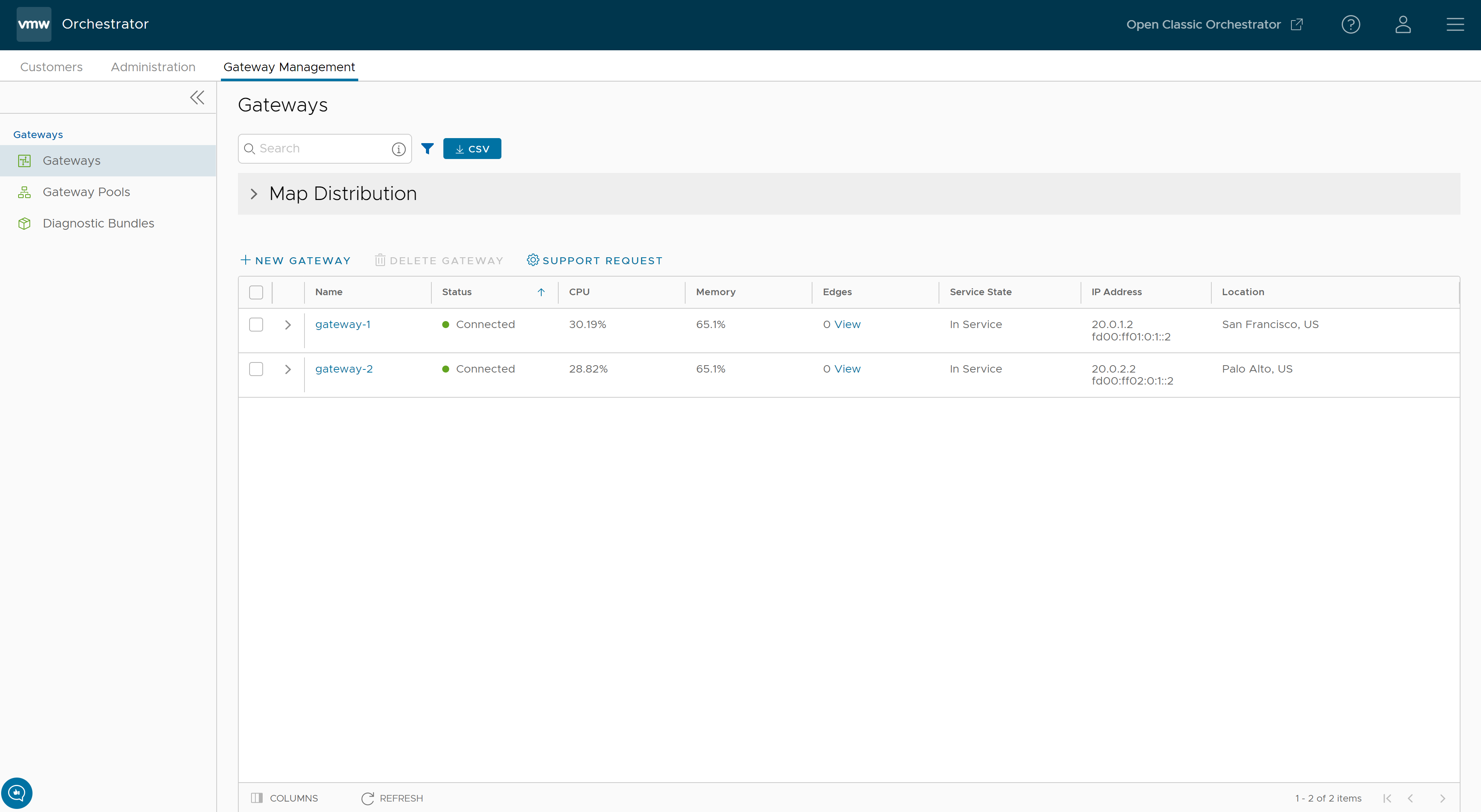
- In the Orchestrator UI, click the Gateway Management tab and go to Gateways in the left navigation pane.
The Gateways page appears.
To search a specific Gateway, enter a relevant search text in the Search box. For advanced search, click the filter icon next to the Search box to filter the results by specific criteria.
The Map Distribution section is used for displaying the Gateways on a map. You can click the + and - buttons to zoom in and zoom out the map, respectively.
The Gateways table displays the existing Gateways with the following details.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Gateway |
| Status |
Reflects the success or failure of periodic heartbeats sent by mgd to the Orchestrator and does not indicate the status of the data and control plane. The following are the possible statuses:
|
| CPU | Average CPU utilization of all the cores in the system at the time of the last heartbeat. |
| Memory | Percentage usage of the physical memory by all processes in the system as reported by psutil.phymem_usage at the time of the last heartbeat. This is similar to estimating the percentage of memory usage using the free command. |
| Edges | Number of Edges connected to the Gateway at the time of the last heartbeat.
Note: Click
View next to the number of Edges, to view all the Edges assigned to the Gateway as well as their online/offline status on the Orchestrator. This option does not display the Edges that are actually connected to the Gateway.
|
| Service State | The user-configured service state of the Gateway and whether it is eligible to be assigned to new Edges. |
| IP Address | The public IP address that public WAN links of an Edge use to connect to the Gateway. This IP address is used to uniquely identify the Gateway. If the Gateway is enabled to accommodate both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, this column displays both the IP addresses. |
| Location | Location of the Gateway from GeoIP (by default) or as manually entered by the user. This is used for geographic assignment of the Gateway to Edges and should be verified. |
On the Gateways page, you can perform the following activities:
- New Gateway – Creates a new Gateway. See Create New Gateway.
- Delete Gateway – Deletes the selected Gateway. You cannot delete a Gateway that is already being used by an Enterprise Customer.
- Support Request – Redirects to a Knowledge Base article that has instructions on how to file a support request.